Manoj Bhat
Raj
Trajformer: Trajectory Prediction with Local Self-Attentive Contexts for Autonomous Driving
Nov 30, 2020

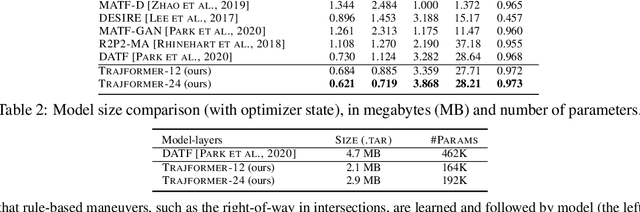
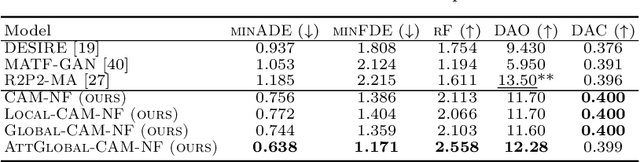
Abstract:Effective feature-extraction is critical to models' contextual understanding, particularly for applications to robotics and autonomous driving, such as multimodal trajectory prediction. However, state-of-the-art generative methods face limitations in representing the scene context, leading to predictions of inadmissible futures. We alleviate these limitations through the use of self-attention, which enables better control over representing the agent's social context; we propose a local feature-extraction pipeline that produces more salient information downstream, with improved parameter efficiency. We show improvements on standard metrics (minADE, minFDE, DAO, DAC) over various baselines on the Argoverse dataset. We release our code at: https://github.com/Manojbhat09/Trajformer
CurbScan: Curb Detection and Tracking Using Multi-Sensor Fusion
Oct 13, 2020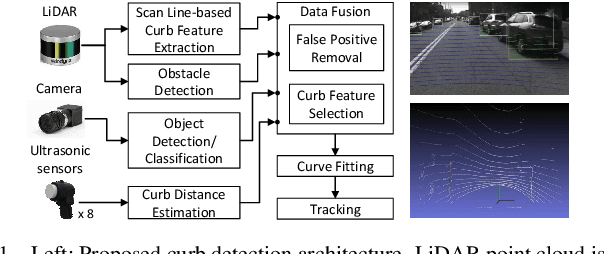
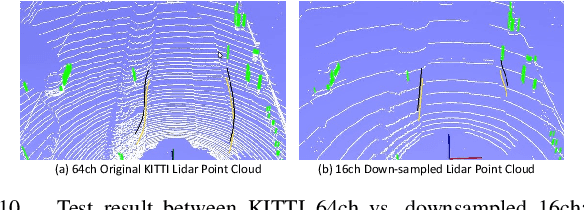
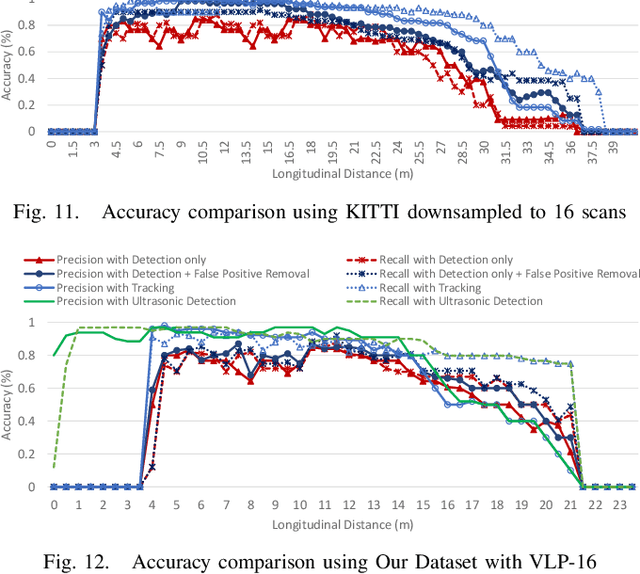
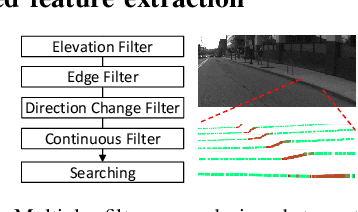
Abstract:Reliable curb detection is critical for safe autonomous driving in urban contexts. Curb detection and tracking are also useful in vehicle localization and path planning. Past work utilized a 3D LiDAR sensor to determine accurate distance information and the geometric attributes of curbs. However, such an approach requires dense point cloud data and is also vulnerable to false positives from obstacles present on both road and off-road areas. In this paper, we propose an approach to detect and track curbs by fusing together data from multiple sensors: sparse LiDAR data, a mono camera and low-cost ultrasonic sensors. The detection algorithm is based on a single 3D LiDAR and a mono camera sensor used to detect candidate curb features and it effectively removes false positives arising from surrounding static and moving obstacles. The detection accuracy of the tracking algorithm is boosted by using Kalman filter-based prediction and fusion with lateral distance information from low-cost ultrasonic sensors. We next propose a line-fitting algorithm that yields robust results for curb locations. Finally, we demonstrate the practical feasibility of our solution by testing in different road environments and evaluating our implementation in a real vehicle\footnote{Demo video clips demonstrating our algorithm have been uploaded to Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w5MwsdWhcy4, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gd506RklfG8.}. Our algorithm maintains over 90\% accuracy within 4.5-22 meters and 0-14 meters for the KITTI dataset and our dataset respectively, and its average processing time per frame is approximately 10 ms on Intel i7 x86 and 100ms on NVIDIA Xavier board.
Diverse and Admissible Trajectory Forecasting through Multimodal Context Understanding
Apr 03, 2020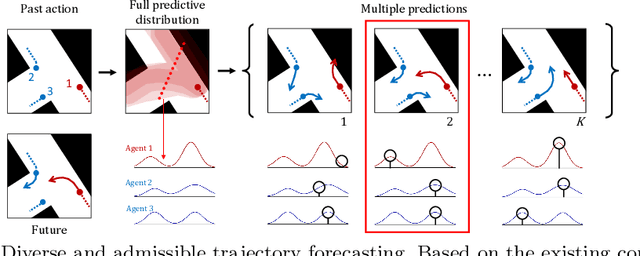

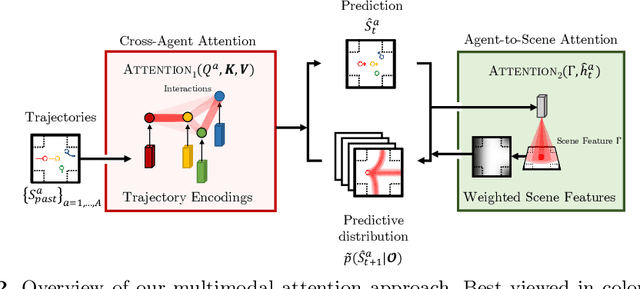
Abstract:Multi-agent trajectory forecasting in autonomous driving requires an agent to accurately anticipate the behaviors of the surrounding vehicles and pedestrians, for safe and reliable decision-making. Due to partial observability over the goals, contexts, and interactions of agents in these dynamical scenes, directly obtaining the posterior distribution over future agent trajectories remains a challenging problem. In realistic embodied environments, each agent's future trajectories should be diverse since multiple plausible sequences of actions can be used to reach its intended goals, and they should be admissible since they must obey physical constraints and stay in drivable areas. In this paper, we propose a model that fully synthesizes multiple input signals from the multimodal world|the environment's scene context and interactions between multiple surrounding agents|to best model all diverse and admissible trajectories. We offer new metrics to evaluate the diversity of trajectory predictions, while ensuring admissibility of each trajectory. Based on our new metrics as well as those used in prior work, we compare our model with strong baselines and ablations across two datasets and show a 35% performance-improvement over the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge