Maofan Zhao
A Survey of Sample-Efficient Deep Learning for Change Detection in Remote Sensing: Tasks, Strategies, and Challenges
Feb 05, 2025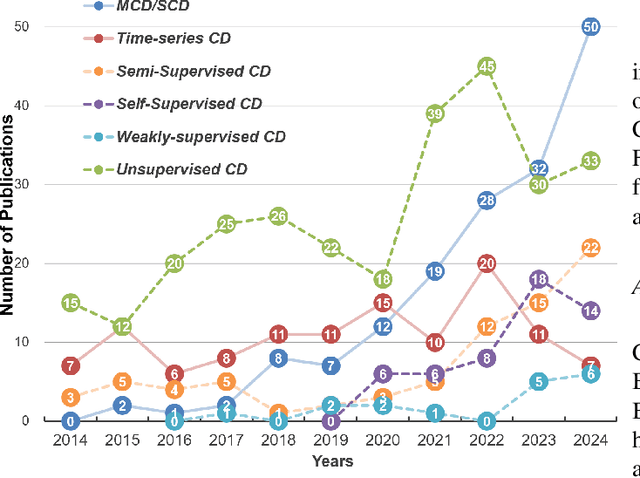
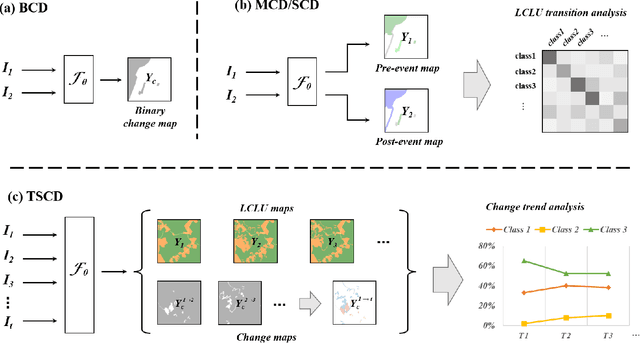
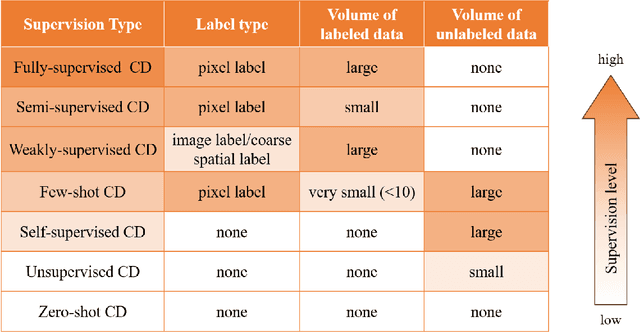
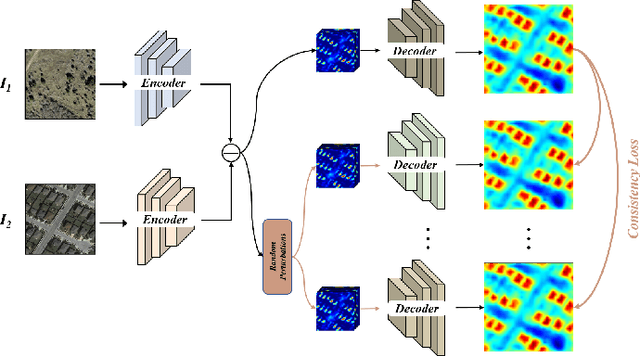
Abstract:In the last decade, the rapid development of deep learning (DL) has made it possible to perform automatic, accurate, and robust Change Detection (CD) on large volumes of Remote Sensing Images (RSIs). However, despite advances in CD methods, their practical application in real-world contexts remains limited due to the diverse input data and the applicational context. For example, the collected RSIs can be time-series observations, and more informative results are required to indicate the time of change or the specific change category. Moreover, training a Deep Neural Network (DNN) requires a massive amount of training samples, whereas in many cases these samples are difficult to collect. To address these challenges, various specific CD methods have been developed considering different application scenarios and training resources. Additionally, recent advancements in image generation, self-supervision, and visual foundation models (VFMs) have opened up new approaches to address the 'data-hungry' issue of DL-based CD. The development of these methods in broader application scenarios requires further investigation and discussion. Therefore, this article summarizes the literature methods for different CD tasks and the available strategies and techniques to train and deploy DL-based CD methods in sample-limited scenarios. We expect that this survey can provide new insights and inspiration for researchers in this field to develop more effective CD methods that can be applied in a wider range of contexts.
Incomplete Multimodal Learning for Remote Sensing Data Fusion
Apr 22, 2023



Abstract:The mechanism of connecting multimodal signals through self-attention operation is a key factor in the success of multimodal Transformer networks in remote sensing data fusion tasks. However, traditional approaches assume access to all modalities during both training and inference, which can lead to severe degradation when dealing with modal-incomplete inputs in downstream applications. To address this limitation, our proposed approach introduces a novel model for incomplete multimodal learning in the context of remote sensing data fusion. This approach can be used in both supervised and self-supervised pretraining paradigms and leverages the additional learned fusion tokens in combination with Bi-LSTM attention and masked self-attention mechanisms to collect multimodal signals. The proposed approach employs reconstruction and contrastive loss to facilitate fusion in pre-training while allowing for random modality combinations as inputs in network training. Our approach delivers state-of-the-art performance on two multimodal datasets for tasks such as building instance / semantic segmentation and land-cover mapping tasks when dealing with incomplete inputs during inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge