Katerina Nikiforaki
MAMA-MIA: A Large-Scale Multi-Center Breast Cancer DCE-MRI Benchmark Dataset with Expert Segmentations
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Current research in breast cancer Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), especially with Artificial Intelligence (AI), faces challenges due to the lack of expert segmentations. To address this, we introduce the MAMA-MIA dataset, comprising 1506 multi-center dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI cases with expert segmentations of primary tumors and non-mass enhancement areas. These cases were sourced from four publicly available collections in The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA). Initially, we trained a deep learning model to automatically segment the cases, generating preliminary segmentations that significantly reduced expert segmentation time. Sixteen experts, averaging 9 years of experience in breast cancer, then corrected these segmentations, resulting in the final expert segmentations. Additionally, two radiologists conducted a visual inspection of the automatic segmentations to support future quality control studies. Alongside the expert segmentations, we provide 49 harmonized demographic and clinical variables and the pretrained weights of the well-known nnUNet architecture trained using the DCE-MRI full-images and expert segmentations. This dataset aims to accelerate the development and benchmarking of deep learning models and foster innovation in breast cancer diagnostics and treatment planning.
INN: Inflated Neural Networks for IPMN Diagnosis
Jun 30, 2019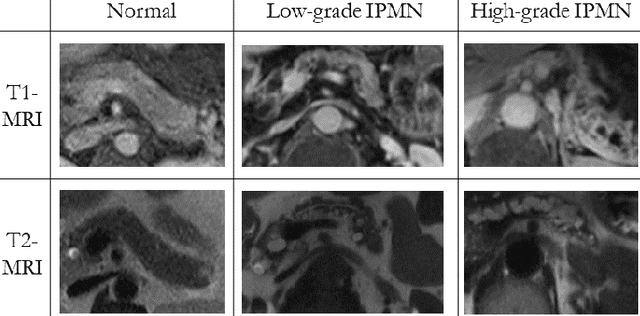
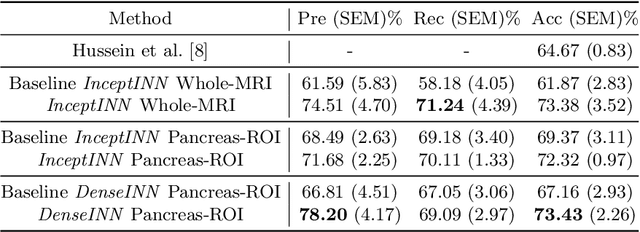
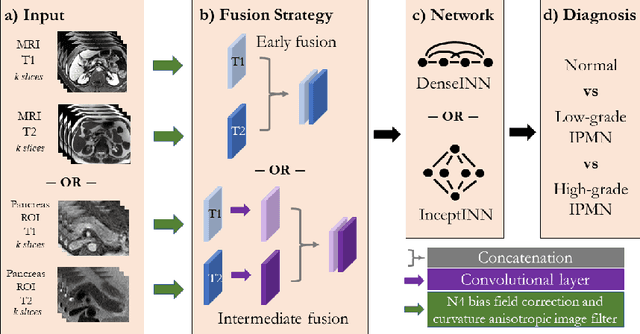

Abstract:Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a precursor to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. While over half of patients are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer at a distant stage, patients who are diagnosed early enjoy a much higher 5-year survival rate of $34\%$ compared to $3\%$ in the former; hence, early diagnosis is key. Unique challenges in the medical imaging domain such as extremely limited annotated data sets and typically large 3D volumetric data have made it difficult for deep learning to secure a strong foothold. In this work, we construct two novel "inflated" deep network architectures, $\textit{InceptINN}$ and $\textit{DenseINN}$, for the task of diagnosing IPMN from multisequence (T1 and T2) MRI. These networks inflate their 2D layers to 3D and bootstrap weights from their 2D counterparts (Inceptionv3 and DenseNet121 respectively) trained on ImageNet to the new 3D kernels. We also extend the inflation process by further expanding the pre-trained kernels to handle any number of input modalities and different fusion strategies. This is one of the first studies to train an end-to-end deep network on multisequence MRI for IPMN diagnosis, and shows that our proposed novel inflated network architectures are able to handle the extremely limited training data (139 MRI scans), while providing an absolute improvement of $8.76\%$ in accuracy for diagnosing IPMN over the current state-of-the-art. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/lalonderodney/INN-Inflated-Neural-Nets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge