Lijiang Yang
Multi-objective fluorescent molecule design with a data-physics dual-driven generative framework
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Designing fluorescent small molecules with tailored optical and physicochemical properties requires navigating vast, underexplored chemical space while satisfying multiple objectives and constraints. Conventional generate-score-screen approaches become impractical under such realistic design specifications, owing to their low search efficiency, unreliable generalizability of machine-learning prediction, and the prohibitive cost of quantum chemical calculation. Here we present LUMOS, a data-and-physics driven framework for inverse design of fluorescent molecules. LUMOS couples generator and predictor within a shared latent representation, enabling direct specification-to-molecule design and efficient exploration. Moreover, LUMOS combines neural networks with a fast time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) calculation workflow to build a suite of complementary predictors spanning different trade-offs in speed, accuracy, and generalizability, enabling reliable property prediction across diverse scenarios. Finally, LUMOS employs a property-guided diffusion model integrated with multi-objective evolutionary algorithms, enabling de novo design and molecular optimization under multiple objectives and constraints. Across comprehensive benchmarks, LUMOS consistently outperforms baseline models in terms of accuracy, generalizability and physical plausibility for fluorescence property prediction, and demonstrates superior performance in multi-objective scaffold- and fragment-level molecular optimization. Further validation using TD-DFT and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations demonstrates that LUMOS can generate valid fluorophores that meet various target specifications. Overall, these results establish LUMOS as a data-physics dual-driven framework for general fluorophore inverse design.
Few-Shot Learning of Accurate Folding Landscape for Protein Structure Prediction
Aug 20, 2022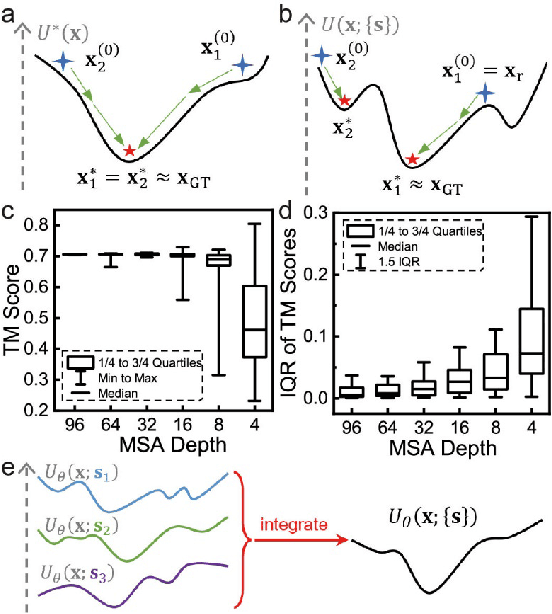
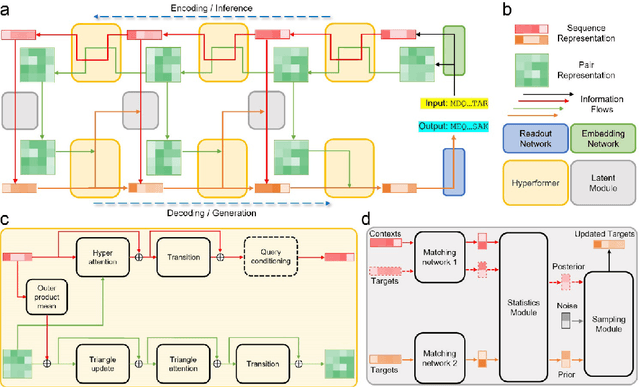
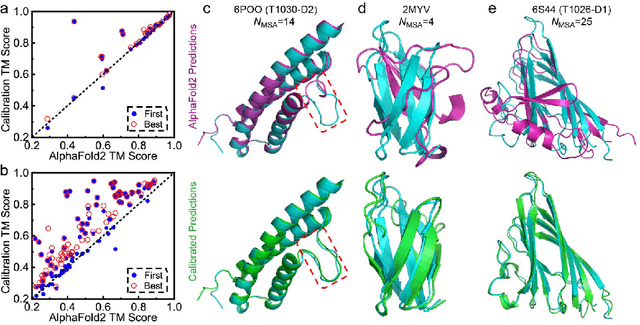
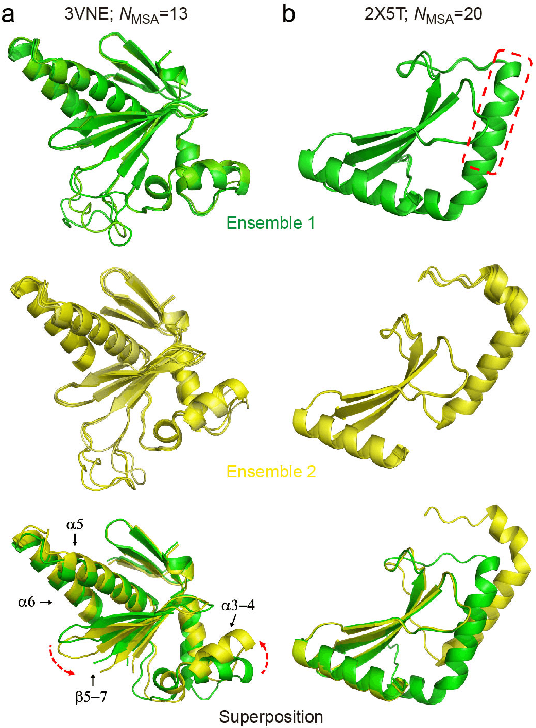
Abstract:Data-driven predictive methods which can efficiently and accurately transform protein sequences into biologically active structures are highly valuable for scientific research and therapeutical development. Determining accurate folding landscape using co-evolutionary information is fundamental to the success of modern protein structure prediction methods. As the state of the art, AlphaFold2 has dramatically raised the accuracy without performing explicit co-evolutionary analysis. Nevertheless, its performance still shows strong dependence on available sequence homologs. We investigated the cause of such dependence and presented EvoGen, a meta generative model, to remedy the underperformance of AlphaFold2 for poor MSA targets. EvoGen allows us to manipulate the folding landscape either by denoising the searched MSA or by generating virtual MSA, and helps AlphaFold2 fold accurately in low-data regime or even achieve encouraging performance with single-sequence predictions. Being able to make accurate predictions with few-shot MSA not only generalizes AlphaFold2 better for orphan sequences, but also democratizes its use for high-throughput applications. Besides, EvoGen combined with AlphaFold2 yields a probabilistic structure generation method which could explore alternative conformations of protein sequences, and the task-aware differentiable algorithm for sequence generation will benefit other related tasks including protein design.
PSP: Million-level Protein Sequence Dataset for Protein Structure Prediction
Jun 24, 2022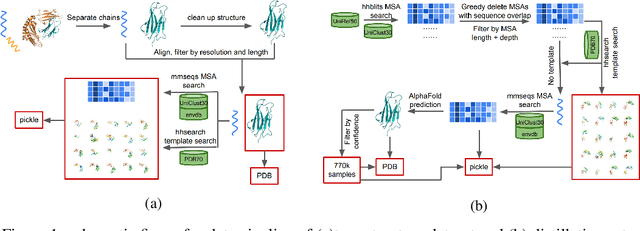
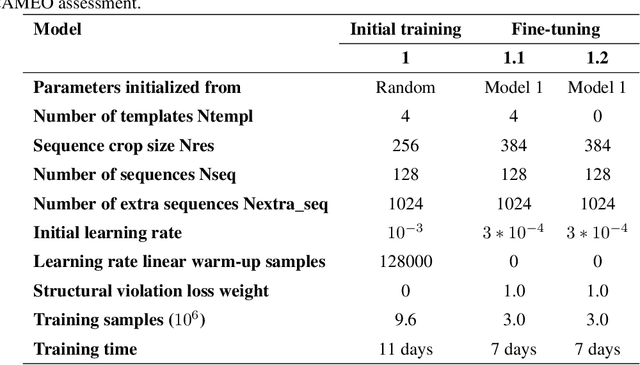
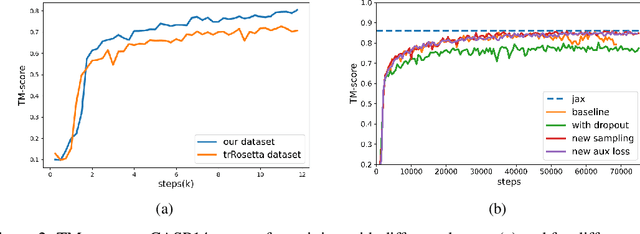
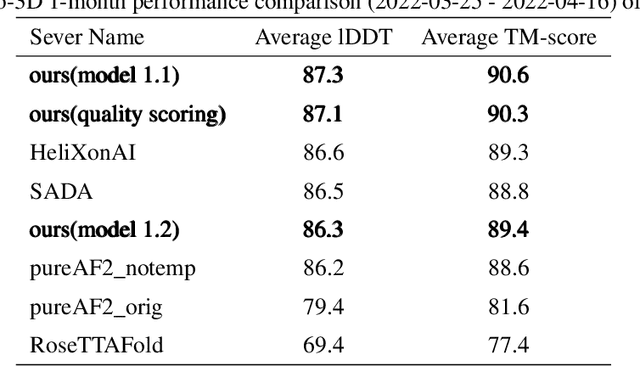
Abstract:Proteins are essential component of human life and their structures are important for function and mechanism analysis. Recent work has shown the potential of AI-driven methods for protein structure prediction. However, the development of new models is restricted by the lack of dataset and benchmark training procedure. To the best of our knowledge, the existing open source datasets are far less to satisfy the needs of modern protein sequence-structure related research. To solve this problem, we present the first million-level protein structure prediction dataset with high coverage and diversity, named as PSP. This dataset consists of 570k true structure sequences (10TB) and 745k complementary distillation sequences (15TB). We provide in addition the benchmark training procedure for SOTA protein structure prediction model on this dataset. We validate the utility of this dataset for training by participating CAMEO contest in which our model won the first place. We hope our PSP dataset together with the training benchmark can enable a broader community of AI/biology researchers for AI-driven protein related research.
Deep Reinforcement Learning of Transition States
Nov 13, 2020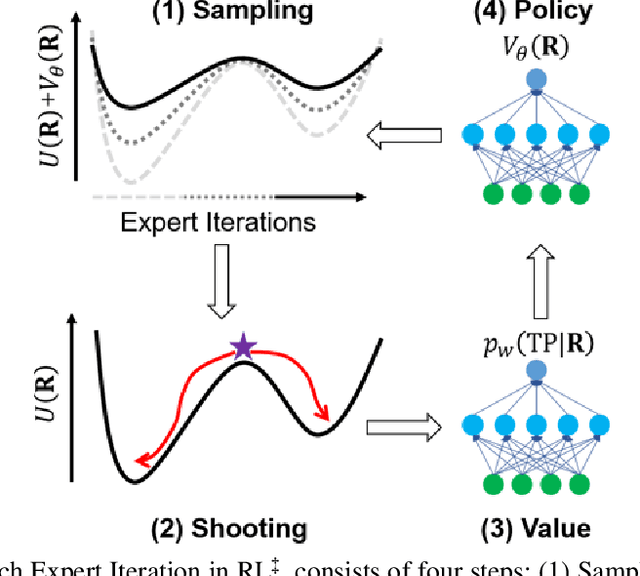
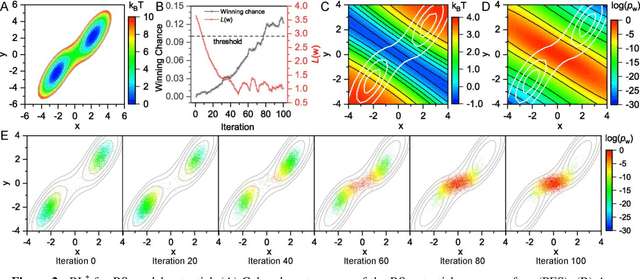
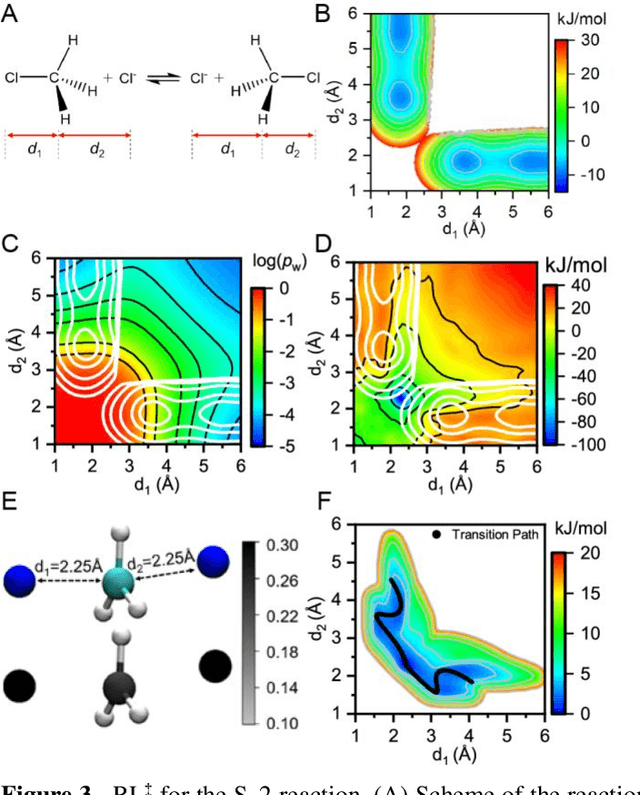
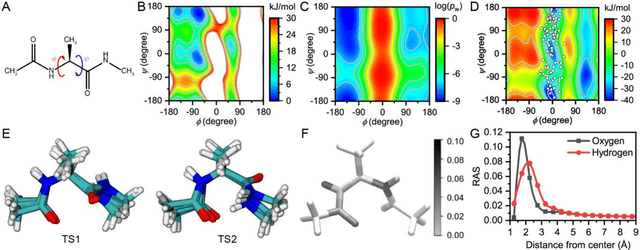
Abstract:Combining reinforcement learning (RL) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we propose a machine-learning approach (RL$^\ddag$) to automatically unravel chemical reaction mechanisms. In RL$^\ddag$, locating the transition state of a chemical reaction is formulated as a game, where a virtual player is trained to shoot simulation trajectories connecting the reactant and product. The player utilizes two functions, one for value estimation and the other for policy making, to iteratively improve the chance of winning this game. We can directly interpret the reaction mechanism according to the value function. Meanwhile, the policy function enables efficient sampling of the transition paths, which can be further used to analyze the reaction dynamics and kinetics. Through multiple experiments, we show that RL{\ddag} can be trained tabula rasa hence allows us to reveal chemical reaction mechanisms with minimal subjective biases.
A Perspective on Deep Learning for Molecular Modeling and Simulations
Apr 25, 2020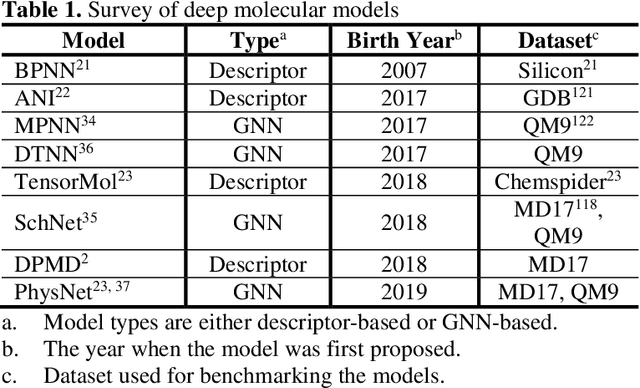
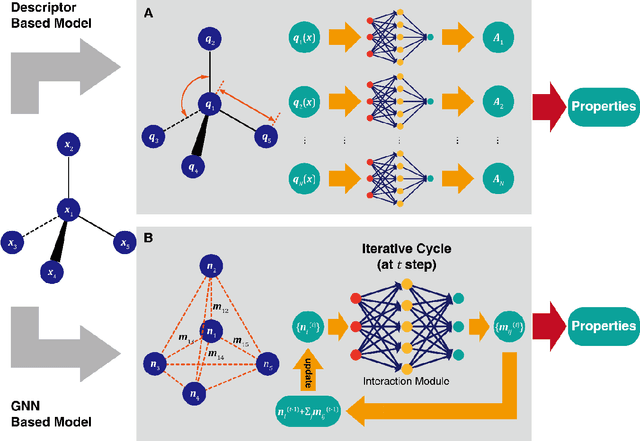
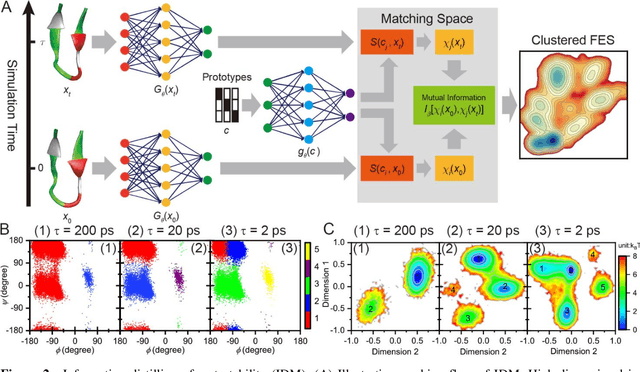
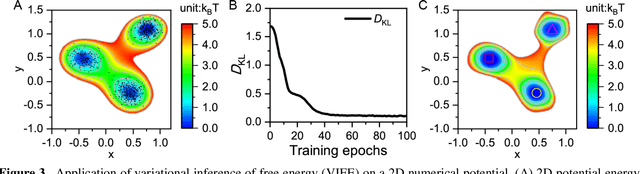
Abstract:Deep learning is transforming many areas in science, and it has great potential in modeling molecular systems. However, unlike the mature deployment of deep learning in computer vision and natural language processing, its development in molecular modeling and simulations is still at an early stage, largely because the inductive biases of molecules are completely different from those of images or texts. Footed on these differences, we first reviewed the limitations of traditional deep learning models from the perspective of molecular physics, and wrapped up some relevant technical advancement at the interface between molecular modeling and deep learning. We do not focus merely on the ever more complex neural network models, instead, we emphasize the theories and ideas behind modern deep learning. We hope that transacting these ideas into molecular modeling will create new opportunities. For this purpose, we summarized several representative applications, ranging from supervised to unsupervised and reinforcement learning, and discussed their connections with the emerging trends in deep learning. Finally, we outlook promising directions which may help address the existing issues in the current framework of deep molecular modeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge