Leonhard Rist
Neural Image Unfolding: Flattening Sparse Anatomical Structures using Neural Fields
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Tomographic imaging reveals internal structures of 3D objects and is crucial for medical diagnoses. Visualizing the morphology and appearance of non-planar sparse anatomical structures that extend over multiple 2D slices in tomographic volumes is inherently difficult but valuable for decision-making and reporting. Hence, various organ-specific unfolding techniques exist to map their densely sampled 3D surfaces to a distortion-minimized 2D representation. However, there is no versatile framework to flatten complex sparse structures including vascular, duct or bone systems. We deploy a neural field to fit the transformation of the anatomy of interest to a 2D overview image. We further propose distortion regularization strategies and combine geometric with intensity-based loss formulations to also display non-annotated and auxiliary targets. In addition to improved versatility, our unfolding technique outperforms mesh-based baselines for sparse structures w.r.t. peak distortion and our regularization scheme yields smoother transformations compared to Jacobian formulations from neural field-based image registration.
Comparative Analysis of Radiomic Features and Gene Expression Profiles in Histopathology Data Using Graph Neural Networks
Dec 25, 2023Abstract:This study leverages graph neural networks to integrate MELC data with Radiomic-extracted features for melanoma classification, focusing on cell-wise analysis. It assesses the effectiveness of gene expression profiles and Radiomic features, revealing that Radiomic features, particularly when combined with UMAP for dimensionality reduction, significantly enhance classification performance. Notably, using Radiomics contributes to increased diagnostic accuracy and computational efficiency, as it allows for the extraction of critical data from fewer stains, thereby reducing operational costs. This methodology marks an advancement in computational dermatology for melanoma cell classification, setting the stage for future research and potential developments.
Employing Graph Representations for Cell-level Characterization of Melanoma MELC Samples
Nov 10, 2022


Abstract:Histopathology imaging is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases. For this reason, computer-assisted approaches have gained popularity and shown promising results in tasks such as segmentation and classification of skin disorders. However, collecting essential data and sufficiently high-quality annotations is a challenge. This work describes a pipeline that uses suspected melanoma samples that have been characterized using Multi-Epitope-Ligand Cartography (MELC). This cellular-level tissue characterisation is then represented as a graph and used to train a graph neural network. This imaging technology, combined with the methodology proposed in this work, achieves a classification accuracy of 87%, outperforming existing approaches by 10%.
Building Brains: Subvolume Recombination for Data Augmentation in Large Vessel Occlusion Detection
May 16, 2022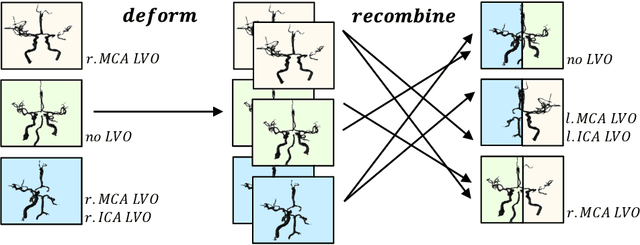
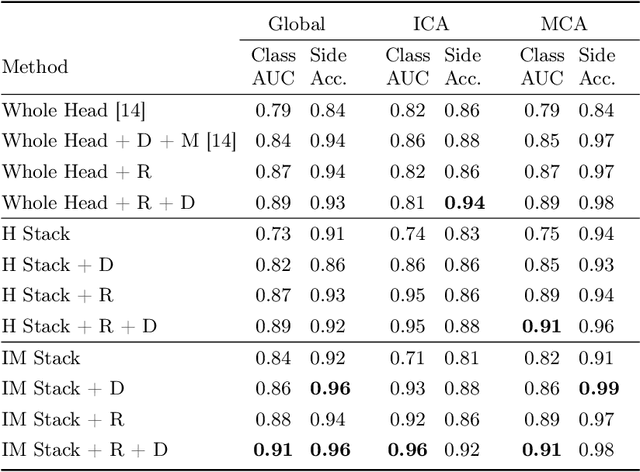
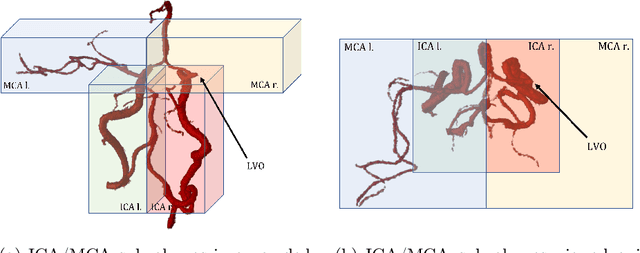
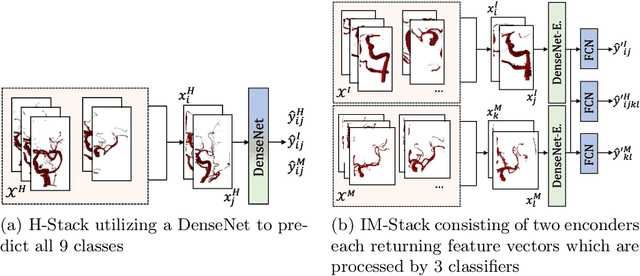
Abstract:Ischemic strokes are often caused by large vessel occlusions (LVOs), which can be visualized and diagnosed with Computed Tomography Angiography scans. As time is brain, a fast, accurate and automated diagnosis of these scans is desirable. Human readers compare the left and right hemispheres in their assessment of strokes. A large training data set is required for a standard deep learning-based model to learn this strategy from data. As labeled medical data in this field is rare, other approaches need to be developed. To both include the prior knowledge of side comparison and increase the amount of training data, we propose an augmentation method that generates artificial training samples by recombining vessel tree segmentations of the hemispheres or hemisphere subregions from different patients. The subregions cover vessels commonly affected by LVOs, namely the internal carotid artery (ICA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA). In line with the augmentation scheme, we use a 3D-DenseNet fed with task-specific input, fostering a side-by-side comparison between the hemispheres. Furthermore, we propose an extension of that architecture to process the individual hemisphere subregions. All configurations predict the presence of an LVO, its side, and the affected subregion. We show the effect of recombination as an augmentation strategy in a 5-fold cross validated ablation study. We enhanced the AUC for patient-wise classification regarding the presence of an LVO of all investigated architectures. For one variant, the proposed method improved the AUC from 0.73 without augmentation to 0.89. The best configuration detects LVOs with an AUC of 0.91, LVOs in the ICA with an AUC of 0.96, and in the MCA with 0.91 while accurately predicting the affected side.
An Algorithm for the Labeling and Interactive Visualization of the Cerebrovascular System of Ischemic Strokes
Apr 26, 2022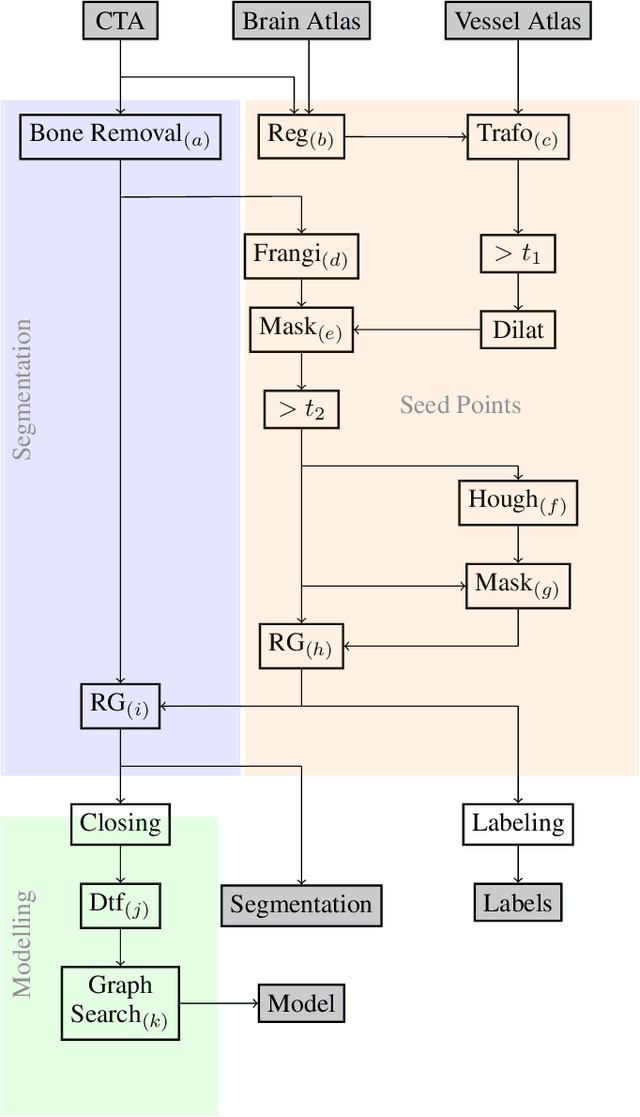
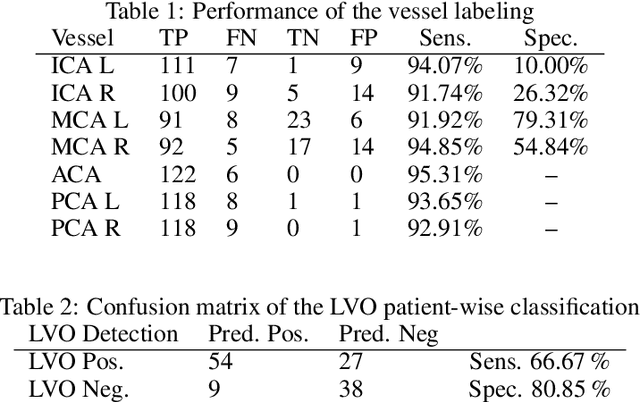
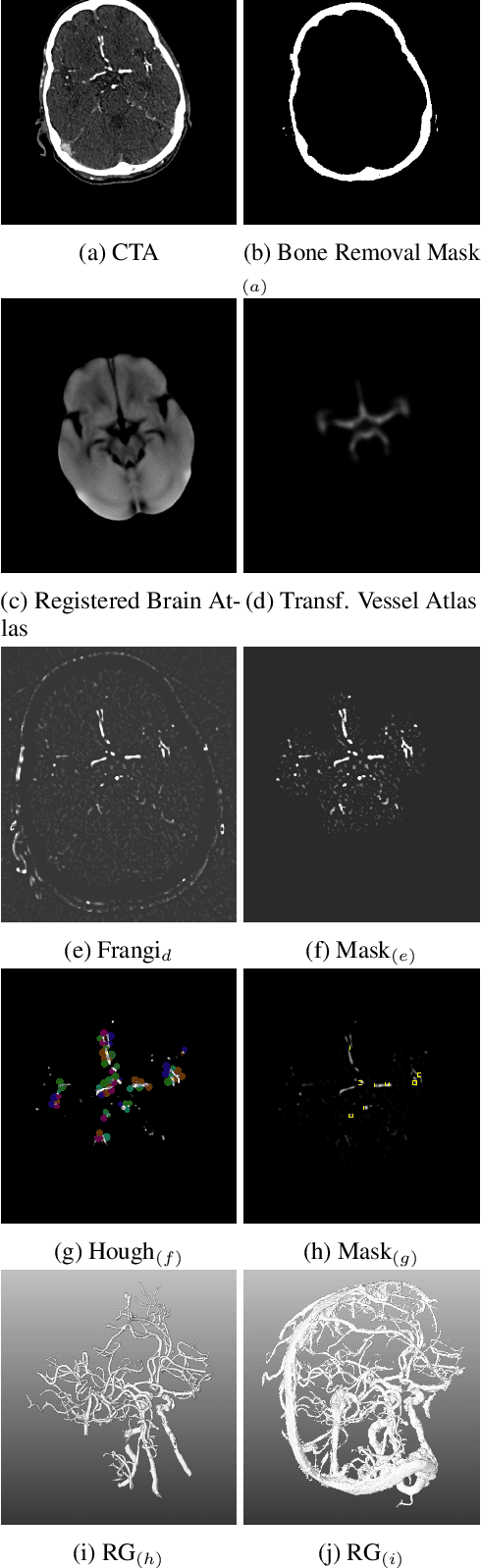

Abstract:During the diagnosis of ischemic strokes, the Circle of Willis and its surrounding vessels are the arteries of interest. Their visualization in case of an acute stroke is often enabled by Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA). Still, the identification and analysis of the cerebral arteries remain time consuming in such scans due to a large number of peripheral vessels which may disturb the visual impression. In previous work we proposed VirtualDSA++, an algorithm designed to segment and label the cerebrovascular tree on CTA scans. Especially with stroke patients, labeling is a delicate procedure, as in the worst case whole hemispheres may not be present due to impeded perfusion. Hence, we extended the labeling mechanism for the cerebral arteries to identify occluded vessels. In the work at hand, we place the algorithm in a clinical context by evaluating the labeling and occlusion detection on stroke patients, where we have achieved labeling sensitivities comparable to other works between 92\,\% and 95\,\%. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first work to address labeling and occlusion detection at once, whereby a sensitivity of 67\,\% and a specificity of 81\,\% were obtained for the latter. VirtualDSA++ also automatically segments and models the intracranial system, which we further used in a deep learning driven follow up work. We present the generic concept of iterative systematic search for pathways on all nodes of said model, which enables new interactive features. Exemplary, we derive in detail, firstly, the interactive planning of vascular interventions like the mechanical thrombectomy and secondly, the interactive suppression of vessel structures that are not of interest in diagnosing strokes (like veins). We discuss both features as well as further possibilities emerging from the proposed concept.
Segmentation of the Carotid Lumen and Vessel Wall using Deep Learning and Location Priors
Jan 17, 2022
Abstract:In this report we want to present our method and results for the Carotid Artery Vessel Wall Segmentation Challenge. We propose an image-based pipeline utilizing the U-Net architecture and location priors to solve the segmentation problem at hand.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge