Liqiang Lin
CRAYM: Neural Field Optimization via Camera RAY Matching
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:We introduce camera ray matching (CRAYM) into the joint optimization of camera poses and neural fields from multi-view images. The optimized field, referred to as a feature volume, can be "probed" by the camera rays for novel view synthesis (NVS) and 3D geometry reconstruction. One key reason for matching camera rays, instead of pixels as in prior works, is that the camera rays can be parameterized by the feature volume to carry both geometric and photometric information. Multi-view consistencies involving the camera rays and scene rendering can be naturally integrated into the joint optimization and network training, to impose physically meaningful constraints to improve the final quality of both the geometric reconstruction and photorealistic rendering. We formulate our per-ray optimization and matched ray coherence by focusing on camera rays passing through keypoints in the input images to elevate both the efficiency and accuracy of scene correspondences. Accumulated ray features along the feature volume provide a means to discount the coherence constraint amid erroneous ray matching. We demonstrate the effectiveness of CRAYM for both NVS and geometry reconstruction, over dense- or sparse-view settings, with qualitative and quantitative comparisons to state-of-the-art alternatives.
Learning Reconstructability for Drone Aerial Path Planning
Sep 21, 2022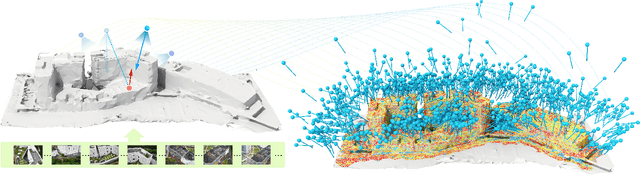
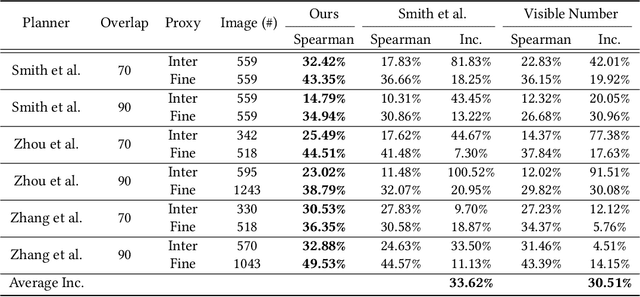
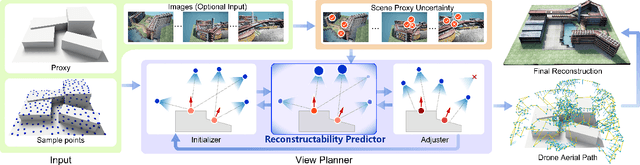
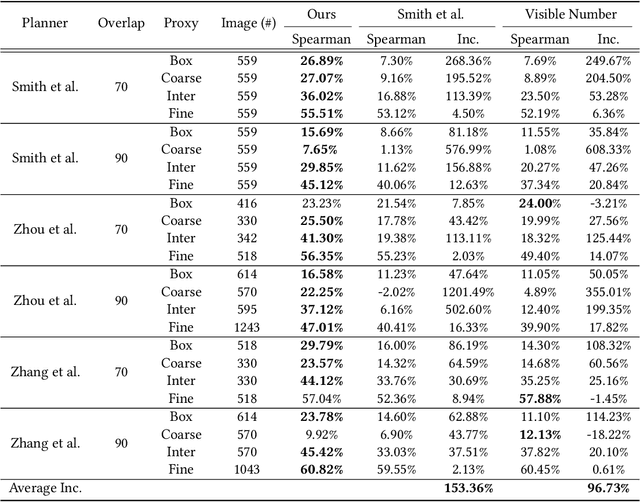
Abstract:We introduce the first learning-based reconstructability predictor to improve view and path planning for large-scale 3D urban scene acquisition using unmanned drones. In contrast to previous heuristic approaches, our method learns a model that explicitly predicts how well a 3D urban scene will be reconstructed from a set of viewpoints. To make such a model trainable and simultaneously applicable to drone path planning, we simulate the proxy-based 3D scene reconstruction during training to set up the prediction. Specifically, the neural network we design is trained to predict the scene reconstructability as a function of the proxy geometry, a set of viewpoints, and optionally a series of scene images acquired in flight. To reconstruct a new urban scene, we first build the 3D scene proxy, then rely on the predicted reconstruction quality and uncertainty measures by our network, based off of the proxy geometry, to guide the drone path planning. We demonstrate that our data-driven reconstructability predictions are more closely correlated to the true reconstruction quality than prior heuristic measures. Further, our learned predictor can be easily integrated into existing path planners to yield improvements. Finally, we devise a new iterative view planning framework, based on the learned reconstructability, and show superior performance of the new planner when reconstructing both synthetic and real scenes.
ShapeFormer: Transformer-based Shape Completion via Sparse Representation
Jan 25, 2022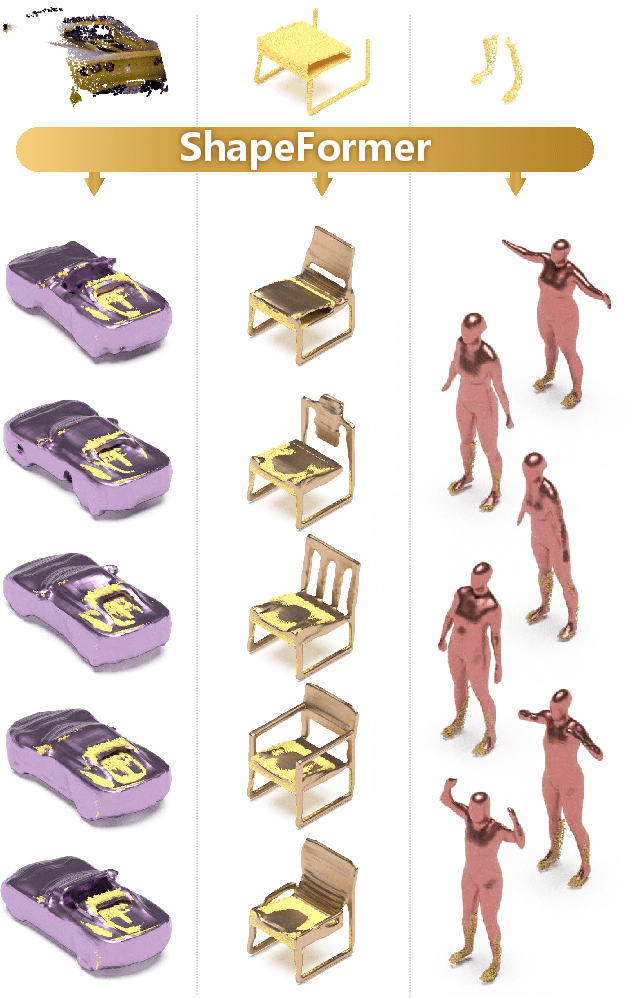
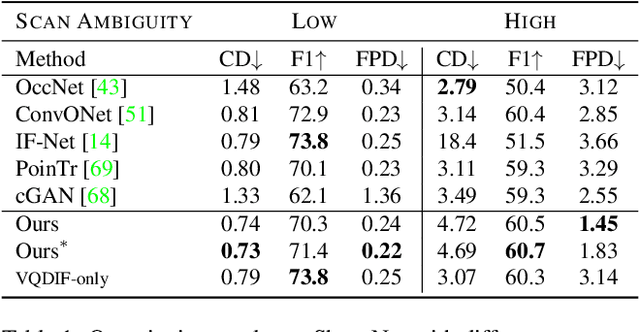
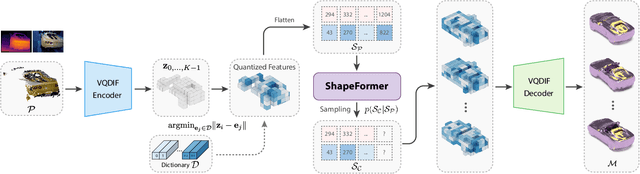
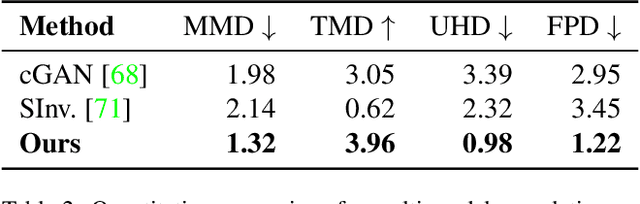
Abstract:We present ShapeFormer, a transformer-based network that produces a distribution of object completions, conditioned on incomplete, and possibly noisy, point clouds. The resultant distribution can then be sampled to generate likely completions, each exhibiting plausible shape details while being faithful to the input. To facilitate the use of transformers for 3D, we introduce a compact 3D representation, vector quantized deep implicit function, that utilizes spatial sparsity to represent a close approximation of a 3D shape by a short sequence of discrete variables. Experiments demonstrate that ShapeFormer outperforms prior art for shape completion from ambiguous partial inputs in terms of both completion quality and diversity. We also show that our approach effectively handles a variety of shape types, incomplete patterns, and real-world scans.
Hausdorff Point Convolution with Geometric Priors
Dec 24, 2020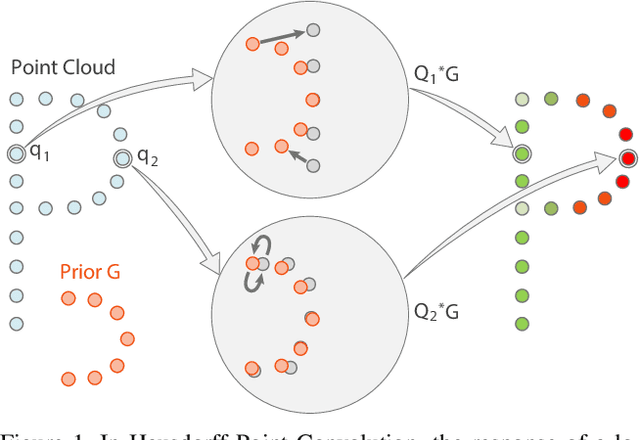
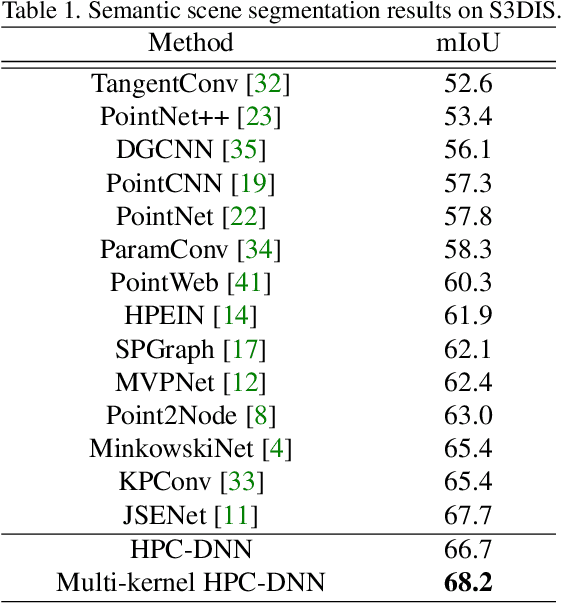
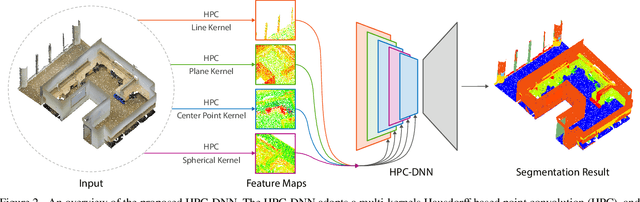
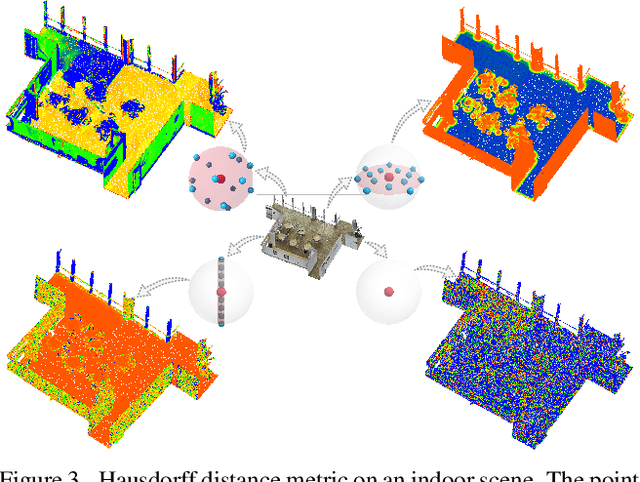
Abstract:Without a shape-aware response, it is hard to characterize the 3D geometry of a point cloud efficiently with a compact set of kernels. In this paper, we advocate the use of Hausdorff distance as a shape-aware distance measure for calculating point convolutional responses. The technique we present, coined Hausdorff Point Convolution (HPC), is shape-aware. We show that HPC constitutes a powerful point feature learning with a rather compact set of only four types of geometric priors as kernels. We further develop a HPC-based deep neural network (HPC-DNN). Task-specific learning can be achieved by tuning the network weights for combining the shortest distances between input and kernel point sets. We also realize hierarchical feature learning by designing a multi-kernel HPC for multi-scale feature encoding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HPC-DNN outperforms strong point convolution baselines (e.g., KPConv), achieving 2.8% mIoU performance boost on S3DIS and 1.5% on SemanticKITTI for semantic segmentation task.
Autonomous Outdoor Scanning via Online Topological and Geometric Path Optimization
Dec 23, 2020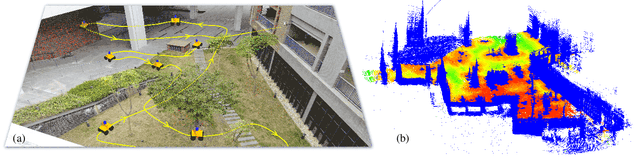
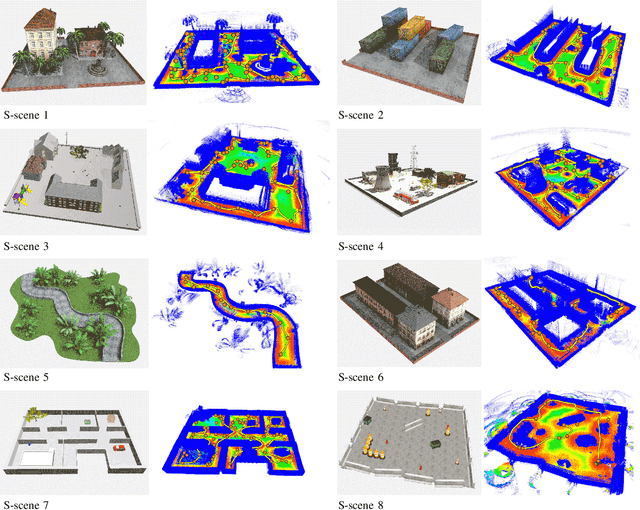
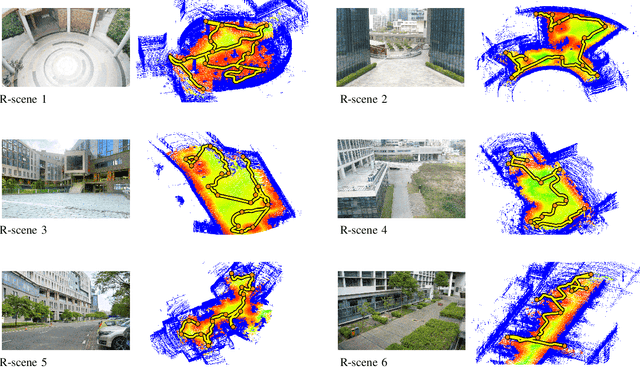
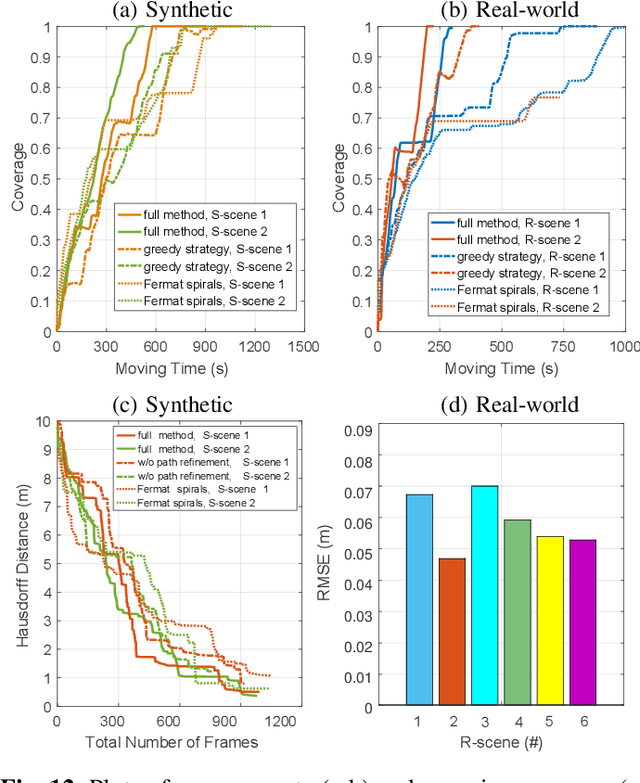
Abstract:Autonomous 3D acquisition of outdoor environments poses special challenges. Different from indoor scenes, where the room space is delineated by clear boundaries and separations (e.g., walls and furniture), an outdoor environment is spacious and unbounded (thinking of a campus). Therefore, unlike for indoor scenes where the scanning effort is mainly devoted to the discovery of boundary surfaces, scanning an open and unbounded area requires actively delimiting the extent of scanning region and dynamically planning a traverse path within that region. Thus, for outdoor scenes, we formulate the planning of an energy-efficient autonomous scanning through a discrete-continuous optimization of robot scanning paths. The discrete optimization computes a topological map, through solving an online traveling sales problem (Online TSP), which determines the scanning goals and paths on-the-fly. The dynamic goals are determined as a collection of visit sites with high reward of visibility-to-unknown. A visit graph is constructed via connecting the visit sites with edges weighted by traversing cost. This topological map evolves as the robot scans via deleting outdated sites that are either visited or become rewardless and inserting newly discovered ones. The continuous part optimizes the traverse paths geometrically between two neighboring visit sites via maximizing the information gain of scanning along the paths. The discrete and continuous processes alternate until the traverse cost of the current graph exceeds the remaining energy capacity of the robot. Our approach is evaluated with both synthetic and field tests, demonstrating its effectiveness and advantages over alternatives. The project is at http://vcc.szu.edu.cn/research/2020/Husky, and the codes are available at https://github.com/alualu628628/Autonomous-Outdoor-Scanning-via-Online-Topological-and-Geometric-Path-Optimization.
* Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
One Point is All You Need: Directional Attention Point for Feature Learning
Dec 14, 2020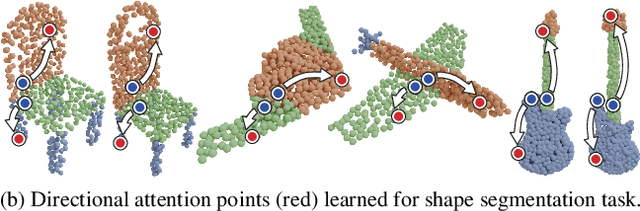
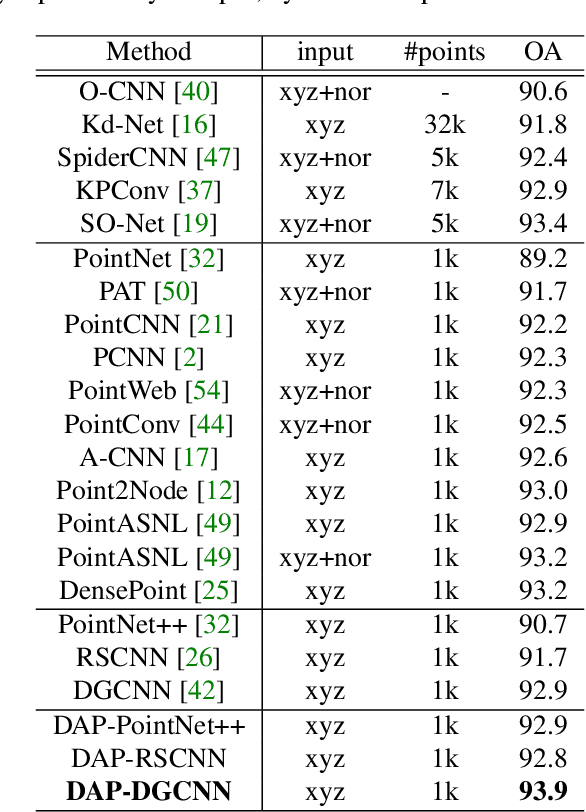
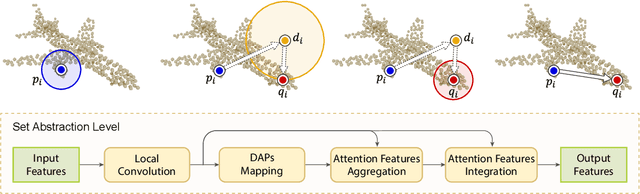
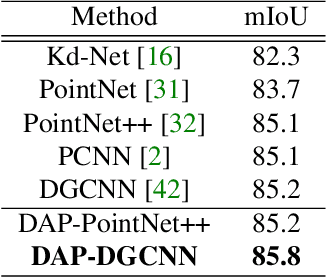
Abstract:We present a novel attention-based mechanism for learning enhanced point features for tasks such as point cloud classification and segmentation. Our key message is that if the right attention point is selected, then "one point is all you need" -- not a sequence as in a recurrent model and not a pre-selected set as in all prior works. Also, where the attention point is should be learned, from data and specific to the task at hand. Our mechanism is characterized by a new and simple convolution, which combines the feature at an input point with the feature at its associated attention point. We call such a point a directional attention point (DAP), since it is found by adding to the original point an offset vector that is learned by maximizing the task performance in training. We show that our attention mechanism can be easily incorporated into state-of-the-art point cloud classification and segmentation networks. Extensive experiments on common benchmarks such as ModelNet40, ShapeNetPart, and S3DIS demonstrate that our DAP-enabled networks consistently outperform the respective original networks, as well as all other competitive alternatives, including those employing pre-selected sets of attention points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge