Krzysztof Wolski
Learning Images Across Scales Using Adversarial Training
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:The real world exhibits rich structure and detail across many scales of observation. It is difficult, however, to capture and represent a broad spectrum of scales using ordinary images. We devise a novel paradigm for learning a representation that captures an orders-of-magnitude variety of scales from an unstructured collection of ordinary images. We treat this collection as a distribution of scale-space slices to be learned using adversarial training, and additionally enforce coherency across slices. Our approach relies on a multiscale generator with carefully injected procedural frequency content, which allows to interactively explore the emerging continuous scale space. Training across vastly different scales poses challenges regarding stability, which we tackle using a supervision scheme that involves careful sampling of scales. We show that our generator can be used as a multiscale generative model, and for reconstructions of scale spaces from unstructured patches. Significantly outperforming the state of the art, we demonstrate zoom-in factors of up to 256x at high quality and scale consistency.
Cinematic Gaussians: Real-Time HDR Radiance Fields with Depth of Field
Jun 11, 2024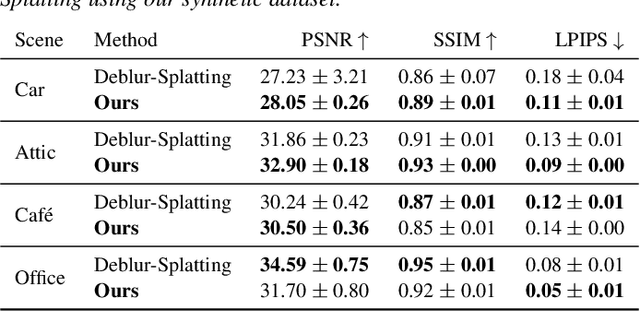
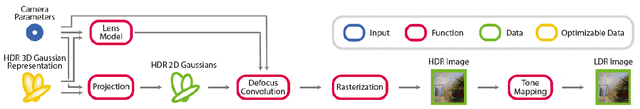
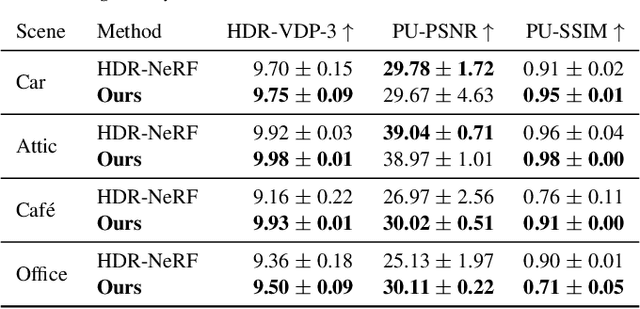

Abstract:Radiance field methods represent the state of the art in reconstructing complex scenes from multi-view photos. However, these reconstructions often suffer from one or both of the following limitations: First, they typically represent scenes in low dynamic range (LDR), which restricts their use to evenly lit environments and hinders immersive viewing experiences. Secondly, their reliance on a pinhole camera model, assuming all scene elements are in focus in the input images, presents practical challenges and complicates refocusing during novel-view synthesis. Addressing these limitations, we present a lightweight method based on 3D Gaussian Splatting that utilizes multi-view LDR images of a scene with varying exposure times, apertures, and focus distances as input to reconstruct a high-dynamic-range (HDR) radiance field. By incorporating analytical convolutions of Gaussians based on a thin-lens camera model as well as a tonemapping module, our reconstructions enable the rendering of HDR content with flexible refocusing capabilities. We demonstrate that our combined treatment of HDR and depth of field facilitates real-time cinematic rendering, outperforming the state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge