Lei Geng
Direct May Not Be the Best: An Incremental Evolution View of Pose Generation
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Pose diversity is an inherent representative characteristic of 2D images. Due to the 3D to 2D projection mechanism, there is evident content discrepancy among distinct pose images. This is the main obstacle bothering pose transformation related researches. To deal with this challenge, we propose a fine-grained incremental evolution centered pose generation framework, rather than traditional direct one-to-one in a rush. Since proposed approach actually bypasses the theoretical difficulty of directly modeling dramatic non-linear variation, the incurred content distortion and blurring could be effectively constrained, at the same time the various individual pose details, especially clothes texture, could be precisely maintained. In order to systematically guide the evolution course, both global and incremental evolution constraints are elaborately designed and merged into the overall framework. And a novel triple-path knowledge fusion structure is worked out to take full advantage of all available valuable knowledge to conduct high-quality pose synthesis. In addition, our framework could generate a series of valuable byproducts, namely the various intermediate poses. Extensive experiments have been conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Code is available at https://github.com/Xiaofei-CN/Incremental-Evolution-Pose-Generation.
Multi-Scale Subgraph Contrastive Learning
Mar 05, 2024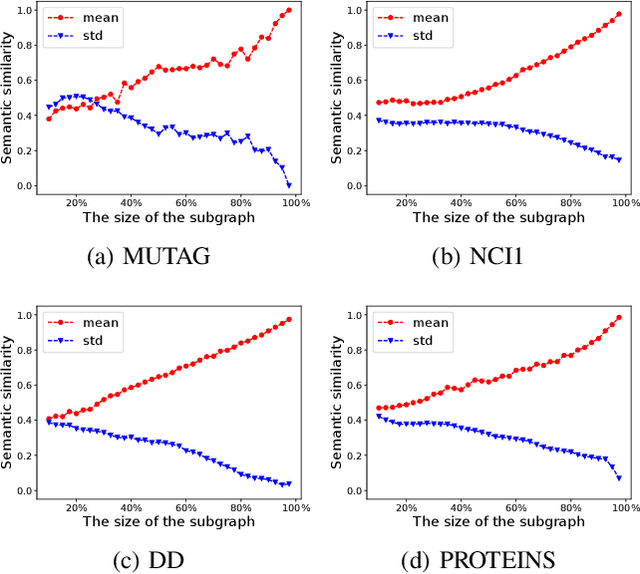
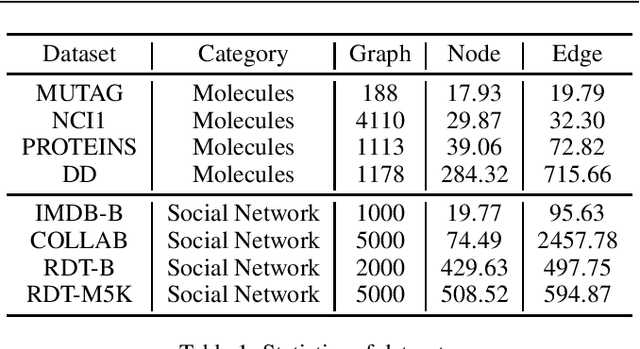
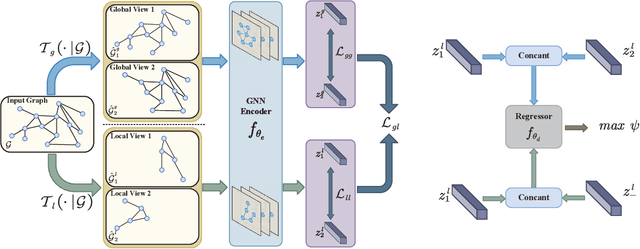
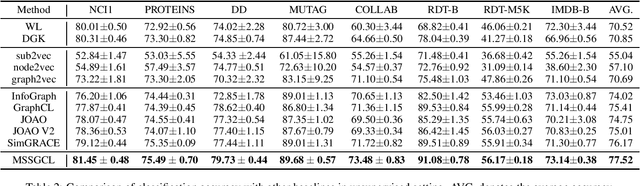
Abstract:Graph-level contrastive learning, aiming to learn the representations for each graph by contrasting two augmented graphs, has attracted considerable attention. Previous studies usually simply assume that a graph and its augmented graph as a positive pair, otherwise as a negative pair. However, it is well known that graph structure is always complex and multi-scale, which gives rise to a fundamental question: after graph augmentation, will the previous assumption still hold in reality? By an experimental analysis, we discover the semantic information of an augmented graph structure may be not consistent as original graph structure, and whether two augmented graphs are positive or negative pairs is highly related with the multi-scale structures. Based on this finding, we propose a multi-scale subgraph contrastive learning method which is able to characterize the fine-grained semantic information. Specifically, we generate global and local views at different scales based on subgraph sampling, and construct multiple contrastive relationships according to their semantic associations to provide richer self-supervised signals. Extensive experiments and parametric analysis on eight graph classification real-world datasets well demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
KBioXLM: A Knowledge-anchored Biomedical Multilingual Pretrained Language Model
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:Most biomedical pretrained language models are monolingual and cannot handle the growing cross-lingual requirements. The scarcity of non-English domain corpora, not to mention parallel data, poses a significant hurdle in training multilingual biomedical models. Since knowledge forms the core of domain-specific corpora and can be translated into various languages accurately, we propose a model called KBioXLM, which transforms the multilingual pretrained model XLM-R into the biomedical domain using a knowledge-anchored approach. We achieve a biomedical multilingual corpus by incorporating three granularity knowledge alignments (entity, fact, and passage levels) into monolingual corpora. Then we design three corresponding training tasks (entity masking, relation masking, and passage relation prediction) and continue training on top of the XLM-R model to enhance its domain cross-lingual ability. To validate the effectiveness of our model, we translate the English benchmarks of multiple tasks into Chinese. Experimental results demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms monolingual and multilingual pretrained models in cross-lingual zero-shot and few-shot scenarios, achieving improvements of up to 10+ points. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/ngwlh-gl/KBioXLM.
RSpell: Retrieval-augmented Framework for Domain Adaptive Chinese Spelling Check
Aug 16, 2023



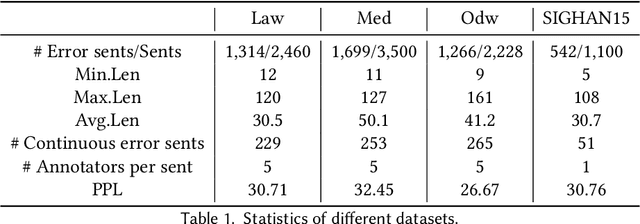
Abstract:Chinese Spelling Check (CSC) refers to the detection and correction of spelling errors in Chinese texts. In practical application scenarios, it is important to make CSC models have the ability to correct errors across different domains. In this paper, we propose a retrieval-augmented spelling check framework called RSpell, which searches corresponding domain terms and incorporates them into CSC models. Specifically, we employ pinyin fuzzy matching to search for terms, which are combined with the input and fed into the CSC model. Then, we introduce an adaptive process control mechanism to dynamically adjust the impact of external knowledge on the model. Additionally, we develop an iterative strategy for the RSpell framework to enhance reasoning capabilities. We conducted experiments on CSC datasets in three domains: law, medicine, and official document writing. The results demonstrate that RSpell achieves state-of-the-art performance in both zero-shot and fine-tuning scenarios, demonstrating the effectiveness of the retrieval-augmented CSC framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/47777777/Rspell.
General and Domain Adaptive Chinese Spelling Check with Error Consistent Pretraining
Mar 21, 2022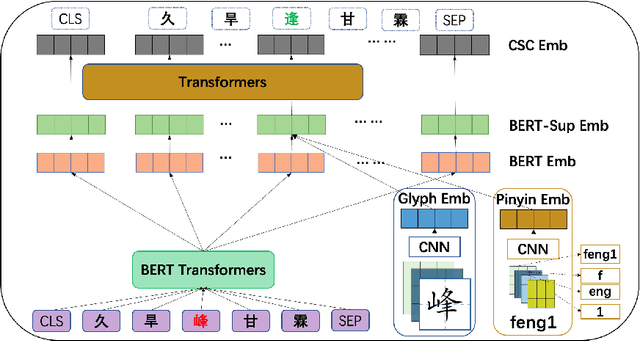
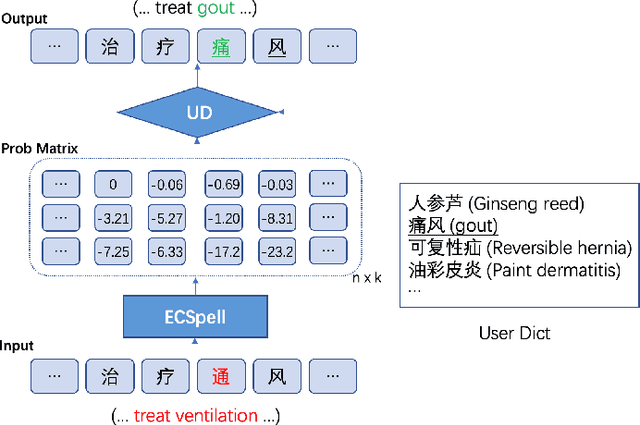

Abstract:The lack of label data is one of the significant bottlenecks for Chinese Spelling Check (CSC). Existing researches use the method of automatic generation by exploiting unlabeled data to expand the supervised corpus. However, there is a big gap between the real input scenario and automatic generated corpus. Thus, we develop a competitive general speller ECSpell which adopts the Error Consistent masking strategy to create data for pretraining. This error consistency masking strategy is used to specify the error types of automatically generated sentences which is consistent with real scene. The experimental result indicates our model outperforms previous state-of-the-art models on the general benchmark. Moreover, spellers often work within a particular domain in real life. Due to lots of uncommon domain terms, experiments on our built domain specific datasets show that general models perform terribly. Inspired by the common practice of input methods, we propose to add an alterable user dictionary to handle the zero-shot domain adaption problem. Specifically, we attach a User Dictionary guided inference module (UD) to a general token classification based speller. Our experiments demonstrate that ECSpell$^{UD}$, namely ECSpell combined with UD, surpasses all the other baselines largely, even approaching the performance on the general benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge