Lan Ni
Spatial Parsing and Dynamic Temporal Pooling networks for Human-Object Interaction detection
Jun 07, 2022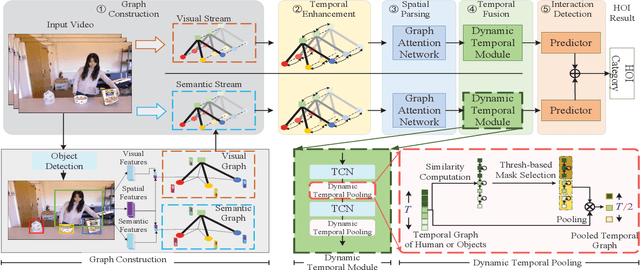
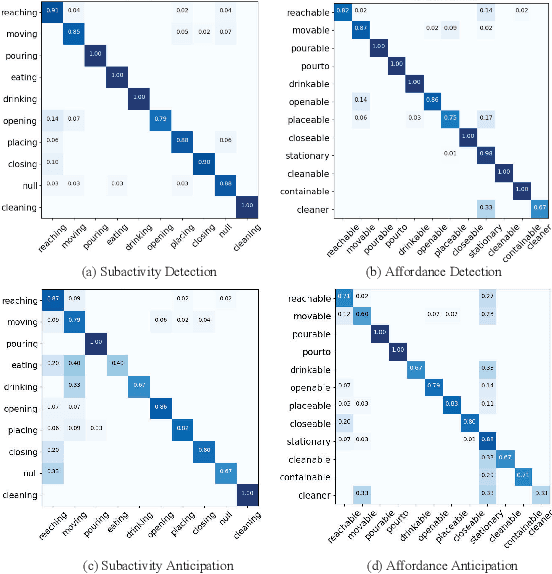


Abstract:The key of Human-Object Interaction(HOI) recognition is to infer the relationship between human and objects. Recently, the image's Human-Object Interaction(HOI) detection has made significant progress. However, there is still room for improvement in video HOI detection performance. Existing one-stage methods use well-designed end-to-end networks to detect a video segment and directly predict an interaction. It makes the model learning and further optimization of the network more complex. This paper introduces the Spatial Parsing and Dynamic Temporal Pooling (SPDTP) network, which takes the entire video as a spatio-temporal graph with human and object nodes as input. Unlike existing methods, our proposed network predicts the difference between interactive and non-interactive pairs through explicit spatial parsing, and then performs interaction recognition. Moreover, we propose a learnable and differentiable Dynamic Temporal Module(DTM) to emphasize the keyframes of the video and suppress the redundant frame. Furthermore, the experimental results show that SPDTP can pay more attention to active human-object pairs and valid keyframes. Overall, we achieve state-of-the-art performance on CAD-120 dataset and Something-Else dataset.
Hate Speech Detection in Clubhouse
Jul 11, 2021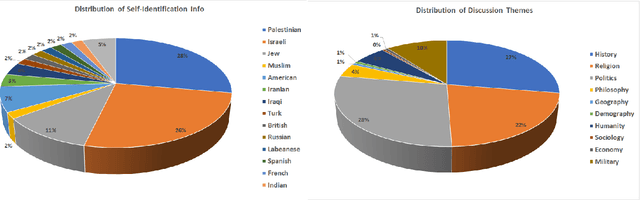

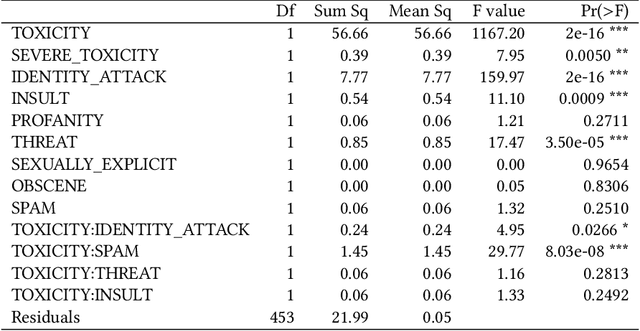
Abstract:With the rise of voice chat rooms, a gigantic resource of data can be exposed to the research community for natural language processing tasks. Moderators in voice chat rooms actively monitor the discussions and remove the participants with offensive language. However, it makes the hate speech detection even more difficult since some participants try to find creative ways to articulate hate speech. This makes the hate speech detection challenging in new social media like Clubhouse. To the best of our knowledge all the hate speech datasets have been collected from text resources like Twitter. In this paper, we take the first step to collect a significant dataset from Clubhouse as the rising star in social media industry. We analyze the collected instances from statistical point of view using the Google Perspective Scores. Our experiments show that, the Perspective Scores can outperform Bag of Words and Word2Vec as high level text features.
Statistical Analysis of Perspective Scores on Hate Speech Detection
Jun 22, 2021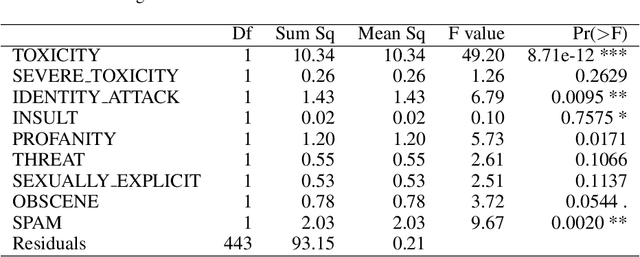
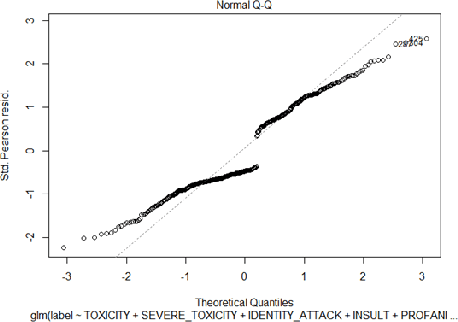
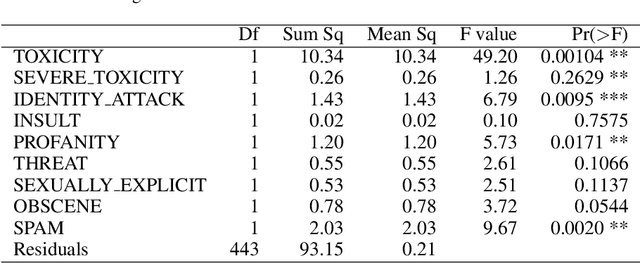
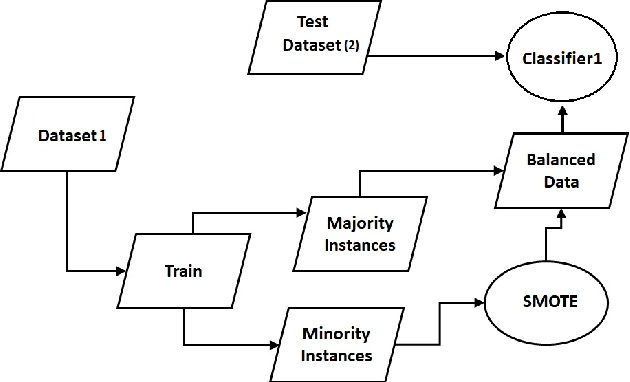
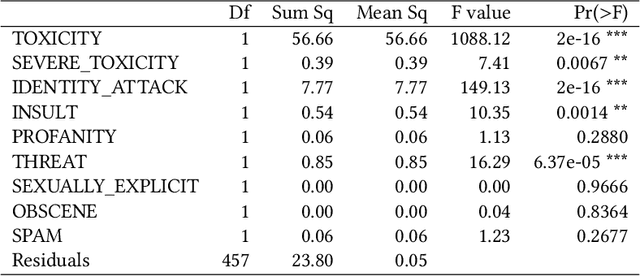
Abstract:Hate speech detection has become a hot topic in recent years due to the exponential growth of offensive language in social media. It has proven that, state-of-the-art hate speech classifiers are efficient only when tested on the data with the same feature distribution as training data. As a consequence, model architecture plays the second role to improve the current results. In such a diverse data distribution relying on low level features is the main cause of deficiency due to natural bias in data. That's why we need to use high level features to avoid a biased judgement. In this paper, we statistically analyze the Perspective Scores and their impact on hate speech detection. We show that, different hate speech datasets are very similar when it comes to extract their Perspective Scores. Eventually, we prove that, over-sampling the Perspective Scores of a hate speech dataset can significantly improve the generalization performance when it comes to be tested on other hate speech datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge