Maria Skoularidou
Position Paper: Bayesian Deep Learning in the Age of Large-Scale AI
Feb 06, 2024
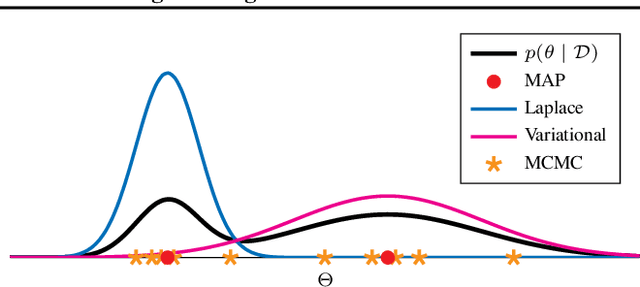
Abstract:In the current landscape of deep learning research, there is a predominant emphasis on achieving high predictive accuracy in supervised tasks involving large image and language datasets. However, a broader perspective reveals a multitude of overlooked metrics, tasks, and data types, such as uncertainty, active and continual learning, and scientific data, that demand attention. Bayesian deep learning (BDL) constitutes a promising avenue, offering advantages across these diverse settings. This paper posits that BDL can elevate the capabilities of deep learning. It revisits the strengths of BDL, acknowledges existing challenges, and highlights some exciting research avenues aimed at addressing these obstacles. Looking ahead, the discussion focuses on possible ways to combine large-scale foundation models with BDL to unlock their full potential.
Modeling Tabular data using Conditional GAN
Jul 01, 2019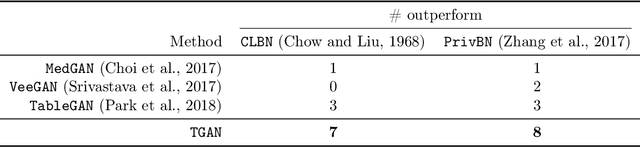
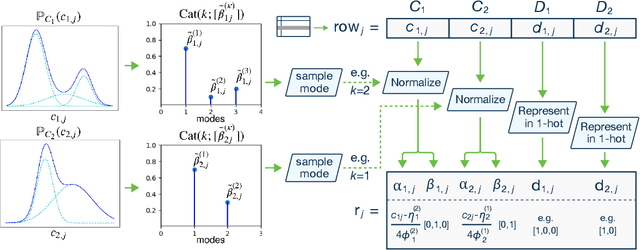
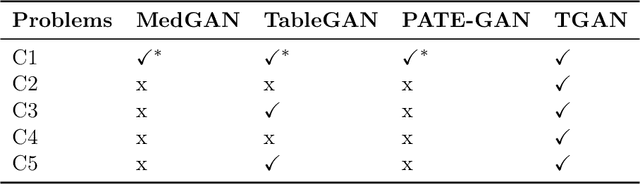
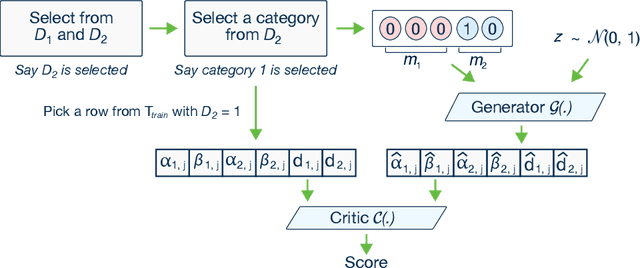
Abstract:Modeling the probability distribution of rows in tabular data and generating realistic synthetic data is a non-trivial task. Tabular data usually contains a mix of discrete and continuous columns. Continuous columns may have multiple modes whereas discrete columns are sometimes imbalanced making the modeling difficult. Existing statistical and deep neural network models fail to properly model this type of data. We design TGAN, which uses a conditional generative adversarial network to address these challenges. To aid in a fair and thorough comparison, we design a benchmark with 7 simulated and 8 real datasets and several Bayesian network baselines. TGAN outperforms Bayesian methods on most of the real datasets whereas other deep learning methods could not.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge