Maoji Zheng
Seg2Box: 3D Object Detection by Point-Wise Semantics Supervision
Mar 21, 2025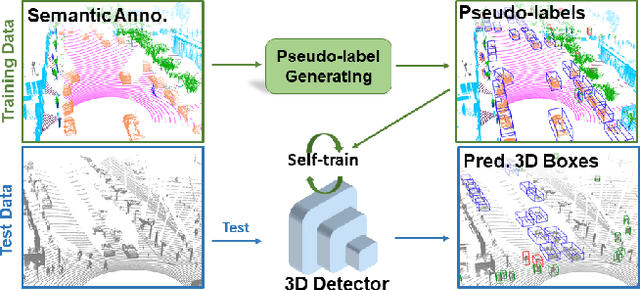
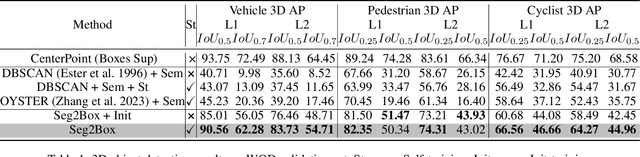
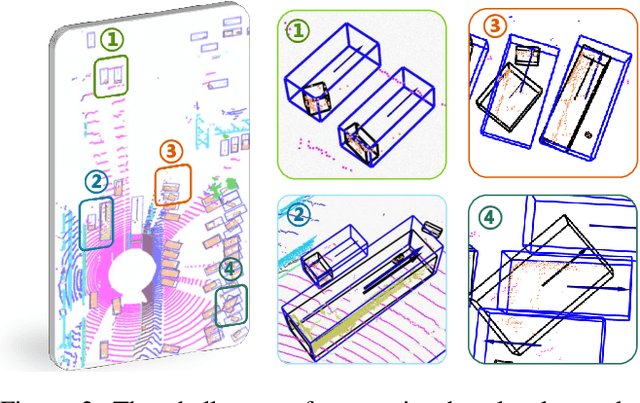
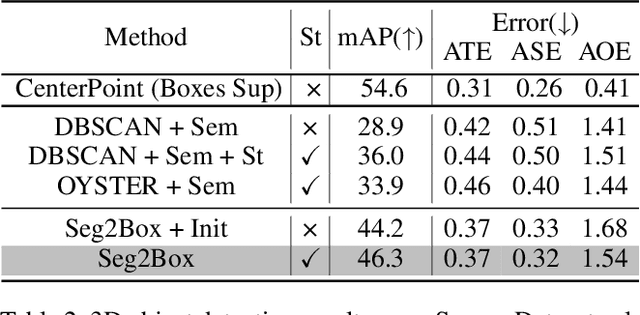
Abstract:LiDAR-based 3D object detection and semantic segmentation are critical tasks in 3D scene understanding. Traditional detection and segmentation methods supervise their models through bounding box labels and semantic mask labels. However, these two independent labels inherently contain significant redundancy. This paper aims to eliminate the redundancy by supervising 3D object detection using only semantic labels. However, the challenge arises due to the incomplete geometry structure and boundary ambiguity of point-cloud instances, leading to inaccurate pseudo labels and poor detection results. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method, named Seg2Box. We first introduce a Multi-Frame Multi-Scale Clustering (MFMS-C) module, which leverages the spatio-temporal consistency of point clouds to generate accurate box-level pseudo-labels. Additionally, the Semantic?Guiding Iterative-Mining Self-Training (SGIM-ST) module is proposed to enhance the performance by progressively refining the pseudo-labels and mining the instances without generating pseudo-labels. Experiments on the Waymo Open Dataset and nuScenes Dataset show that our method significantly outperforms other competitive methods by 23.7\% and 10.3\% in mAP, respectively. The results demonstrate the great label-efficient potential and advancement of our method.
SP3D: Boosting Sparsely-Supervised 3D Object Detection via Accurate Cross-Modal Semantic Prompts
Mar 09, 2025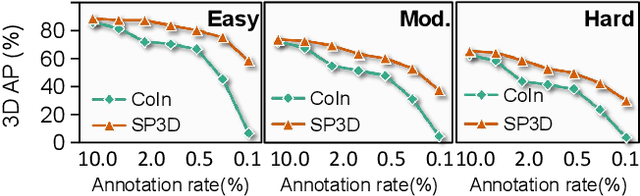
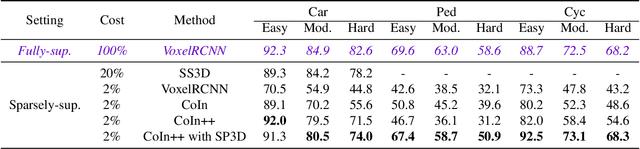
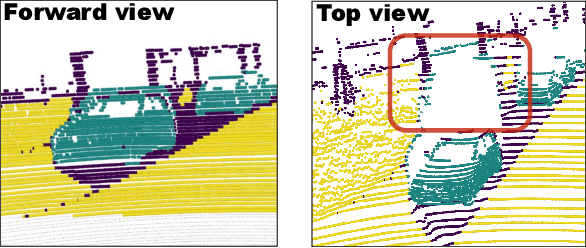
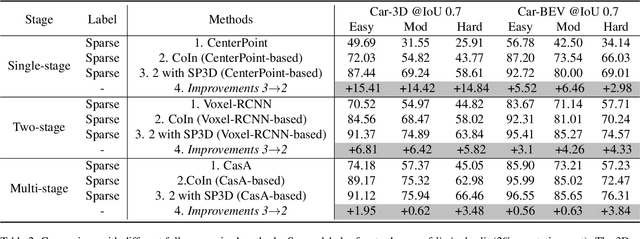
Abstract:Recently, sparsely-supervised 3D object detection has gained great attention, achieving performance close to fully-supervised 3D objectors while requiring only a few annotated instances. Nevertheless, these methods suffer challenges when accurate labels are extremely absent. In this paper, we propose a boosting strategy, termed SP3D, explicitly utilizing the cross-modal semantic prompts generated from Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) to boost the 3D detector with robust feature discrimination capability under sparse annotation settings. Specifically, we first develop a Confident Points Semantic Transfer (CPST) module that generates accurate cross-modal semantic prompts through boundary-constrained center cluster selection. Based on these accurate semantic prompts, which we treat as seed points, we introduce a Dynamic Cluster Pseudo-label Generation (DCPG) module to yield pseudo-supervision signals from the geometry shape of multi-scale neighbor points. Additionally, we design a Distribution Shape score (DS score) that chooses high-quality supervision signals for the initial training of the 3D detector. Experiments on the KITTI dataset and Waymo Open Dataset (WOD) have validated that SP3D can enhance the performance of sparsely supervised detectors by a large margin under meager labeling conditions. Moreover, we verified SP3D in the zero-shot setting, where its performance exceeded that of the state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/xmuqimingxia/SP3D.
SPEAL: Skeletal Prior Embedded Attention Learning for Cross-Source Point Cloud Registration
Dec 14, 2023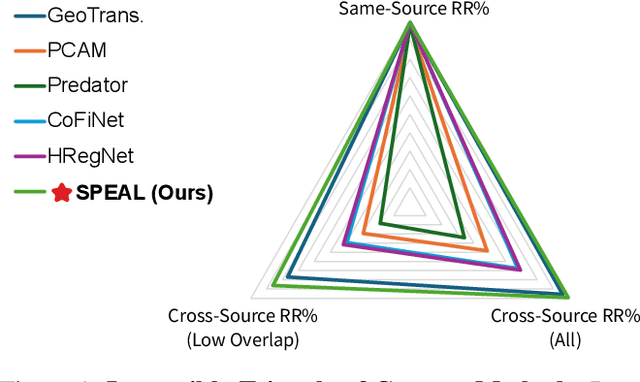
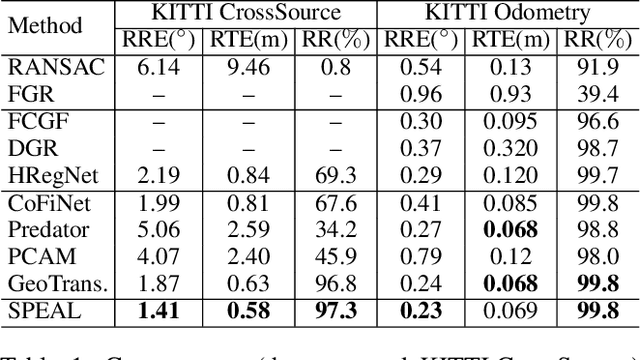
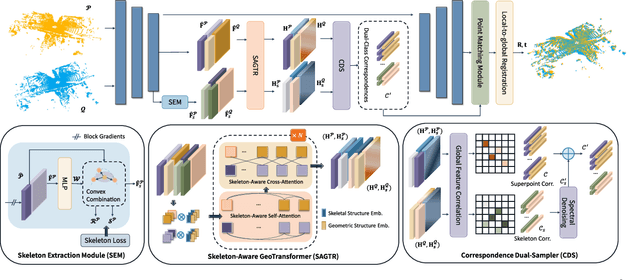
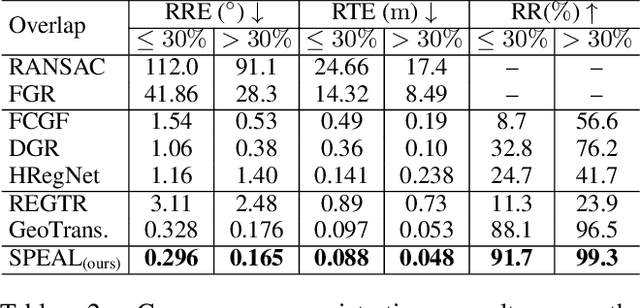
Abstract:Point cloud registration, a fundamental task in 3D computer vision, has remained largely unexplored in cross-source point clouds and unstructured scenes. The primary challenges arise from noise, outliers, and variations in scale and density. However, neglected geometric natures of point clouds restricts the performance of current methods. In this paper, we propose a novel method termed SPEAL to leverage skeletal representations for effective learning of intrinsic topologies of point clouds, facilitating robust capture of geometric intricacy. Specifically, we design the Skeleton Extraction Module to extract skeleton points and skeletal features in an unsupervised manner, which is inherently robust to noise and density variances. Then, we propose the Skeleton-Aware GeoTransformer to encode high-level skeleton-aware features. It explicitly captures the topological natures and inter-point-cloud skeletal correlations with the noise-robust and density-invariant skeletal representations. Next, we introduce the Correspondence Dual-Sampler to facilitate correspondences by augmenting the correspondence set with skeletal correspondences. Furthermore, we construct a challenging novel large-scale cross-source point cloud dataset named KITTI CrossSource for benchmarking cross-source point cloud registration methods. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments are conducted to demonstrate our approach's superiority and robustness on both cross-source and same-source datasets. To the best of our knowledge, our approach is the first to facilitate point cloud registration with skeletal geometric priors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge