Kevin Gao
MATCHA: Can Multi-Agent Collaboration Build a Trustworthy Conversational Recommender?
Apr 26, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a multi-agent collaboration framework called MATCHA for conversational recommendation system, leveraging large language models (LLMs) to enhance personalization and user engagement. Users can request recommendations via free-form text and receive curated lists aligned with their interests, preferences, and constraints. Our system introduces specialized agents for intent analysis, candidate generation, ranking, re-ranking, explainability, and safeguards. These agents collaboratively improve recommendations accuracy, diversity, and safety. On eight metrics, our model achieves superior or comparable performance to the current state-of-the-art. Through comparisons with six baseline models, our approach addresses key challenges in conversational recommendation systems for game recommendations, including: (1) handling complex, user-specific requests, (2) enhancing personalization through multi-agent collaboration, (3) empirical evaluation and deployment, and (4) ensuring safe and trustworthy interactions.
PyPulse: A Python Library for Biosignal Imputation
Dec 09, 2024


Abstract:We introduce PyPulse, a Python package for imputation of biosignals in both clinical and wearable sensor settings. Missingness is commonplace in these settings and can arise from multiple causes, such as insecure sensor attachment or data transmission loss. PyPulse's framework provides a modular and extendable framework with high ease-of-use for a broad userbase, including non-machine-learning bioresearchers. Specifically, its new capabilities include using pre-trained imputation methods out-of-the-box on custom datasets, running the full workflow of training or testing a baseline method with a single line of code, and comparing baseline methods in an interactive visualization tool. We released PyPulse under the MIT License on Github and PyPI. The source code can be found at: https://github.com/rehg-lab/pulseimpute.
OMuleT: Orchestrating Multiple Tools for Practicable Conversational Recommendation
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we present a systematic effort to design, evaluate, and implement a realistic conversational recommender system (CRS). The objective of our system is to allow users to input free-form text to request recommendations, and then receive a list of relevant and diverse items. While previous work on synthetic queries augments large language models (LLMs) with 1-3 tools, we argue that a more extensive toolbox is necessary to effectively handle real user requests. As such, we propose a novel approach that equips LLMs with over 10 tools, providing them access to the internal knowledge base and API calls used in production. We evaluate our model on a dataset of real users and show that it generates relevant, novel, and diverse recommendations compared to vanilla LLMs. Furthermore, we conduct ablation studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of using the full range of tools in our toolbox. We share our designs and lessons learned from deploying the system for internal alpha release. Our contribution is the addressing of all four key aspects of a practicable CRS: (1) real user requests, (2) augmenting LLMs with a wide variety of tools, (3) extensive evaluation, and (4) deployment insights.
Modeling Heterogeneous Statistical Patterns in High-dimensional Data by Adversarial Distributions: An Unsupervised Generative Framework
Dec 15, 2020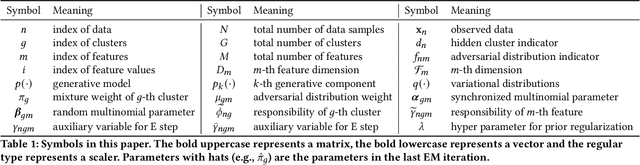
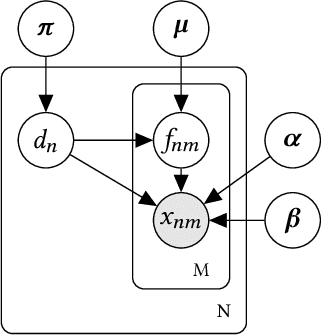
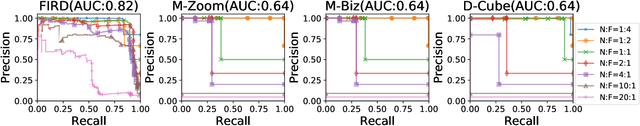
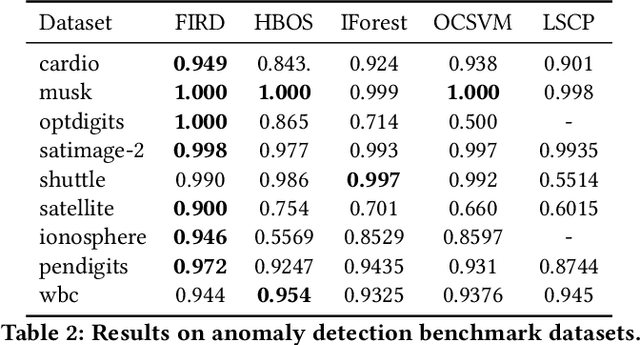
Abstract:Since the label collecting is prohibitive and time-consuming, unsupervised methods are preferred in applications such as fraud detection. Meanwhile, such applications usually require modeling the intrinsic clusters in high-dimensional data, which usually displays heterogeneous statistical patterns as the patterns of different clusters may appear in different dimensions. Existing methods propose to model the data clusters on selected dimensions, yet globally omitting any dimension may damage the pattern of certain clusters. To address the above issues, we propose a novel unsupervised generative framework called FIRD, which utilizes adversarial distributions to fit and disentangle the heterogeneous statistical patterns. When applying to discrete spaces, FIRD effectively distinguishes the synchronized fraudsters from normal users. Besides, FIRD also provides superior performance on anomaly detection datasets compared with SOTA anomaly detection methods (over 5% average AUC improvement). The significant experiment results on various datasets verify that the proposed method can better model the heterogeneous statistical patterns in high-dimensional data and benefit downstream applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge