Robot-Assisted Surgical Training Over Several Days in a Virtual Surgical Environment with Divergent and Convergent Force Fields
Paper and Code
Sep 23, 2021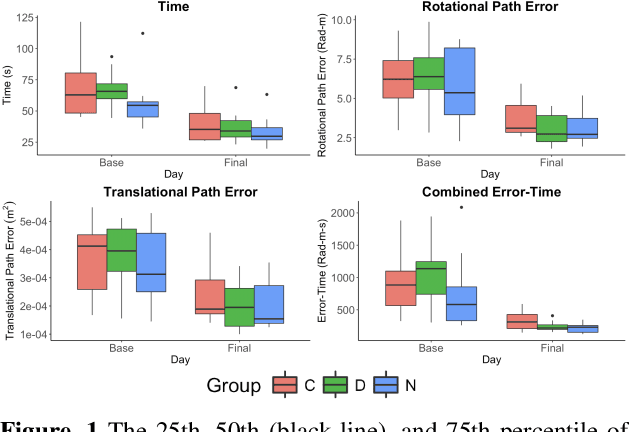
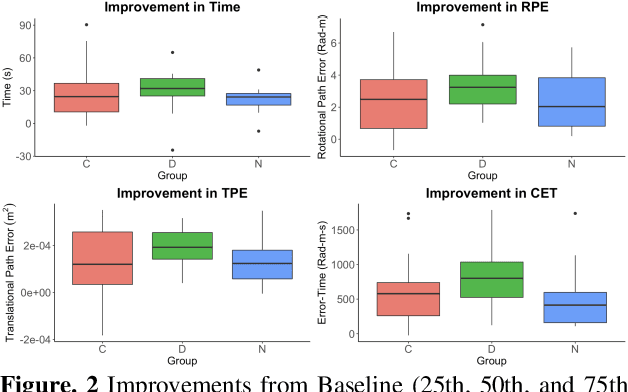
Surgical procedures require a high level of technical skill to ensure efficiency and patient safety. Due to the direct effect of surgeon skill on patient outcomes, the development of cost-effective and realistic training methods is imperative to accelerate skill acquisition. Teleoperated robotic devices allow for intuitive ergonomic control, but the learning curve for these systems remains steep. Recent studies in motor learning have shown that visual or physical exaggeration of errors helps trainees to learn to perform tasks faster and more accurately. In this study, we extended the work from two previous studies to investigate the performance of subjects in different force field training conditions, including convergent (assistive), divergent (resistive), and no force field (null).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge