Margaret M. Coad
Soft Everting Prosthetic Hand and Comparison with Existing Body-Powered Terminal Devices
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we explore the use of a soft gripper, specifically a soft inverting-everting toroidal hydrostat, as a prosthetic hand. We present a design of the gripper integrated into a body-powered elbow-driven system and evaluate its performance compared to similar body-powered terminal devices: the Kwawu 3D-printed hand and the Hosmer hook. Our experiments highlight advantages of the Everting hand, such as low required cable tension for operation (1.6 N for Everting, 30.0 N for Kwawu, 28.1 N for Hosmer), limited restriction on the elbow angle range, and secure grasping capability (peak pulling force required to remove an object: 15.8 N for Everting, 6.9 N for Kwawu, 4.0 N for Hosmer). In our pilot user study, six able-bodied participants performed standardized hand dexterity tests. With the Everting hand compared to the Kwawu hand, users transferred more blocks in one minute and completed three tasks (moving small common objects, simulated feeding with a spoon, and moving large empty cans) faster (p~$\leq$~0.05). With the Everting hand compared to the Hosmer hook, users moved large empty cans faster (p~$\leq$~0.05) and achieved similar performance on all other tasks. Overall, user preference leaned toward the Everting hand for its adaptable grip and ease of use, although its abilities could be improved in tasks requiring high precision such as writing with a pen, and in handling heavier objects such as large heavy cans.
Stretchable Pneumatic Sleeve for Adaptable, Low-Displacement Anchoring in Exosuits
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Despite recent advances in wearable technology, interfacing movement assistance devices with the human body remains challenging. We present a stretchable pneumatic sleeve that can anchor an exosuit actuator to the human arm with a low displacement of the actuator's mounting point relative to the body during operation. Our sleeve has the potential to serve as an adaptable attachment mechanism for exosuits, since it can adjust its pressure to only compress the arm as much as needed to transmit the applied exosuit forces without a large displacement. We discuss the design of our sleeve, which is made of fabric pneumatic artificial muscle (fPAM) actuators formed into bands. We quantify the performance of nine fPAM bands of various lengths and widths, as well as three sleeves (an fPAM sleeve, a series pouch motor (SPM) sleeve as in previous literature, and an off the shelf hook and loop sleeve), through the measurement of the compressing force as a function of pressure and the localized pulling force that can be resisted as a function of both pressure and mounting point displacement. Our experimental results show that fPAM bands with smaller resting length and/or larger resting width produce higher forces. Also, when inflated, an fPAM sleeve that has equivalent dimensions to the SPM sleeve while fully stretched has similar performance to the SPM sleeve. While inflated, both pneumatic sleeves decrease the mounting point displacement compared to the hook and loop sleeve. Compared to the SPM sleeve, the fPAM sleeve is able to hold larger internal pressure before bursting, increasing its possible force range. Also, when not inflated, the fPAM sleeve resists the pulling force well, indicating its ability to provide anchoring when not actuated.
Soft Wrist Exosuit Actuated by Fabric Pneumatic Artificial Muscles
Oct 27, 2023Abstract:Recently, soft actuator-based exosuits have gained interest, due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, inherent safety, and low cost. We present a novel wrist exosuit actuated by fabric pneumatic artificial muscles that can move the wrist in flexion/extension and ulnar/radial deviation. We derive a model representing the torque exerted by the exosuit and introduce a model-based optimization methodology for the selection of placement parameters of the exosuit muscles. We evaluate the accuracy of the model by measuring the exosuit torques throughout the full range of wrist flexion/extension. When accounting for the displacement of the mounting points, the model predicts the exosuit torque with a mean absolute error of 0.279 Nm, which is 26.1% of the average measured torque. To explore the capabilities of the exosuit to move the human body, we measure its range of motion on a passive human wrist; the exosuit is able to achieve 55.0% of the active biological range in flexion, 69.1% in extension, 68.6% in ulnar deviation, and 68.4% in radial deviation. Finally, we demonstrate the device controlling the passive human wrist to move to a desired orientation in the flexion/extension plane and along a two-degree-of-freedom trajectory.
Haptic Guidance and Haptic Error Amplification in a Virtual Surgical Robotic Training Environment
Sep 11, 2023Abstract:Teleoperated robotic systems have introduced more intuitive control for minimally invasive surgery, but the optimal method for training remains unknown. Recent motor learning studies have demonstrated that exaggeration of errors helps trainees learn to perform tasks with greater speed and accuracy. We hypothesized that training in a force field that pushes the operator away from a desired path would improve their performance on a virtual reality ring-on-wire task. Forty surgical novices trained under a no-force, guidance, or error-amplifying force field over five days. Completion time, translational and rotational path error, and combined error-time were evaluated under no force field on the final day. The groups significantly differed in combined error-time, with the guidance group performing the worst. Error-amplifying field participants showed the most improvement and did not plateau in their performance during training, suggesting that learning was still ongoing. Guidance field participants had the worst performance on the final day, confirming the guidance hypothesis. Participants with high initial path error benefited more from guidance. Participants with high initial combined error-time benefited more from guidance and error-amplifying force field training. Our results suggest that error-amplifying and error-reducing haptic training for robot-assisted telesurgery benefits trainees of different abilities differently.
Soft Air Pocket Force Sensors for Large Scale Flexible Robots
Jul 26, 2023



Abstract:Flexible robots have advantages over rigid robots in their ability to conform physically to their environment and to form a wide variety of shapes. Sensing the force applied by or to flexible robots is useful for both navigation and manipulation tasks, but it is challenging due to the need for the sensors to withstand the robots' shape change without encumbering their functionality. Also, for robots with long or large bodies, the number of sensors required to cover the entire surface area of the robot body can be prohibitive due to high cost and complexity. We present a novel soft air pocket force sensor that is highly flexible, lightweight, relatively inexpensive, and easily scalable to various sizes. Our sensor produces a change in internal pressure that is linear with the applied force. We present results of experimental testing of how uncontrollable factors (contact location and contact area) and controllable factors (initial internal pressure, thickness, size, and number of interior seals) affect the sensitivity. We demonstrate our sensor applied to a vine robot-a soft inflatable robot that "grows" from the tip via eversion-and we show that the robot can successfully grow and steer towards an object with which it senses contact.
Collapse of Straight Soft Growing Inflated Beam Robots Under Their Own Weight
Jun 30, 2023Abstract:Soft, growing inflated beam robots, also known as everting vine robots, have previously been shown to navigate confined spaces with ease. Less is known about their ability to navigate three-dimensional open spaces where they have the potential to collapse under their own weight as they attempt to move through a space. Previous work has studied collapse of inflated beams and vine robots due to purely transverse or purely axial external loads. Here, we extend previous models to predict the length at which straight vine robots will collapse under their own weight at arbitrary launch angle relative to gravity, inflated diameter, and internal pressure. Our model successfully predicts the general trends of collapse behavior of straight vine robots. We find that collapse length increases non-linearly with the robot's launch angle magnitude, linearly with the robot's diameter, and with the square root of the robot's internal pressure. We also demonstrate the use of our model to determine the robot parameters required to grow a vine robot across a gap in the floor. This work forms the foundation of an approach for modeling the collapse of vine robots and inflated beams in arbitrary shapes.
Hybrid Soft-Rigid Continuum Robot Inspired by Spider Monkey Tail
Jun 20, 2023



Abstract:Spider monkeys (genus Ateles) have a prehensile tail that functions as a flexible, multipurpose fifth limb, enabling them to navigate complex terrains, grasp objects of various sizes, and swing between supports. Inspired by the spider monkey tail, we present a life size hybrid soft-rigid continuum robot designed to imitate the function of the tail. Our planar design has a rigid skeleton with soft elements at its joints that achieve decreasing stiffness along its length. Five manually-operated wires along this central structure control the motion of the tail to form a variety of possible shapes in the 2D plane. Our design also includes a skin-like silicone and fabric tail pad that moves with the tail's tip and assists with object grasping. We quantify the force required to pull various objects out of the robot's grasp and demonstrate that this force increases with the object diameter and the number of edges in a polygonal object. We demonstrate the robot's ability to grasp, move, and release objects of various diameters, as well as to navigate around obstacles, and to retrieve an object after passing under a low passageway.
Self-Propelled Soft Everting Toroidal Robot for Navigation and Climbing in Confined Spaces
Mar 28, 2022



Abstract:There are many spaces inaccessible to humans where robots could help deliver sensors and equipment. Many of these spaces contain three-dimensional passageways and uneven terrain that pose challenges for robot design and control. Everting toroidal robots, which move via simultaneous eversion and inversion of their body material, are promising for navigation in these types of spaces. We present a novel soft everting toroidal robot that propels itself using a motorized device inside an air-filled membrane. Our robot requires only a single control signal to move, can conform to its environment, and can climb vertically with a motor torque that is independent of the force used to brace the robot against its environment. We derive and validate models of the forces involved in its motion, and we demonstrate the robot's ability to navigate a maze and climb a pipe.
Robot-Assisted Surgical Training Over Several Days in a Virtual Surgical Environment with Divergent and Convergent Force Fields
Sep 23, 2021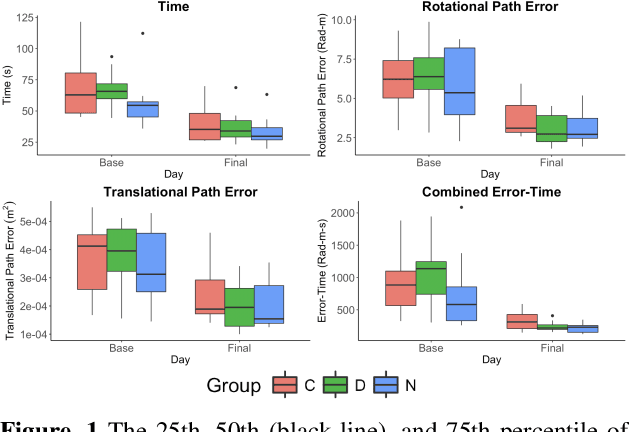
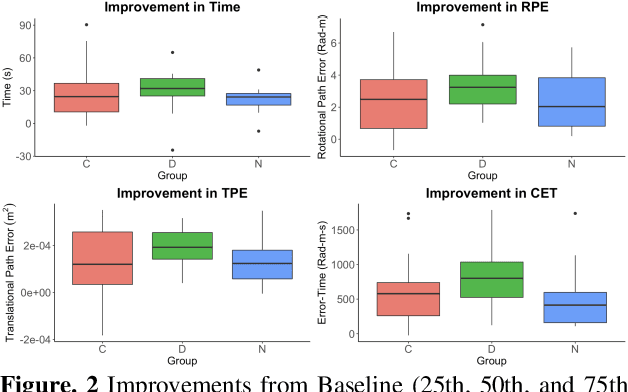
Abstract:Surgical procedures require a high level of technical skill to ensure efficiency and patient safety. Due to the direct effect of surgeon skill on patient outcomes, the development of cost-effective and realistic training methods is imperative to accelerate skill acquisition. Teleoperated robotic devices allow for intuitive ergonomic control, but the learning curve for these systems remains steep. Recent studies in motor learning have shown that visual or physical exaggeration of errors helps trainees to learn to perform tasks faster and more accurately. In this study, we extended the work from two previous studies to investigate the performance of subjects in different force field training conditions, including convergent (assistive), divergent (resistive), and no force field (null).
* 2 pages, 2 figures, Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics 2019
Task-Specific Design Optimization and Fabrication for Inflated-Beam Soft Robots with Growable Discrete Joints
Mar 08, 2021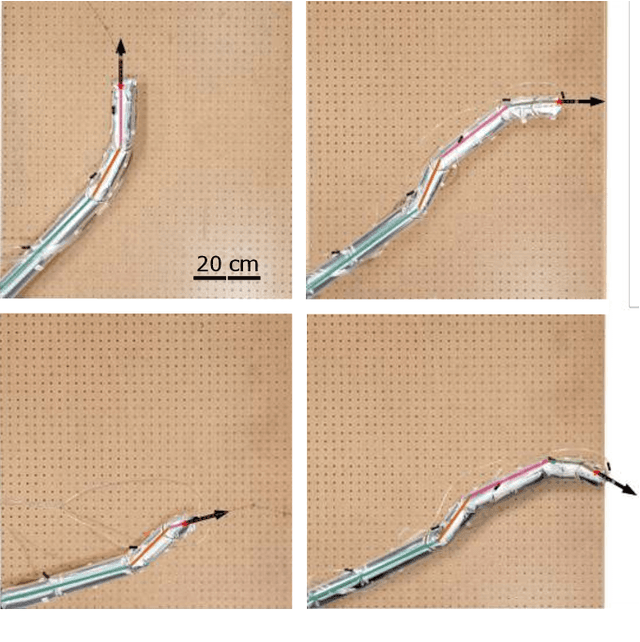
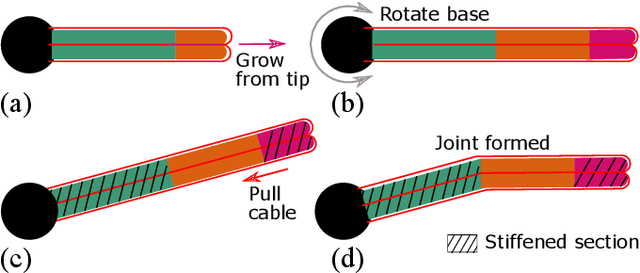
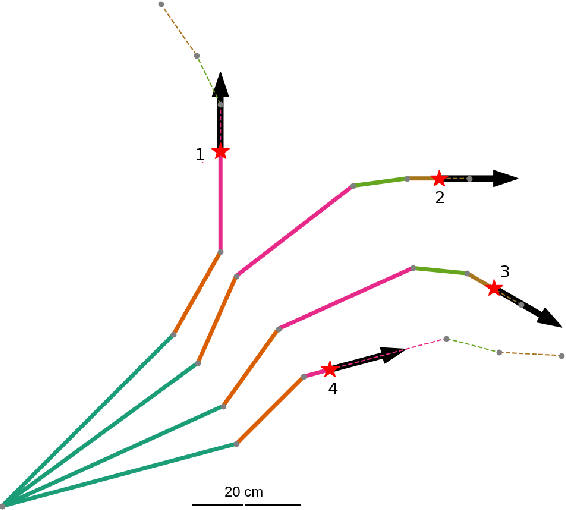
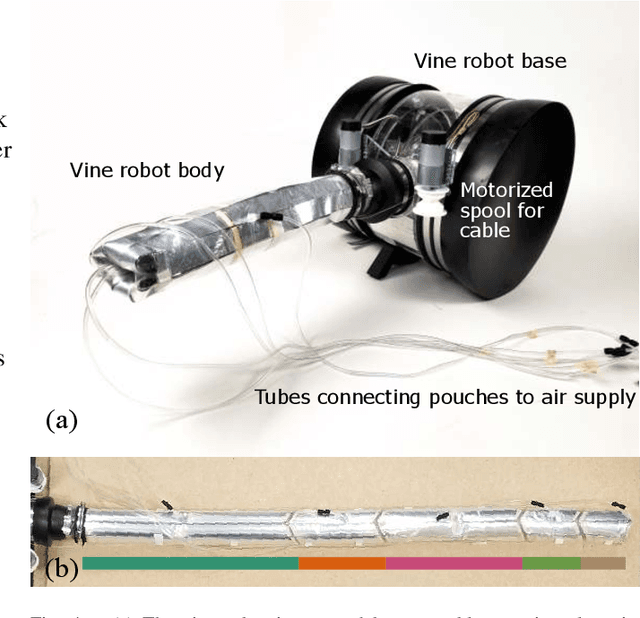
Abstract:Soft robot serial chain manipulators with the capability for growth, stiffness control, and discrete joints have the potential to approach the dexterity of traditional robot arms, while improving safety, lowering cost, and providing an increased workspace, with potential application in home environments. This paper presents an approach for design optimization of such robots to reach specified targets while minimizing the number of discrete joints and thus construction and actuation costs. We define a maximum number of allowable joints, as well as hardware constraints imposed by the materials and actuation available for soft growing robots, and we formulate and solve an optimization problem to output a robot design, i.e., the total number of potential joints and their locations along the robot body, which reaches all the desired targets. We then rapidly construct the resulting soft growing robot design using readily available, low-cost materials, and we demonstrate its ability to reach the desired targets. Finally, we use our algorithm to evaluate the ability of this design to reach new targets, and we demonstrate the algorithm's utility as a design tool to explore robot capabilities given various constraints and objectives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge