Jae-Seok Choi
S3: A Spectral-Spatial Structure Loss for Pan-Sharpening Networks
Jun 13, 2019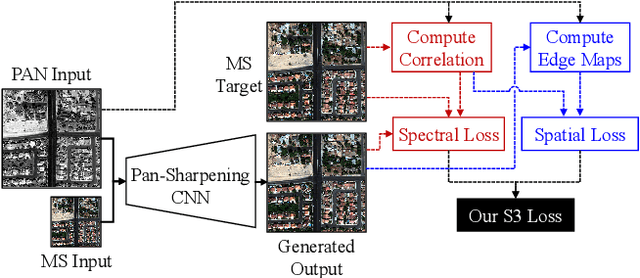


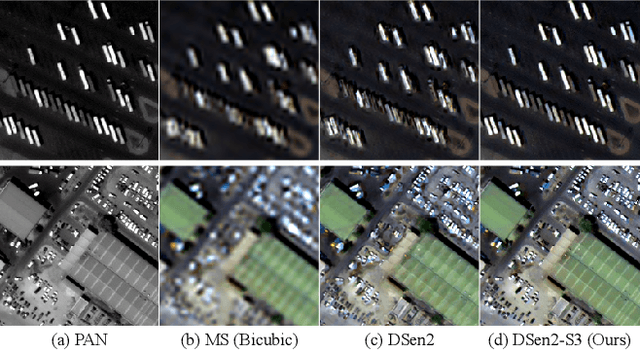
Abstract:Recently, many deep-learning-based pan-sharpening methods have been proposed for generating high-quality pan-sharpened (PS) satellite images. These methods focused on various types of convolutional neural network (CNN) structures, which were trained by simply minimizing L1 or L2 losses between network outputs and the corresponding high-resolution multi-spectral (MS) target images. However, due to different sensor characteristics and acquisition times, high-resolution panchromatic (PAN) and low-resolution MS image pairs tend to have large pixel misalignments, especially for moving objects in the images. Conventional CNNs trained with L1 or L2 losses with these satellite image datasets often produce PS images of low visual quality including double-edge artifacts along strong edges and ghosting artifacts on moving objects. In this letter, we propose a novel loss function, called a spectral-spatial structure (S3) loss, based on the correlation maps between MS targets and PAN inputs. Our proposed S3 loss can be very effectively utilized for pan-sharpening with various types of CNN structures, resulting in significant visual improvements on PS images with suppressed artifacts.
PIRM Challenge on Perceptual Image Enhancement on Smartphones: Report
Oct 03, 2018
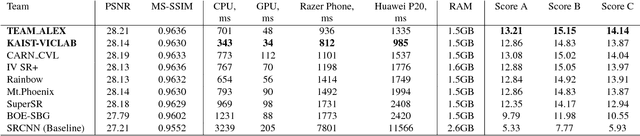

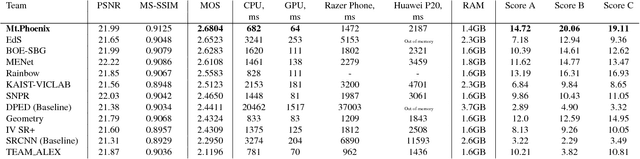
Abstract:This paper reviews the first challenge on efficient perceptual image enhancement with the focus on deploying deep learning models on smartphones. The challenge consisted of two tracks. In the first one, participants were solving the classical image super-resolution problem with a bicubic downscaling factor of 4. The second track was aimed at real-world photo enhancement, and the goal was to map low-quality photos from the iPhone 3GS device to the same photos captured with a DSLR camera. The target metric used in this challenge combined the runtime, PSNR scores and solutions' perceptual results measured in the user study. To ensure the efficiency of the submitted models, we additionally measured their runtime and memory requirements on Android smartphones. The proposed solutions significantly improved baseline results defining the state-of-the-art for image enhancement on smartphones.
Can Maxout Units Downsize Restoration Networks? - Single Image Super-Resolution Using Lightweight CNN with Maxout Units
Nov 07, 2017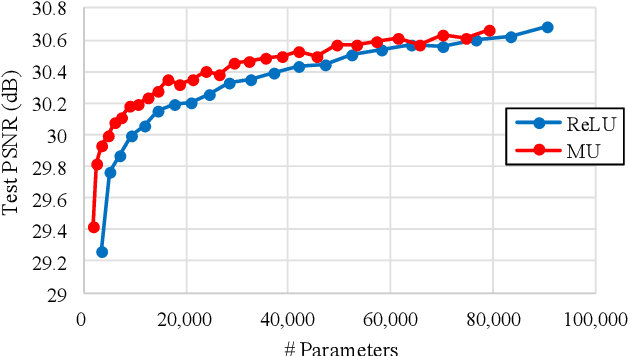
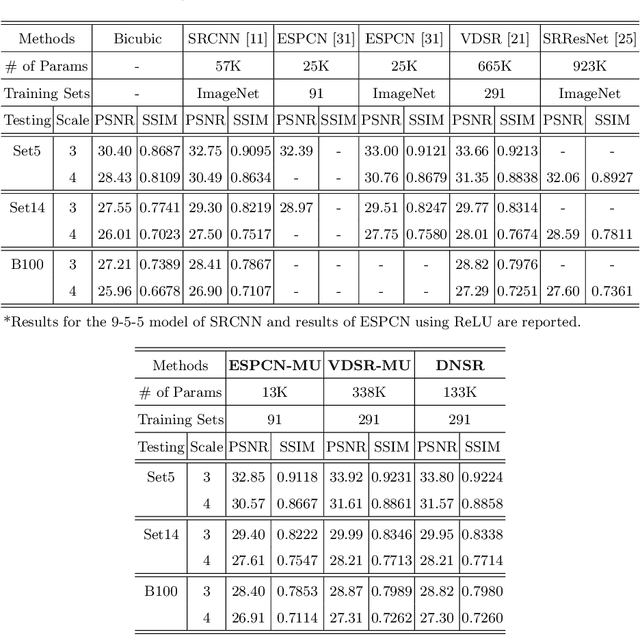
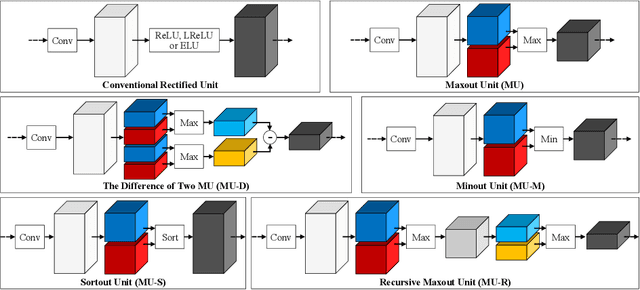
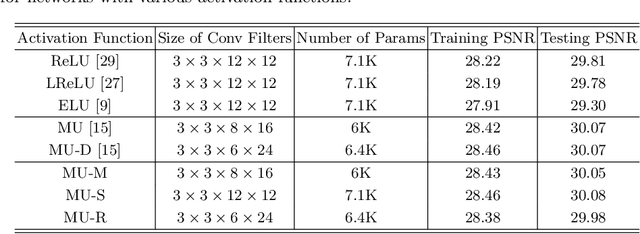
Abstract:Rectified linear units (ReLU) are well-known to be helpful in obtaining faster convergence and thus higher performance for many deep-learning-based applications. However, networks with ReLU tend to perform poorly when the number of filter parameters is constrained to a small number. To overcome it, in this paper, we propose a novel network utilizing maxout units (MU), and show its effectiveness on super-resolution (SR) applications. In general, the MU has been known to make the filter sizes doubled in generating the feature maps of the same sizes in classification problems. In this paper, we first reveal that the MU can even make the filter sizes halved in restoration problems thus leading to compaction of the network sizes. To show this, our SR network is designed without increasing the filter sizes with MU, which outperforms the state of the art SR methods with a smaller number of filter parameters. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to incorporate MU into SR applications and show promising performance results. In MU, feature maps from a previous convolutional layer are divided into two parts along channels, which are then compared element-wise and only their max values are passed to a next layer. Along with some interesting properties of MU to be analyzed, we further investigate other variants of MU and their effects. In addition, while ReLU have a trouble for learning in networks with a very small number of convolutional filter parameters, MU do not. For SR applications, our MU-based network reconstructs high-resolution images with comparable quality compared to previous deep-learning-based SR methods, with lower filter parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge