Kunal Handa
Values in the Wild: Discovering and Analyzing Values in Real-World Language Model Interactions
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:AI assistants can impart value judgments that shape people's decisions and worldviews, yet little is known empirically about what values these systems rely on in practice. To address this, we develop a bottom-up, privacy-preserving method to extract the values (normative considerations stated or demonstrated in model responses) that Claude 3 and 3.5 models exhibit in hundreds of thousands of real-world interactions. We empirically discover and taxonomize 3,307 AI values and study how they vary by context. We find that Claude expresses many practical and epistemic values, and typically supports prosocial human values while resisting values like "moral nihilism". While some values appear consistently across contexts (e.g. "transparency"), many are more specialized and context-dependent, reflecting the diversity of human interlocutors and their varied contexts. For example, "harm prevention" emerges when Claude resists users, "historical accuracy" when responding to queries about controversial events, "healthy boundaries" when asked for relationship advice, and "human agency" in technology ethics discussions. By providing the first large-scale empirical mapping of AI values in deployment, our work creates a foundation for more grounded evaluation and design of values in AI systems.
Clio: Privacy-Preserving Insights into Real-World AI Use
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:How are AI assistants being used in the real world? While model providers in theory have a window into this impact via their users' data, both privacy concerns and practical challenges have made analyzing this data difficult. To address these issues, we present Clio (Claude insights and observations), a privacy-preserving platform that uses AI assistants themselves to analyze and surface aggregated usage patterns across millions of conversations, without the need for human reviewers to read raw conversations. We validate this can be done with a high degree of accuracy and privacy by conducting extensive evaluations. We demonstrate Clio's usefulness in two broad ways. First, we share insights about how models are being used in the real world from one million Claude.ai Free and Pro conversations, ranging from providing advice on hairstyles to providing guidance on Git operations and concepts. We also identify the most common high-level use cases on Claude.ai (coding, writing, and research tasks) as well as patterns that differ across languages (e.g., conversations in Japanese discuss elder care and aging populations at higher-than-typical rates). Second, we use Clio to make our systems safer by identifying coordinated attempts to abuse our systems, monitoring for unknown unknowns during critical periods like launches of new capabilities or major world events, and improving our existing monitoring systems. We also discuss the limitations of our approach, as well as risks and ethical concerns. By enabling analysis of real-world AI usage, Clio provides a scalable platform for empirically grounded AI safety and governance.
Bayesian Preference Elicitation with Language Models
Mar 08, 2024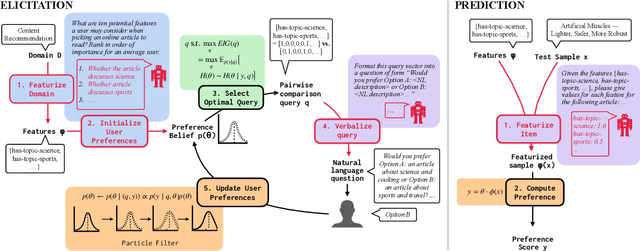
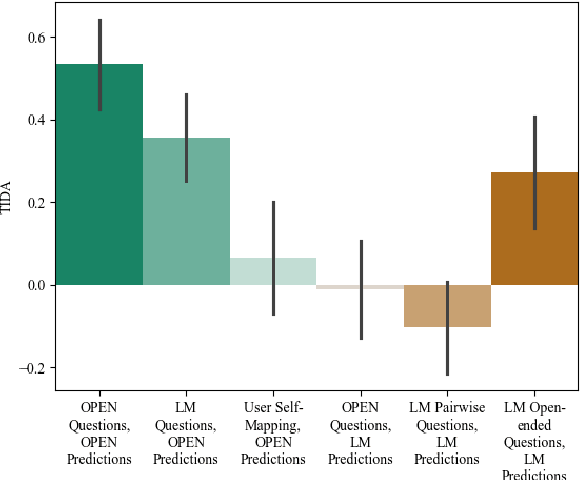
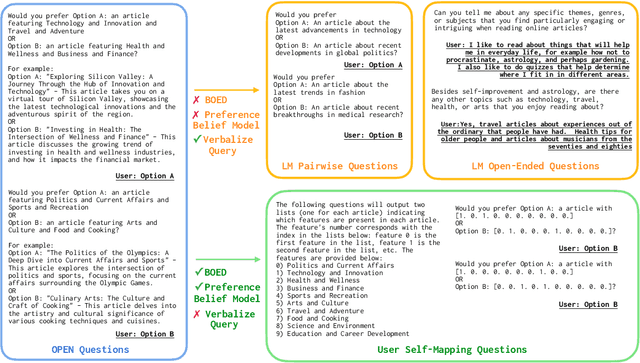

Abstract:Aligning AI systems to users' interests requires understanding and incorporating humans' complex values and preferences. Recently, language models (LMs) have been used to gather information about the preferences of human users. This preference data can be used to fine-tune or guide other LMs and/or AI systems. However, LMs have been shown to struggle with crucial aspects of preference learning: quantifying uncertainty, modeling human mental states, and asking informative questions. These challenges have been addressed in other areas of machine learning, such as Bayesian Optimal Experimental Design (BOED), which focus on designing informative queries within a well-defined feature space. But these methods, in turn, are difficult to scale and apply to real-world problems where simply identifying the relevant features can be difficult. We introduce OPEN (Optimal Preference Elicitation with Natural language) a framework that uses BOED to guide the choice of informative questions and an LM to extract features and translate abstract BOED queries into natural language questions. By combining the flexibility of LMs with the rigor of BOED, OPEN can optimize the informativity of queries while remaining adaptable to real-world domains. In user studies, we find that OPEN outperforms existing LM- and BOED-based methods for preference elicitation.
Emergence of Abstract State Representations in Embodied Sequence Modeling
Nov 07, 2023Abstract:Decision making via sequence modeling aims to mimic the success of language models, where actions taken by an embodied agent are modeled as tokens to predict. Despite their promising performance, it remains unclear if embodied sequence modeling leads to the emergence of internal representations that represent the environmental state information. A model that lacks abstract state representations would be liable to make decisions based on surface statistics which fail to generalize. We take the BabyAI environment, a grid world in which language-conditioned navigation tasks are performed, and build a sequence modeling Transformer, which takes a language instruction, a sequence of actions, and environmental observations as its inputs. In order to investigate the emergence of abstract state representations, we design a "blindfolded" navigation task, where only the initial environmental layout, the language instruction, and the action sequence to complete the task are available for training. Our probing results show that intermediate environmental layouts can be reasonably reconstructed from the internal activations of a trained model, and that language instructions play a role in the reconstruction accuracy. Our results suggest that many key features of state representations can emerge via embodied sequence modeling, supporting an optimistic outlook for applications of sequence modeling objectives to more complex embodied decision-making domains.
"Mistakes Help Us Grow": Facilitating and Evaluating Growth Mindset Supportive Language in Classrooms
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:Teachers' growth mindset supportive language (GMSL)--rhetoric emphasizing that one's skills can be improved over time--has been shown to significantly reduce disparities in academic achievement and enhance students' learning outcomes. Although teachers espouse growth mindset principles, most find it difficult to adopt GMSL in their practice due the lack of effective coaching in this area. We explore whether large language models (LLMs) can provide automated, personalized coaching to support teachers' use of GMSL. We establish an effective coaching tool to reframe unsupportive utterances to GMSL by developing (i) a parallel dataset containing GMSL-trained teacher reframings of unsupportive statements with an accompanying annotation guide, (ii) a GMSL prompt framework to revise teachers' unsupportive language, and (iii) an evaluation framework grounded in psychological theory for evaluating GMSL with the help of students and teachers. We conduct a large-scale evaluation involving 174 teachers and 1,006 students, finding that both teachers and students perceive GMSL-trained teacher and model reframings as more effective in fostering a growth mindset and promoting challenge-seeking behavior, among other benefits. We also find that model-generated reframings outperform those from the GMSL-trained teachers. These results show promise for harnessing LLMs to provide automated GMSL feedback for teachers and, more broadly, LLMs' potentiality for supporting students' learning in the classroom. Our findings also demonstrate the benefit of large-scale human evaluations when applying LLMs in educational domains.
Task Ambiguity in Humans and Language Models
Dec 20, 2022



Abstract:Language models have recently achieved strong performance across a wide range of NLP benchmarks. However, unlike benchmarks, real world tasks are often poorly specified, and agents must deduce the user's intended behavior from a combination of context, instructions, and examples. We investigate how both humans and models behave in the face of such task ambiguity by proposing AmbiBench, a new benchmark of six ambiguously-specified classification tasks. We evaluate humans and models on AmbiBench by seeing how well they identify the intended task using 1) instructions with varying degrees of ambiguity, and 2) different numbers of labeled examples. We find that the combination of model scaling (to 175B parameters) and training with human feedback data enables models to approach or exceed the accuracy of human participants across tasks, but that either one alone is not sufficient. In addition, we show how to dramatically improve the accuracy of language models trained without large-scale human feedback training by finetuning on a small number of ambiguous in-context examples, providing a promising direction for teaching models to generalize well in the face of ambiguity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge