Lingling Zhu
Baichuan-Omni-1.5 Technical Report
Jan 26, 2025
Abstract:We introduce Baichuan-Omni-1.5, an omni-modal model that not only has omni-modal understanding capabilities but also provides end-to-end audio generation capabilities. To achieve fluent and high-quality interaction across modalities without compromising the capabilities of any modality, we prioritized optimizing three key aspects. First, we establish a comprehensive data cleaning and synthesis pipeline for multimodal data, obtaining about 500B high-quality data (text, audio, and vision). Second, an audio-tokenizer (Baichuan-Audio-Tokenizer) has been designed to capture both semantic and acoustic information from audio, enabling seamless integration and enhanced compatibility with MLLM. Lastly, we designed a multi-stage training strategy that progressively integrates multimodal alignment and multitask fine-tuning, ensuring effective synergy across all modalities. Baichuan-Omni-1.5 leads contemporary models (including GPT4o-mini and MiniCPM-o 2.6) in terms of comprehensive omni-modal capabilities. Notably, it achieves results comparable to leading models such as Qwen2-VL-72B across various multimodal medical benchmarks.
DOA Estimation for Hybrid Massive MIMO Systems using Mixed-ADCs: Performance Loss and Energy Efficiency
Jul 21, 2021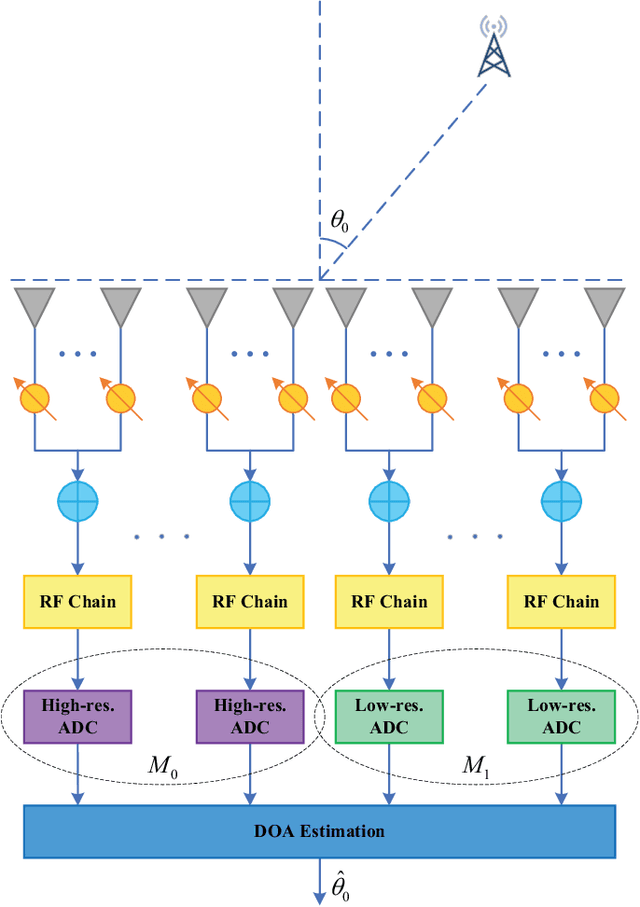
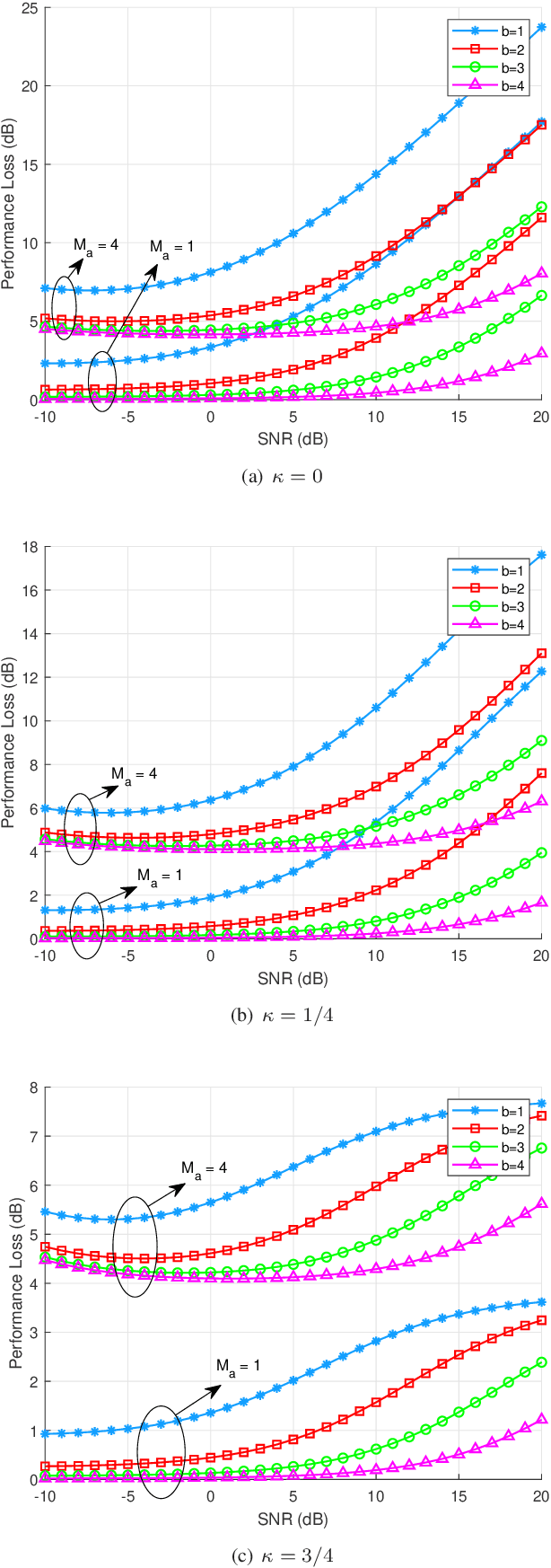
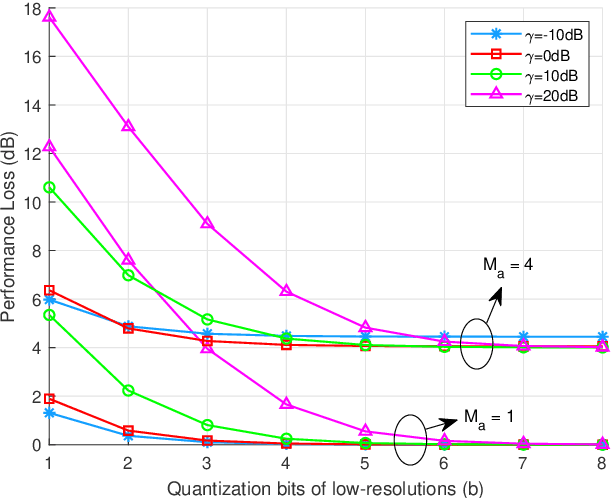
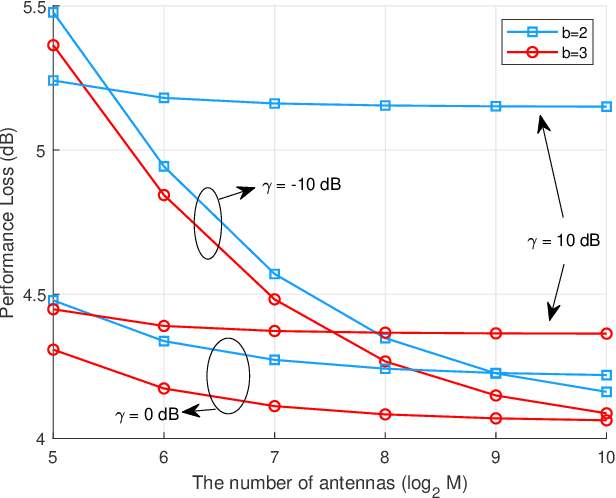
Abstract:Due to the power consumption and high circuit cost in antenna arrays, the practical application of massive multipleinput multiple-output (MIMO) in the sixth generation (6G) and future wireless networks is still challenging. Employing lowresolution analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and hybrid analog and digital (HAD) structure is two low-cost choice with acceptable performance loss. In this paper, the combination of the mixedADC architecture and HAD structure employed at receiver is proposed for direction of arrival (DOA) estimation, which will be applied to the beamforming tracking and alignment in 6G. By adopting the additive quantization noise model, the exact closedform expression of the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) for the HAD architecture with mixed-ADCs is derived. Moreover, the closed-form expression of the performance loss factor is derived as a benchmark. In addition, to take power consumption into account, energy efficiency is also investigated in our paper. The numerical results reveal that the HAD structure with mixedADCs can significantly reduce the power consumption and hardware cost. Furthermore, that architecture is able to achieve a better trade-off between the performance loss and the power consumption. Finally, adopting 2-4 bits of resolution may be a good choice in practical massive MIMO systems.
On Performance Loss of DOA Measurement Using Massive MIMO Receiver with Mixed-ADCs
Apr 06, 2021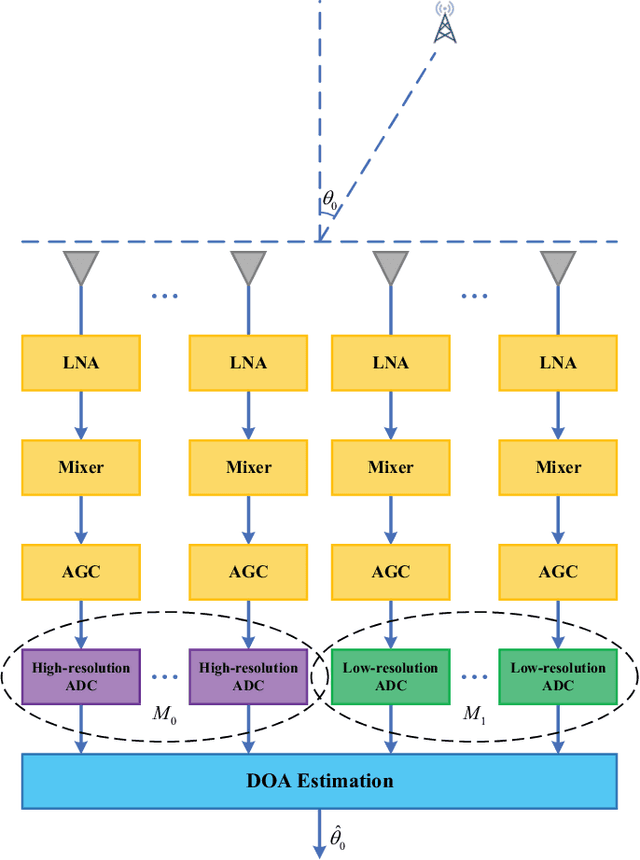
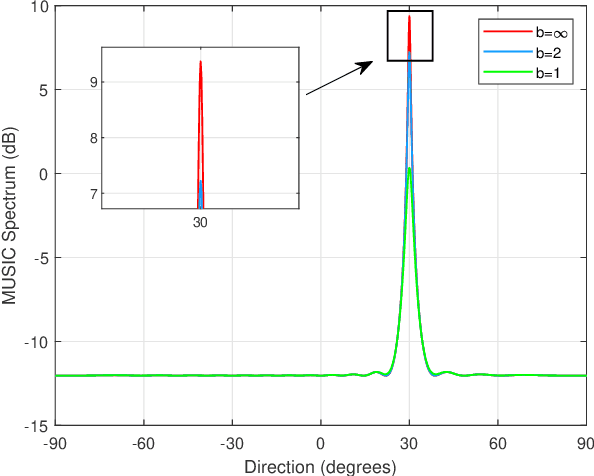
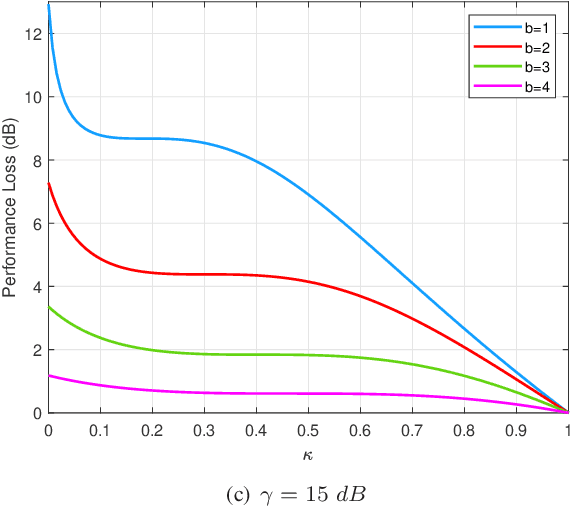
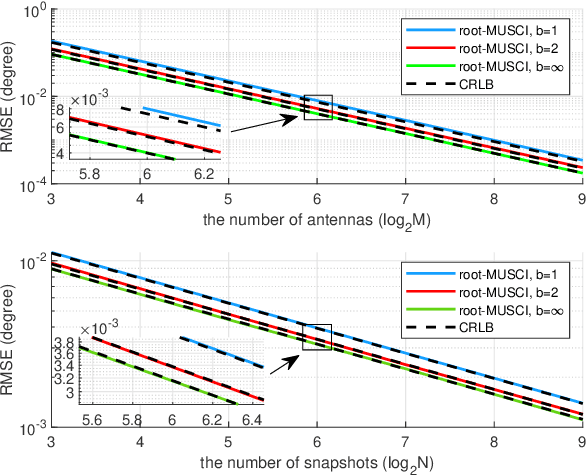
Abstract:High hardware cost and high power consumption of massive multiple-input and multiple output (MIMO) are still two challenges for the future wireless communications including beyond 5G. Adopting the low-resolution analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is viewed as a promising solution. Additionally, the direction of arrival (DOA) estimation is an indispensable technology for beam alignment and tracking in massive MIMO systems. Thus, in this paper, the performance of DOA estimation for massive MIMO receive array with mixed-ADC structure is first investigated, where one part of radio frequency (RF) chains are connected with high-resolution ADCs and the remaining ones are connected with low-resolution ADCs. Moreover, the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) for this architecture is derived based on the additive quantization noise model approximation for the effect of low-resolution ADCs. Then, the root-MUSIC method is designed for such a receive structure. Eventually, a performance loss factor and the associated energy efficiency factor is defined for analysis in detail. Simulation results find that a mixed-ADC architecture can strike a good balance among RMSE performance, circuit cost and energy efficiency. More importantly, just 1-4 bits of low-resolution ADCs can achieve a satisfactory performance for DOA measurement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge