Liudi Yang
CoVAR: Co-generation of Video and Action for Robotic Manipulation via Multi-Modal Diffusion
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:We present a method to generate video-action pairs that follow text instructions, starting from an initial image observation and the robot's joint states. Our approach automatically provides action labels for video diffusion models, overcoming the common lack of action annotations and enabling their full use for robotic policy learning. Existing methods either adopt two-stage pipelines, which limit tightly coupled cross-modal information sharing, or rely on adapting a single-modal diffusion model for a joint distribution that cannot fully leverage pretrained video knowledge. To overcome these limitations, we (1) extend a pretrained video diffusion model with a parallel, dedicated action diffusion model that preserves pretrained knowledge, (2) introduce a Bridge Attention mechanism to enable effective cross-modal interaction, and (3) design an action refinement module to convert coarse actions into precise controls for low-resolution datasets. Extensive evaluations on multiple public benchmarks and real-world datasets demonstrate that our method generates higher-quality videos, more accurate actions, and significantly outperforms existing baselines, offering a scalable framework for leveraging large-scale video data for robotic learning.
DRAW2ACT: Turning Depth-Encoded Trajectories into Robotic Demonstration Videos
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Video diffusion models provide powerful real-world simulators for embodied AI but remain limited in controllability for robotic manipulation. Recent works on trajectory-conditioned video generation address this gap but often rely on 2D trajectories or single modality conditioning, which restricts their ability to produce controllable and consistent robotic demonstrations. We present DRAW2ACT, a depth-aware trajectory-conditioned video generation framework that extracts multiple orthogonal representations from the input trajectory, capturing depth, semantics, shape and motion, and injects them into the diffusion model. Moreover, we propose to jointly generate spatially aligned RGB and depth videos, leveraging cross-modality attention mechanisms and depth supervision to enhance the spatio-temporal consistency. Finally, we introduce a multimodal policy model conditioned on the generated RGB and depth sequences to regress the robot's joint angles. Experiments on Bridge V2, Berkeley Autolab, and simulation benchmarks show that DRAW2ACT achieves superior visual fidelity and consistency while yielding higher manipulation success rates compared to existing baselines.
RoboSwap: A GAN-driven Video Diffusion Framework For Unsupervised Robot Arm Swapping
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in generative models have revolutionized video synthesis and editing. However, the scarcity of diverse, high-quality datasets continues to hinder video-conditioned robotic learning, limiting cross-platform generalization. In this work, we address the challenge of swapping a robotic arm in one video with another: a key step for crossembodiment learning. Unlike previous methods that depend on paired video demonstrations in the same environmental settings, our proposed framework, RoboSwap, operates on unpaired data from diverse environments, alleviating the data collection needs. RoboSwap introduces a novel video editing pipeline integrating both GANs and diffusion models, combining their isolated advantages. Specifically, we segment robotic arms from their backgrounds and train an unpaired GAN model to translate one robotic arm to another. The translated arm is blended with the original video background and refined with a diffusion model to enhance coherence, motion realism and object interaction. The GAN and diffusion stages are trained independently. Our experiments demonstrate that RoboSwap outperforms state-of-the-art video and image editing models on three benchmarks in terms of both structural coherence and motion consistency, thereby offering a robust solution for generating reliable, cross-embodiment data in robotic learning.
CE-NPBG: Connectivity Enhanced Neural Point-Based Graphics for Novel View Synthesis in Autonomous Driving Scenes
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Current point-based approaches encounter limitations in scalability and rendering quality when using large 3D point cloud maps because using them directly for novel view synthesis (NVS) leads to degraded visualizations. We identify the primary issue behind these low-quality renderings as a visibility mismatch between geometry and appearance, stemming from using these two modalities together. To address this problem, we present CE-NPBG, a new approach for novel view synthesis (NVS) in large-scale autonomous driving scenes. Our method is a neural point-based technique that leverages two modalities: posed images (cameras) and synchronized raw 3D point clouds (LiDAR). We first employ a connectivity relationship graph between appearance and geometry, which retrieves points from a large 3D point cloud map observed from the current camera perspective and uses them for rendering. By leveraging this connectivity, our method significantly improves rendering quality and enhances run-time and scalability by using only a small subset of points from the large 3D point cloud map. Our approach associates neural descriptors with the points and uses them to synthesize views. To enhance the encoding of these descriptors and elevate rendering quality, we propose a joint adversarial and point rasterization training. During training, we pair an image-synthesizer network with a multi-resolution discriminator. At inference, we decouple them and use the image-synthesizer to generate novel views. We also integrate our proposal into the recent 3D Gaussian Splatting work to highlight its benefits for improved rendering and scalability.
LiDAR Loop Closure Detection using Semantic Graphs with Graph Attention Networks
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel loop closure detection algorithm that uses graph attention neural networks to encode semantic graphs to perform place recognition and then use semantic registration to estimate the 6 DoF relative pose constraint. Our place recognition algorithm has two key modules, namely, a semantic graph encoder module and a graph comparison module. The semantic graph encoder employs graph attention networks to efficiently encode spatial, semantic and geometric information from the semantic graph of the input point cloud. We then use self-attention mechanism in both node-embedding and graph-embedding steps to create distinctive graph vectors. The graph vectors of the current scan and a keyframe scan are then compared in the graph comparison module to identify a possible loop closure. Specifically, employing the difference of the two graph vectors showed a significant improvement in performance, as shown in ablation studies. Lastly, we implemented a semantic registration algorithm that takes in loop closure candidate scans and estimates the relative 6 DoF pose constraint for the LiDAR SLAM system. Extensive evaluation on public datasets shows that our model is more accurate and robust, achieving 13% improvement in maximum F1 score on the SemanticKITTI dataset, when compared to the baseline semantic graph algorithm. For the benefit of the community, we open-source the complete implementation of our proposed algorithm and custom implementation of semantic registration at https://github.com/crepuscularlight/SemanticLoopClosure
Lifelong 3D Mapping Framework for Hand-held & Robot-mounted LiDAR Mapping Systems
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:We propose a lifelong 3D mapping framework that is modular, cloud-native by design and more importantly, works for both hand-held and robot-mounted 3D LiDAR mapping systems. Our proposed framework comprises of dynamic point removal, multi-session map alignment, map change detection and map version control. First, our sensor-setup agnostic dynamic point removal algorithm works seamlessly with both hand-held and robot-mounted setups to produce clean static 3D maps. Second, the multi-session map alignment aligns these clean static maps automatically, without manual parameter fine-tuning, into a single reference frame, using a two stage approach based on feature descriptor matching and fine registration. Third, our novel map change detection identifies positive and negative changes between two aligned maps. Finally, the map version control maintains a single base map that represents the current state of the environment, and stores the detected positive and negative changes, and boundary information. Our unique map version control system can reconstruct any of the previous clean session maps and allows users to query changes between any two random mapping sessions, all without storing any input raw session maps, making it very unique. Extensive experiments are performed using hand-held commercial LiDAR mapping devices and open-source robot-mounted LiDAR SLAM algorithms to evaluate each module and the whole 3D lifelong mapping framework.
3D Textured Shape Recovery with Learned Geometric Priors
Sep 07, 2022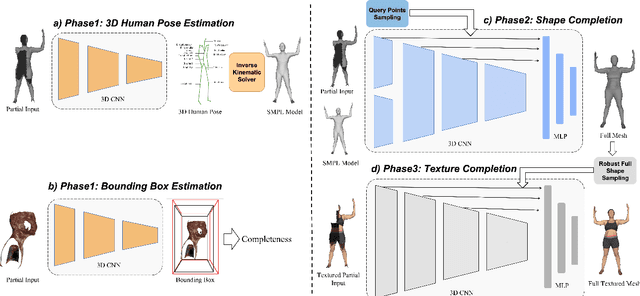
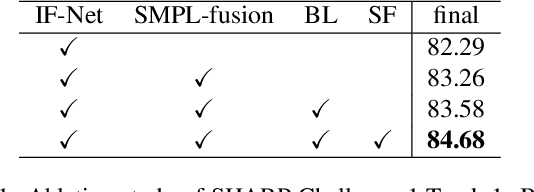

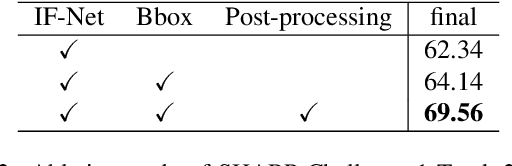
Abstract:3D textured shape recovery from partial scans is crucial for many real-world applications. Existing approaches have demonstrated the efficacy of implicit function representation, but they suffer from partial inputs with severe occlusions and varying object types, which greatly hinders their application value in the real world. This technical report presents our approach to address these limitations by incorporating learned geometric priors. To this end, we generate a SMPL model from learned pose prediction and fuse it into the partial input to add prior knowledge of human bodies. We also propose a novel completeness-aware bounding box adaptation for handling different levels of scales and partialness of partial scans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge