Liwu Xu
u-LLaVA: Unifying Multi-Modal Tasks via Large Language Model
Nov 09, 2023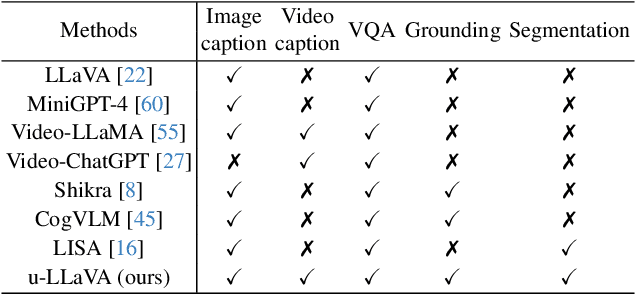
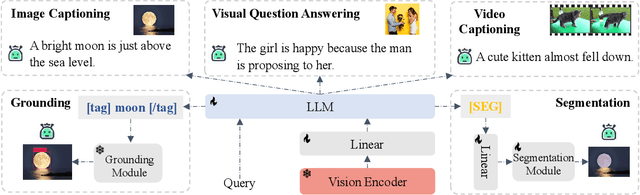
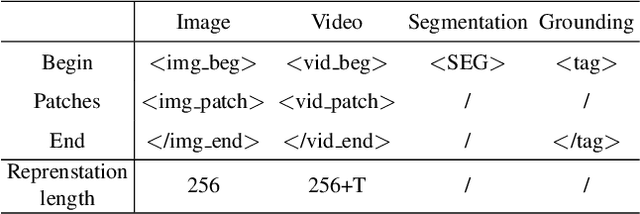

Abstract:Recent advances such as LLaVA and Mini-GPT4 have successfully integrated visual information into LLMs, yielding inspiring outcomes and giving rise to a new generation of multi-modal LLMs, or MLLMs. Nevertheless, these methods struggle with hallucinations and the mutual interference between tasks. To tackle these problems, we propose an efficient and accurate approach to adapt to downstream tasks by utilizing LLM as a bridge to connect multiple expert models, namely u-LLaVA. Firstly, we incorporate the modality alignment module and multi-task modules into LLM. Then, we reorganize or rebuild multi-type public datasets to enable efficient modality alignment and instruction following. Finally, task-specific information is extracted from the trained LLM and provided to different modules for solving downstream tasks. The overall framework is simple, effective, and achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks. We also release our model, the generated data, and the code base publicly available.
CLIP Brings Better Features to Visual Aesthetics Learners
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:The success of pre-training approaches on a variety of downstream tasks has revitalized the field of computer vision. Image aesthetics assessment (IAA) is one of the ideal application scenarios for such methods due to subjective and expensive labeling procedure. In this work, an unified and flexible two-phase \textbf{C}LIP-based \textbf{S}emi-supervised \textbf{K}nowledge \textbf{D}istillation paradigm is proposed, namely \textbf{\textit{CSKD}}. Specifically, we first integrate and leverage a multi-source unlabeled dataset to align rich features between a given visual encoder and an off-the-shelf CLIP image encoder via feature alignment loss. Notably, the given visual encoder is not limited by size or structure and, once well-trained, it can seamlessly serve as a better visual aesthetic learner for both student and teacher. In the second phase, the unlabeled data is also utilized in semi-supervised IAA learning to further boost student model performance when applied in latency-sensitive production scenarios. By analyzing the attention distance and entropy before and after feature alignment, we notice an alleviation of feature collapse issue, which in turn showcase the necessity of feature alignment instead of training directly based on CLIP image encoder. Extensive experiments indicate the superiority of CSKD, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple widely used IAA benchmarks.
Online Distillation with Mixed Sample Augmentation
Jun 24, 2022



Abstract:Mixed Sample Regularization (MSR), such as MixUp or CutMix, is a powerful data augmentation strategy to generalize convolutional neural networks. Previous empirical analysis has illustrated an orthogonal performance gain between MSR and the conventional offline Knowledge Distillation (KD). To be more specific, student networks can be enhanced with the involvement of MSR in the training stage of the sequential distillation. Yet, the interplay between MSR and online knowledge distillation, a stronger distillation paradigm, where an ensemble of peer students learn mutually from each other, remains unexplored. To bridge the gap, we make the first attempt at incorporating CutMix into online distillation, where we empirically observe a significant improvement. Encouraged by this fact, we propose an even stronger MSR specifically for online distillation, named as Cut^nMix. Furthermore, a novel online distillation framework is designed upon Cut^nMix, to enhance the distillation with feature level mutual learning and a self-ensemble teacher. Comprehensive evaluations on CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 with six network architectures show that our approach can consistently outperform state-of-the-art distillation methods.
Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment with Rich Attributes
Mar 31, 2022



Abstract:Personalized image aesthetics assessment (PIAA) is challenging due to its highly subjective nature. People's aesthetic tastes depend on diversified factors, including image characteristics and subject characters. The existing PIAA databases are limited in terms of annotation diversity, especially the subject aspect, which can no longer meet the increasing demands of PIAA research. To solve the dilemma, we conduct so far, the most comprehensive subjective study of personalized image aesthetics and introduce a new Personalized image Aesthetics database with Rich Attributes (PARA), which consists of 31,220 images with annotations by 438 subjects. PARA features wealthy annotations, including 9 image-oriented objective attributes and 4 human-oriented subjective attributes. In addition, desensitized subject information, such as personality traits, is also provided to support study of PIAA and user portraits. A comprehensive analysis of the annotation data is provided and statistic study indicates that the aesthetic preferences can be mirrored by proposed subjective attributes. We also propose a conditional PIAA model by utilizing subject information as conditional prior. Experimental results indicate that the conditional PIAA model can outperform the control group, which is also the first attempt to demonstrate how image aesthetics and subject characters interact to produce the intricate personalized tastes on image aesthetics. We believe the database and the associated analysis would be useful for conducting next-generation PIAA study. The project page of PARA can be found at: https://cv-datasets.institutecv.com/#/data-sets.
Self-Distillation from the Last Mini-Batch for Consistency Regularization
Mar 30, 2022



Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) shows a bright promise as a powerful regularization strategy to boost generalization ability by leveraging learned sample-level soft targets. Yet, employing a complex pre-trained teacher network or an ensemble of peer students in existing KD is both time-consuming and computationally costly. Various self KD methods have been proposed to achieve higher distillation efficiency. However, they either require extra network architecture modification or are difficult to parallelize. To cope with these challenges, we propose an efficient and reliable self-distillation framework, named Self-Distillation from Last Mini-Batch (DLB). Specifically, we rearrange the sequential sampling by constraining half of each mini-batch coinciding with the previous iteration. Meanwhile, the rest half will coincide with the upcoming iteration. Afterwards, the former half mini-batch distills on-the-fly soft targets generated in the previous iteration. Our proposed mechanism guides the training stability and consistency, resulting in robustness to label noise. Moreover, our method is easy to implement, without taking up extra run-time memory or requiring model structure modification. Experimental results on three classification benchmarks illustrate that our approach can consistently outperform state-of-the-art self-distillation approaches with different network architectures. Additionally, our method shows strong compatibility with augmentation strategies by gaining additional performance improvement. The code is available at https://github.com/Meta-knowledge-Lab/DLB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge