Lirui Deng
Building an Invisible Shield for Your Portrait against Deepfakes
May 22, 2023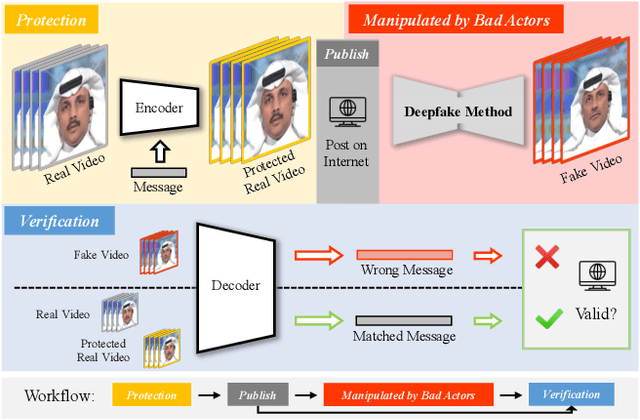



Abstract:The issue of detecting deepfakes has garnered significant attention in the research community, with the goal of identifying facial manipulations for abuse prevention. Although recent studies have focused on developing generalized models that can detect various types of deepfakes, their performance is not always be reliable and stable, which poses limitations in real-world applications. Instead of learning a forgery detector, in this paper, we propose a novel framework - Integrity Encryptor, aiming to protect portraits in a proactive strategy. Our methodology involves covertly encoding messages that are closely associated with key facial attributes into authentic images prior to their public release. Unlike authentic images, where the hidden messages can be extracted with precision, manipulating the facial attributes through deepfake techniques can disrupt the decoding process. Consequently, the modified facial attributes serve as a mean of detecting manipulated images through a comparison of the decoded messages. Our encryption approach is characterized by its brevity and efficiency, and the resulting method exhibits a good robustness against typical image processing traces, such as image degradation and noise. When compared to baselines that struggle to detect deepfakes in a black-box setting, our method utilizing conditional encryption showcases superior performance when presented with a range of different types of forgeries. In experiments conducted on our protected data, our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods by a significant margin.
PIRM Challenge on Perceptual Image Enhancement on Smartphones: Report
Oct 03, 2018
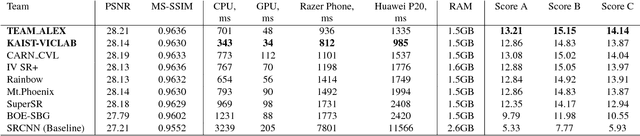

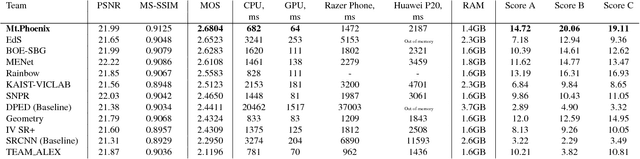
Abstract:This paper reviews the first challenge on efficient perceptual image enhancement with the focus on deploying deep learning models on smartphones. The challenge consisted of two tracks. In the first one, participants were solving the classical image super-resolution problem with a bicubic downscaling factor of 4. The second track was aimed at real-world photo enhancement, and the goal was to map low-quality photos from the iPhone 3GS device to the same photos captured with a DSLR camera. The target metric used in this challenge combined the runtime, PSNR scores and solutions' perceptual results measured in the user study. To ensure the efficiency of the submitted models, we additionally measured their runtime and memory requirements on Android smartphones. The proposed solutions significantly improved baseline results defining the state-of-the-art for image enhancement on smartphones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge