Leonardo Cotta
Measuring Scientific Capabilities of Language Models with a Systems Biology Dry Lab
Jul 02, 2025
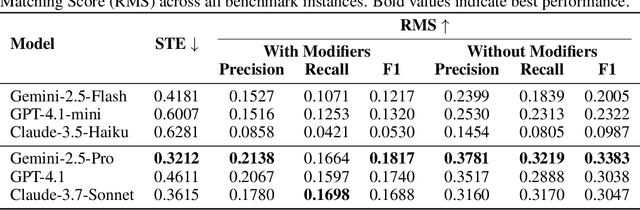
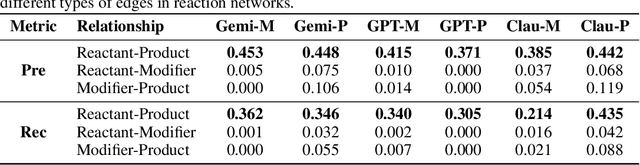
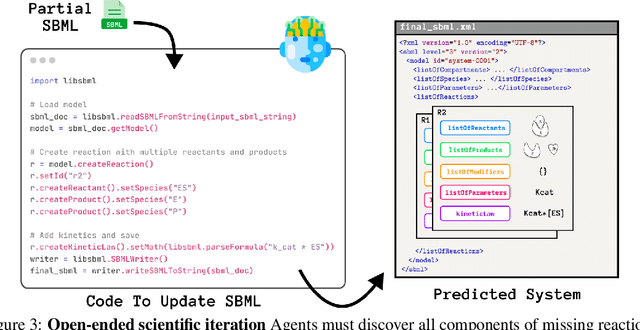
Abstract:Designing experiments and result interpretations are core scientific competencies, particularly in biology, where researchers perturb complex systems to uncover the underlying systems. Recent efforts to evaluate the scientific capabilities of large language models (LLMs) fail to test these competencies because wet-lab experimentation is prohibitively expensive: in expertise, time and equipment. We introduce SciGym, a first-in-class benchmark that assesses LLMs' iterative experiment design and analysis abilities in open-ended scientific discovery tasks. SciGym overcomes the challenge of wet-lab costs by running a dry lab of biological systems. These models, encoded in Systems Biology Markup Language, are efficient for generating simulated data, making them ideal testbeds for experimentation on realistically complex systems. We evaluated six frontier LLMs on 137 small systems, and released a total of 350 systems. Our evaluation shows that while more capable models demonstrated superior performance, all models' performance declined significantly as system complexity increased, suggesting substantial room for improvement in the scientific capabilities of LLM agents.
End-To-End Causal Effect Estimation from Unstructured Natural Language Data
Jul 09, 2024
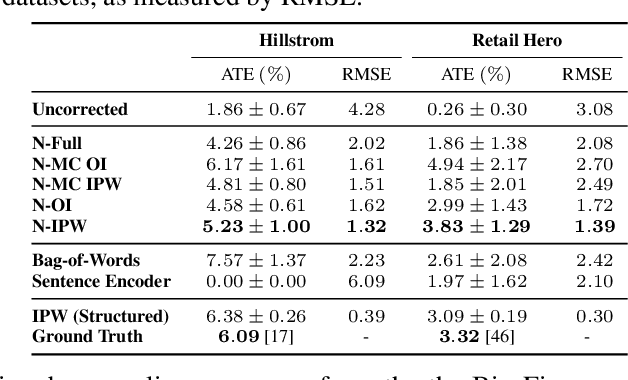


Abstract:Knowing the effect of an intervention is critical for human decision-making, but current approaches for causal effect estimation rely on manual data collection and structuring, regardless of the causal assumptions. This increases both the cost and time-to-completion for studies. We show how large, diverse observational text data can be mined with large language models (LLMs) to produce inexpensive causal effect estimates under appropriate causal assumptions. We introduce NATURAL, a novel family of causal effect estimators built with LLMs that operate over datasets of unstructured text. Our estimators use LLM conditional distributions (over variables of interest, given the text data) to assist in the computation of classical estimators of causal effect. We overcome a number of technical challenges to realize this idea, such as automating data curation and using LLMs to impute missing information. We prepare six (two synthetic and four real) observational datasets, paired with corresponding ground truth in the form of randomized trials, which we used to systematically evaluate each step of our pipeline. NATURAL estimators demonstrate remarkable performance, yielding causal effect estimates that fall within 3 percentage points of their ground truth counterparts, including on real-world Phase 3/4 clinical trials. Our results suggest that unstructured text data is a rich source of causal effect information, and NATURAL is a first step towards an automated pipeline to tap this resource.
Out-Of-Context Prompting Boosts Fairness and Robustness in Large Language Model Predictions
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:Frontier Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly being deployed for high-stakes decision-making. On the other hand, these models are still consistently making predictions that contradict users' or society's expectations, e.g., hallucinating, or discriminating. Thus, it is important that we develop test-time strategies to improve their trustworthiness. Inspired by prior work, we leverage causality as a tool to formally encode two aspects of trustworthiness in LLMs: fairness and robustness. Under this perspective, existing test-time solutions explicitly instructing the model to be fair or robust implicitly depend on the LLM's causal reasoning capabilities. In this work, we explore the opposite approach. Instead of explicitly asking the LLM for trustworthiness, we design prompts to encode the underlying causal inference algorithm that will, by construction, result in more trustworthy predictions. Concretely, we propose out-of-context prompting as a test-time solution to encourage fairness and robustness in LLMs. Out-of-context prompting leverages the user's prior knowledge of the task's causal model to apply (random) counterfactual transformations and improve the model's trustworthiness. Empirically, we show that out-of-context prompting consistently improves the fairness and robustness of frontier LLMs across five different benchmark datasets without requiring additional data, finetuning or pre-training.
Probabilistic Invariant Learning with Randomized Linear Classifiers
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Designing models that are both expressive and preserve known invariances of tasks is an increasingly hard problem. Existing solutions tradeoff invariance for computational or memory resources. In this work, we show how to leverage randomness and design models that are both expressive and invariant but use less resources. Inspired by randomized algorithms, our key insight is that accepting probabilistic notions of universal approximation and invariance can reduce our resource requirements. More specifically, we propose a class of binary classification models called Randomized Linear Classifiers (RLCs). We give parameter and sample size conditions in which RLCs can, with high probability, approximate any (smooth) function while preserving invariance to compact group transformations. Leveraging this result, we design three RLCs that are provably probabilistic invariant for classification tasks over sets, graphs, and spherical data. We show how these models can achieve probabilistic invariance and universality using less resources than (deterministic) neural networks and their invariant counterparts. Finally, we empirically demonstrate the benefits of this new class of models on invariant tasks where deterministic invariant neural networks are known to struggle.
Causal Lifting and Link Prediction
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:Current state-of-the-art causal models for link prediction assume an underlying set of inherent node factors -- an innate characteristic defined at the node's birth -- that governs the causal evolution of links in the graph. In some causal tasks, however, link formation is path-dependent, i.e., the outcome of link interventions depends on existing links. For instance, in the customer-product graph of an online retailer, the effect of an 85-inch TV ad (treatment) likely depends on whether the costumer already has an 85-inch TV. Unfortunately, existing causal methods are impractical in these scenarios. The cascading functional dependencies between links (due to path dependence) are either unidentifiable or require an impractical number of control variables. In order to remedy this shortcoming, this work develops the first causal model capable of dealing with path dependencies in link prediction. It introduces the concept of causal lifting, an invariance in causal models that, when satisfied, allows the identification of causal link prediction queries using limited interventional data. On the estimation side, we show how structural pairwise embeddings -- a type of symmetry-based joint representation of node pairs in a graph -- exhibit lower bias and correctly represent the causal structure of the task, as opposed to existing node embedding methods, e.g., GNNs and matrix factorization. Finally, we validate our theoretical findings on four datasets under three different scenarios for causal link prediction tasks: knowledge base completion, covariance matrix estimation and consumer-product recommendations.
Reconstruction for Powerful Graph Representations
Oct 07, 2021



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have limited expressive power, failing to represent many graph classes correctly. While more expressive graph representation learning (GRL) alternatives can distinguish some of these classes, they are significantly harder to implement, may not scale well, and have not been shown to outperform well-tuned GNNs in real-world tasks. Thus, devising simple, scalable, and expressive GRL architectures that also achieve real-world improvements remains an open challenge. In this work, we show the extent to which graph reconstruction -- reconstructing a graph from its subgraphs -- can mitigate the theoretical and practical problems currently faced by GRL architectures. First, we leverage graph reconstruction to build two new classes of expressive graph representations. Secondly, we show how graph reconstruction boosts the expressive power of any GNN architecture while being a (provably) powerful inductive bias for invariances to vertex removals. Empirically, we show how reconstruction can boost GNN's expressive power -- while maintaining its invariance to permutations of the vertices -- by solving seven graph property tasks not solvable by the original GNN. Further, we demonstrate how it boosts state-of-the-art GNN's performance across nine real-world benchmark datasets.
Unsupervised Joint $k$-node Graph Representations with Compositional Energy-Based Models
Oct 08, 2020



Abstract:Existing Graph Neural Network (GNN) methods that learn inductive unsupervised graph representations focus on learning node and edge representations by predicting observed edges in the graph. Although such approaches have shown advances in downstream node classification tasks, they are ineffective in jointly representing larger $k$-node sets, $k{>}2$. We propose MHM-GNN, an inductive unsupervised graph representation approach that combines joint $k$-node representations with energy-based models (hypergraph Markov networks) and GNNs. To address the intractability of the loss that arises from this combination, we endow our optimization with a loss upper bound using a finite-sample unbiased Markov Chain Monte Carlo estimator. Our experiments show that the unsupervised MHM-GNN representations of MHM-GNN produce better unsupervised representations than existing approaches from the literature.
Graph Pattern Mining and Learning through User-defined Relations (Extended Version)
Sep 14, 2018



Abstract:In this work we propose R-GPM, a parallel computing framework for graph pattern mining (GPM) through a user-defined subgraph relation. More specifically, we enable the computation of statistics of patterns through their subgraph classes, generalizing traditional GPM methods. R-GPM provides efficient estimators for these statistics by employing a MCMC sampling algorithm combined with several optimizations. We provide both theoretical guarantees and empirical evaluations of our estimators in application scenarios such as stochastic optimization of deep high-order graph neural network models and pattern (motif) counting. We also propose and evaluate optimizations that enable improvements of our estimators accuracy, while reducing their computational costs in up to 3-orders-of-magnitude. Finally,we show that R-GPM is scalable, providing near-linear speedups on 44 cores in all of our tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge