Man-Hung Siu
Transformer-based Model for ASR N-Best Rescoring and Rewriting
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Voice assistants increasingly use on-device Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) to ensure speed and privacy. However, due to resource constraints on the device, queries pertaining to complex information domains often require further processing by a search engine. For such applications, we propose a novel Transformer based model capable of rescoring and rewriting, by exploring full context of the N-best hypotheses in parallel. We also propose a new discriminative sequence training objective that can work well for both rescore and rewrite tasks. We show that our Rescore+Rewrite model outperforms the Rescore-only baseline, and achieves up to an average 8.6% relative Word Error Rate (WER) reduction over the ASR system by itself.
Personalization of CTC-based End-to-End Speech Recognition Using Pronunciation-Driven Subword Tokenization
Oct 16, 2023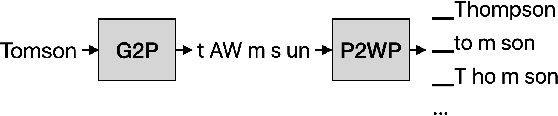


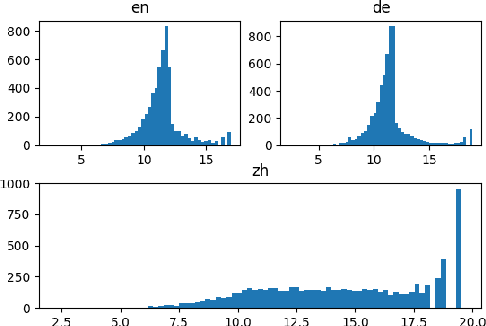
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning and automatic speech recognition have improved the accuracy of end-to-end speech recognition systems, but recognition of personal content such as contact names remains a challenge. In this work, we describe our personalization solution for an end-to-end speech recognition system based on connectionist temporal classification. Building on previous work, we present a novel method for generating additional subword tokenizations for personal entities from their pronunciations. We show that using this technique in combination with two established techniques, contextual biasing and wordpiece prior normalization, we are able to achieve personal named entity accuracy on par with a competitive hybrid system.
Acoustic Model Fusion for End-to-end Speech Recognition
Oct 10, 2023
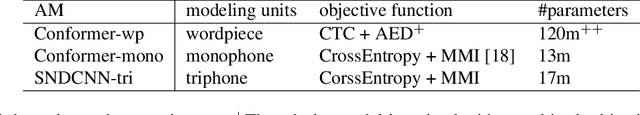
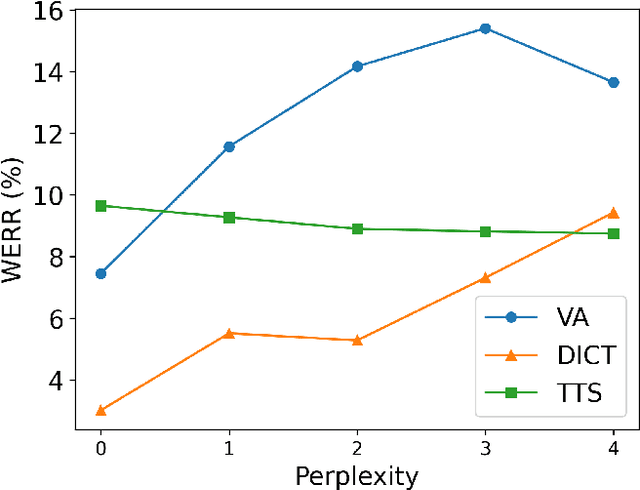
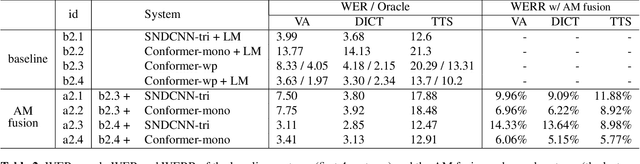
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning and automatic speech recognition (ASR) have enabled the end-to-end (E2E) ASR system and boosted the accuracy to a new level. The E2E systems implicitly model all conventional ASR components, such as the acoustic model (AM) and the language model (LM), in a single network trained on audio-text pairs. Despite this simpler system architecture, fusing a separate LM, trained exclusively on text corpora, into the E2E system has proven to be beneficial. However, the application of LM fusion presents certain drawbacks, such as its inability to address the domain mismatch issue inherent to the internal AM. Drawing inspiration from the concept of LM fusion, we propose the integration of an external AM into the E2E system to better address the domain mismatch. By implementing this novel approach, we have achieved a significant reduction in the word error rate, with an impressive drop of up to 14.3% across varied test sets. We also discovered that this AM fusion approach is particularly beneficial in enhancing named entity recognition.
Learning from Noisy Labels with Noise Modeling Network
May 01, 2020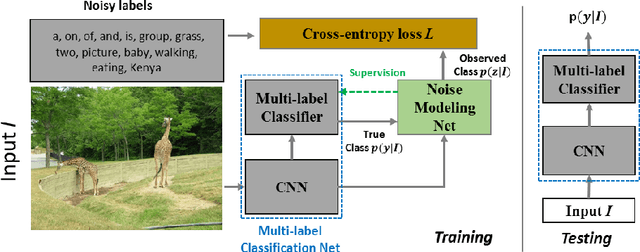
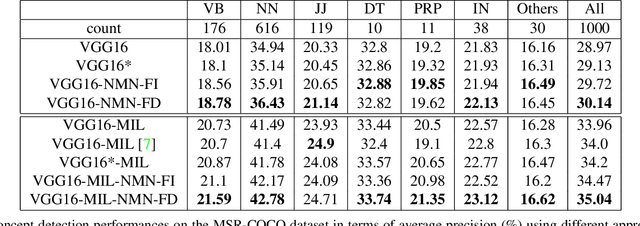
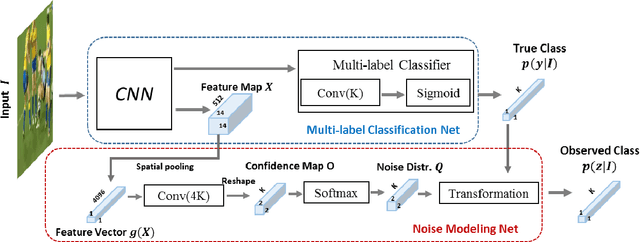
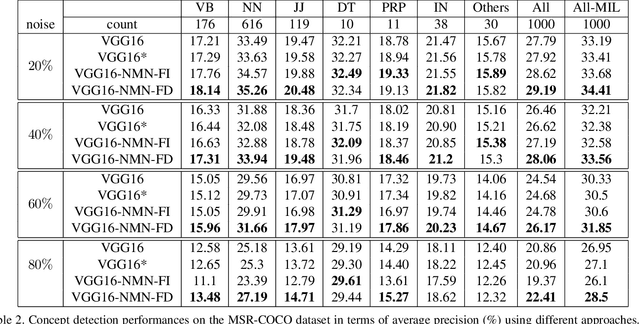
Abstract:Multi-label image classification has generated significant interest in recent years and the performance of such systems often suffers from the not so infrequent occurrence of incorrect or missing labels in the training data. In this paper, we extend the state-of the-art of training classifiers to jointly deal with both forms of errorful data. We accomplish this by modeling noisy and missing labels in multi-label images with a new Noise Modeling Network (NMN) that follows our convolutional neural network (CNN), integrates with it, forming an end-to-end deep learning system, which can jointly learn the noise distribution and CNN parameters. The NMN learns the distribution of noise patterns directly from the noisy data without the need for any clean training data. The NMN can model label noise that depends only on the true label or is also dependent on the image features. We show that the integrated NMN/CNN learning system consistently improves the classification performance, for different levels of label noise, on the MSR-COCO dataset and MSR-VTT dataset. We also show that noise performance improvements are obtained when multiple instance learning methods are used.
Towards a New Understanding of the Training of Neural Networks with Mislabeled Training Data
Sep 18, 2019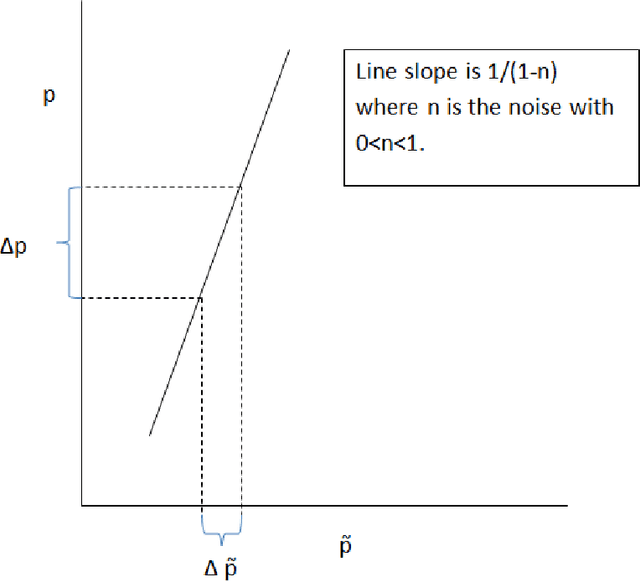
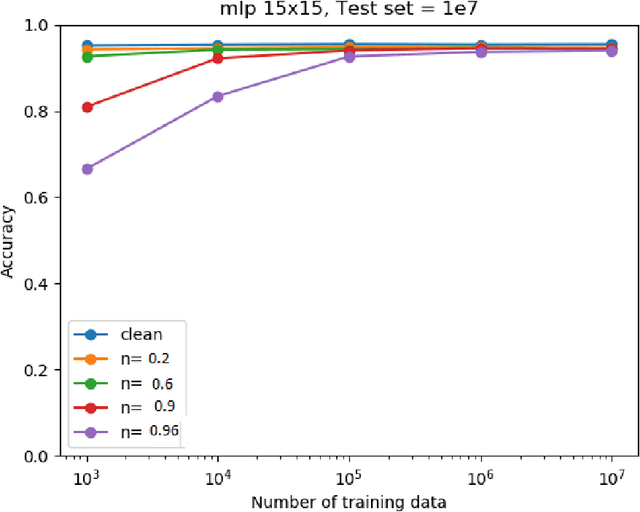
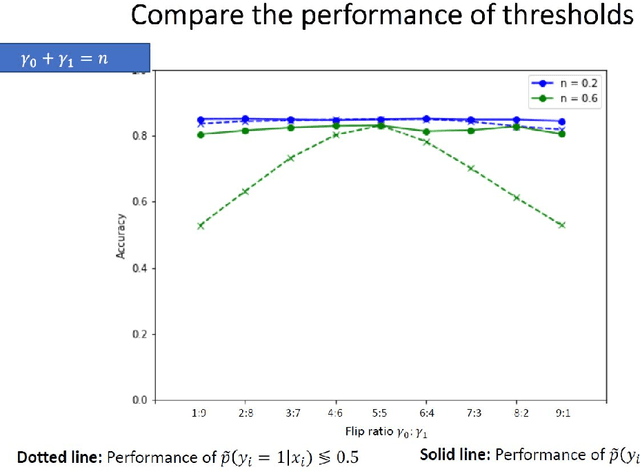
Abstract:We investigate the problem of machine learning with mislabeled training data. We try to make the effects of mislabeled training better understood through analysis of the basic model and equations that characterize the problem. This includes results about the ability of the noisy model to make the same decisions as the clean model and the effects of noise on model performance. In addition to providing better insights we also are able to show that the Maximum Likelihood (ML) estimate of the parameters of the noisy model determine those of the clean model. This property is obtained through the use of the ML invariance property and leads to an approach to developing a classifier when training has been mislabeled: namely train the classifier on noisy data and adjust the decision threshold based on the noise levels and/or class priors. We show how our approach to mislabeled training works with multi-layered perceptrons (MLPs).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge