Kang Huang
Intelligence of Astronomical Optical Telescope: Present Status and Future Perspectives
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Artificial intelligence technology has been widely used in astronomy, and new artificial intelligence technologies and application scenarios are constantly emerging. There have been a large number of papers reviewing the application of artificial intelligence technology in astronomy. However, relevant articles seldom mention telescope intelligence separately, and it is difficult to understand the current development status and research hotspots of telescope intelligence from these papers. This paper combines the development history of artificial intelligence technology and the difficulties of critical technologies of telescopes, comprehensively introduces the development and research hotspots of telescope intelligence, then conducts statistical analysis on various research directions of telescope intelligence and defines the research directions' merits. All kinds of research directions are evaluated, and the research trend of each telescope's intelligence is pointed out. Finally, according to the advantages of artificial intelligence technology and the development trend of telescopes, future research hotspots of telescope intelligence are given.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Wireless Scheduling in Distributed Networked Control
Sep 26, 2021



Abstract:In the literature of transmission scheduling in wireless networked control systems (WNCSs) over shared wireless resources, most research works have focused on partially distributed settings, i.e., where either the controller and actuator, or the sensor and controller are co-located. To overcome this limitation, the present work considers a fully distributed WNCS with distributed plants, sensors, actuators and a controller, sharing a limited number of frequency channels. To overcome communication limitations, the controller schedules the transmissions and generates sequential predictive commands for control. Using elements of stochastic systems theory, we derive a sufficient stability condition of the WNCS, which is stated in terms of both the control and communication system parameters. Once the condition is satisfied, there exists at least one stationary and deterministic scheduling policy that can stabilize all plants of the WNCS. By analyzing and representing the per-step cost function of the WNCS in terms of a finite-length countable vector state, we formulate the optimal transmission scheduling problem into a Markov decision process problem and develop a deep-reinforcement-learning-based algorithm for solving it. Numerical results show that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the benchmark policies.
Robust Handwriting Recognition with Limited and Noisy Data
Aug 18, 2020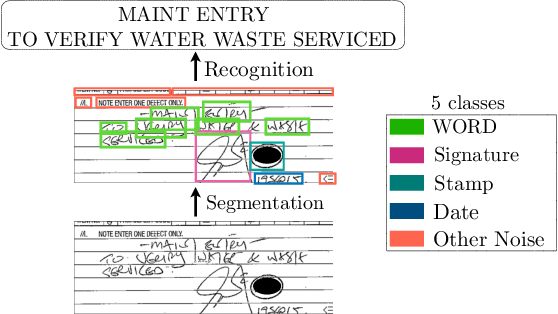

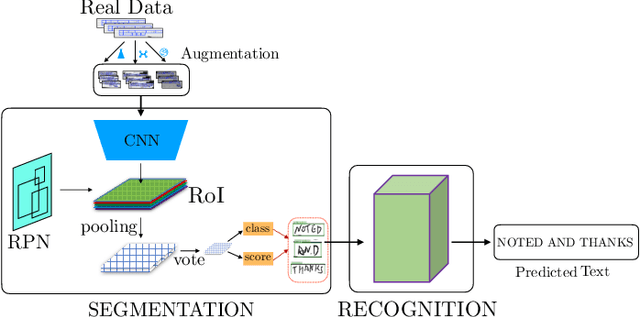
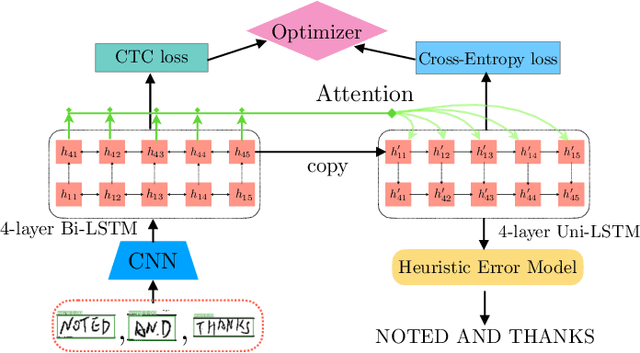
Abstract:Despite the advent of deep learning in computer vision, the general handwriting recognition problem is far from solved. Most existing approaches focus on handwriting datasets that have clearly written text and carefully segmented labels. In this paper, we instead focus on learning handwritten characters from maintenance logs, a constrained setting where data is very limited and noisy. We break the problem into two consecutive stages of word segmentation and word recognition respectively and utilize data augmentation techniques to train both stages. Extensive comparisons with popular baselines for scene-text detection and word recognition show that our system achieves a lower error rate and is more suited to handle noisy and difficult documents
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge