Lizhen Tan
Knowledge Distillation Transfer Sets and their Impact on Downstream NLU Tasks
Oct 11, 2022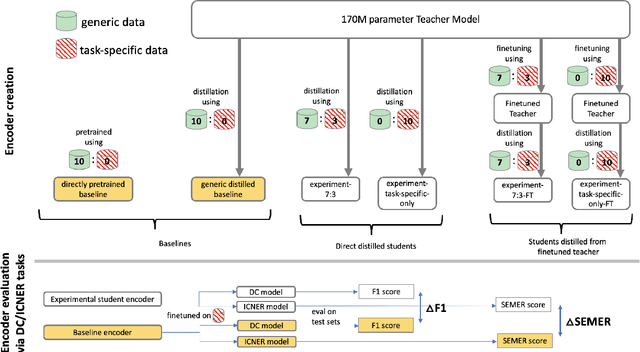
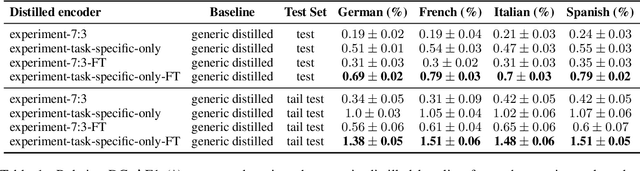
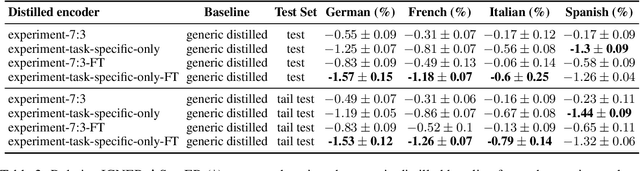
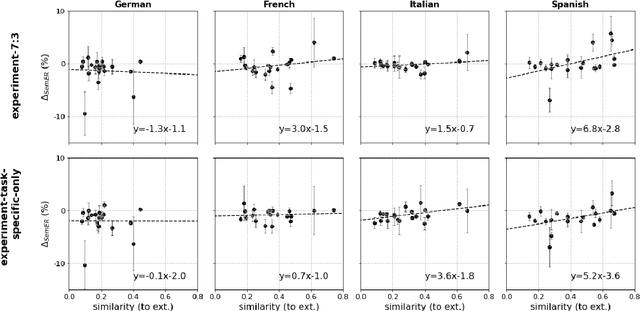
Abstract:Teacher-student knowledge distillation is a popular technique for compressing today's prevailing large language models into manageable sizes that fit low-latency downstream applications. Both the teacher and the choice of transfer set used for distillation are crucial ingredients in creating a high quality student. Yet, the generic corpora used to pretrain the teacher and the corpora associated with the downstream target domain are often significantly different, which raises a natural question: should the student be distilled over the generic corpora, so as to learn from high-quality teacher predictions, or over the downstream task corpora to align with finetuning? Our study investigates this trade-off using Domain Classification (DC) and Intent Classification/Named Entity Recognition (ICNER) as downstream tasks. We distill several multilingual students from a larger multilingual LM with varying proportions of generic and task-specific datasets, and report their performance after finetuning on DC and ICNER. We observe significant improvements across tasks and test sets when only task-specific corpora is used. We also report on how the impact of adding task-specific data to the transfer set correlates with the similarity between generic and task-specific data. Our results clearly indicate that, while distillation from a generic LM benefits downstream tasks, students learn better using target domain data even if it comes at the price of noisier teacher predictions. In other words, target domain data still trumps teacher knowledge.
Case-based Reasoning for Natural Language Queries over Knowledge Bases
Apr 18, 2021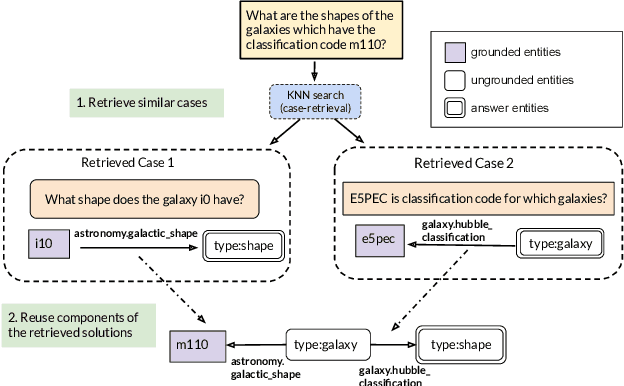
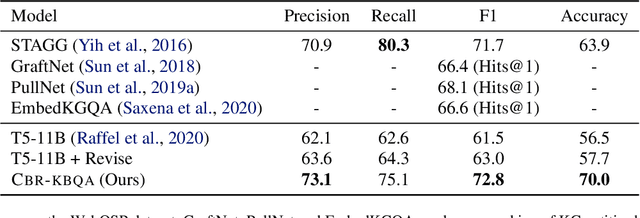
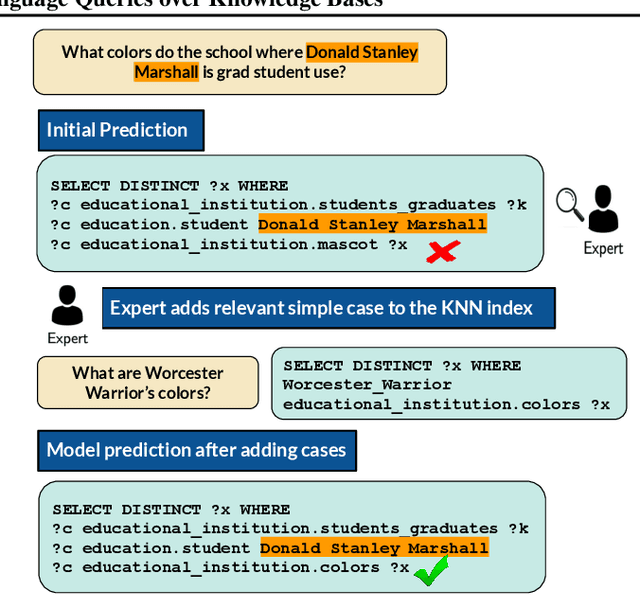
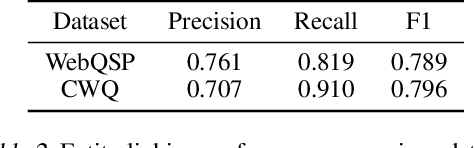
Abstract:It is often challenging for a system to solve a new complex problem from scratch, but much easier if the system can access other similar problems and description of their solutions -- a paradigm known as case-based reasoning (CBR). We propose a neuro-symbolic CBR approach for question answering over large knowledge bases (CBR-KBQA). While the idea of CBR is tempting, composing a solution from cases is nontrivial, when individual cases only contain partial logic to the full solution. To resolve this, CBR-KBQA consists of two modules: a non-parametric memory that stores cases (question and logical forms) and a parametric model which can generate logical forms by retrieving relevant cases from memory. Through experiments, we show that CBR-KBQA can effectively derive novel combination of relations not presented in case memory that is required to answer compositional questions. On several KBQA datasets that test compositional generalization, CBR-KBQA achieves competitive performance. For example, on the challenging ComplexWebQuestions dataset, CBR-KBQA outperforms the current state of the art by 11% accuracy. Furthermore, we show that CBR-KBQA is capable of using new cases \emph{without} any further training. Just by incorporating few human-labeled examples in the non-parametric case memory, CBR-KBQA is able to successfully generate queries containing unseen KB relations.
Evaluating Cross-Lingual Transfer Learning Approaches in Multilingual Conversational Agent Models
Dec 07, 2020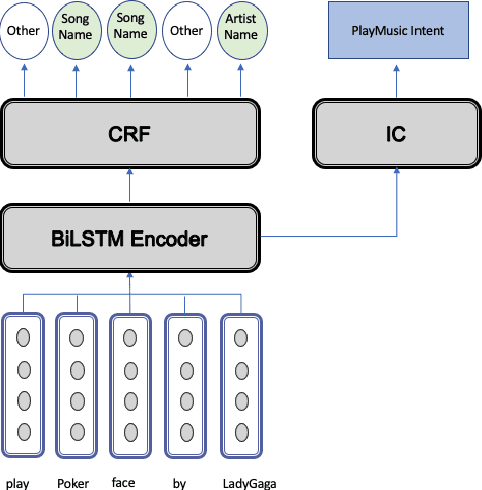
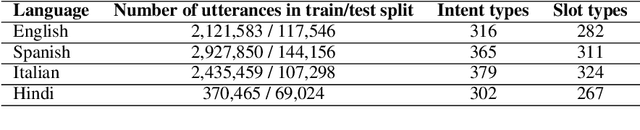
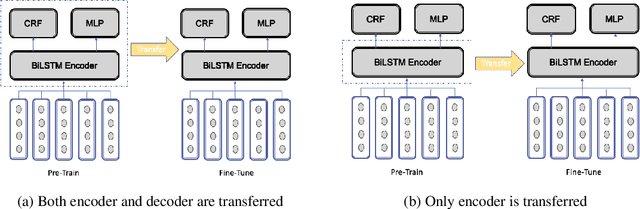
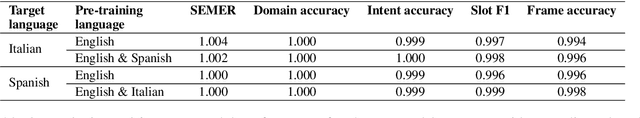
Abstract:With the recent explosion in popularity of voice assistant devices, there is a growing interest in making them available to user populations in additional countries and languages. However, to provide the highest accuracy and best performance for specific user populations, most existing voice assistant models are developed individually for each region or language, which requires linear investment of effort. In this paper, we propose a general multilingual model framework for Natural Language Understanding (NLU) models, which can help bootstrap new language models faster and reduce the amount of effort required to develop each language separately. We explore how different deep learning architectures affect multilingual NLU model performance. Our experimental results show that these multilingual models can reach same or better performance compared to monolingual models across language-specific test data while require less effort in creating features and model maintenance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge