Kaiyue Liu
OriWheelBot: An origami-wheeled robot
Sep 29, 2023Abstract:Origami-inspired robots with multiple advantages, such as being lightweight, requiring less assembly, and exhibiting exceptional deformability, have received substantial and sustained attention. However, the existing origami-inspired robots are usually of limited functionalities and developing feature-rich robots is very challenging. Here, we report an origami-wheeled robot (OriWheelBot) with variable width and outstanding sand walking versatility. The OriWheelBot's ability to adjust wheel width over obstacles is achieved by origami wheels made of Miura origami. An improved version, called iOriWheelBot, is also developed to automatically judge the width of the obstacles. Three actions, namely direct pass, variable width pass, and direct return, will be carried out depending on the width of the channel between the obstacles. We have identified two motion mechanisms, i.e., sand-digging and sand-pushing, with the latter being more conducive to walking on the sand. We have systematically examined numerous sand walking characteristics, including carrying loads, climbing a slope, walking on a slope, and navigating sand pits, small rocks, and sand traps. The OriWheelBot can change its width by 40%, has a loading-carrying ratio of 66.7% on flat sand and can climb a 17-degree sand incline. The OriWheelBot can be useful for planetary subsurface exploration and disaster area rescue.
Underwater target detection based on improved YOLOv7
Feb 14, 2023



Abstract:Underwater target detection is a crucial aspect of ocean exploration. However, conventional underwater target detection methods face several challenges such as inaccurate feature extraction, slow detection speed and lack of robustness in complex underwater environments. To address these limitations, this study proposes an improved YOLOv7 network (YOLOv7-AC) for underwater target detection. The proposed network utilizes an ACmixBlock module to replace the 3x3 convolution block in the E-ELAN structure, and incorporates jump connections and 1x1 convolution architecture between ACmixBlock modules to improve feature extraction and network reasoning speed. Additionally, a ResNet-ACmix module is designed to avoid feature information loss and reduce computation, while a Global Attention Mechanism (GAM) is inserted in the backbone and head parts of the model to improve feature extraction. Furthermore, the K-means++ algorithm is used instead of K-means to obtain anchor boxes and enhance model accuracy. Experimental results show that the improved YOLOv7 network outperforms the original YOLOv7 model and other popular underwater target detection methods. The proposed network achieved a mean average precision (mAP) value of 89.6% and 97.4% on the URPC dataset and Brackish dataset, respectively, and demonstrated a higher frame per second (FPS) compared to the original YOLOv7 model. The source code for this study is publicly available at https://github.com/NZWANG/YOLOV7-AC. In conclusion, the improved YOLOv7 network proposed in this study represents a promising solution for underwater target detection and holds great potential for practical applications in various underwater tasks.
RSI-Net: Two-Stream Deep Neural Network Integrating GCN and Atrous CNN for Semantic Segmentation of High-resolution Remote Sensing Images
Sep 19, 2021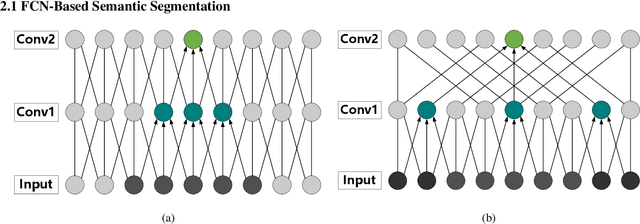
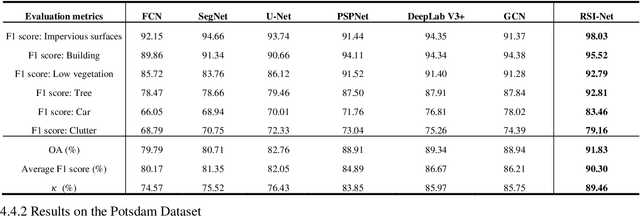
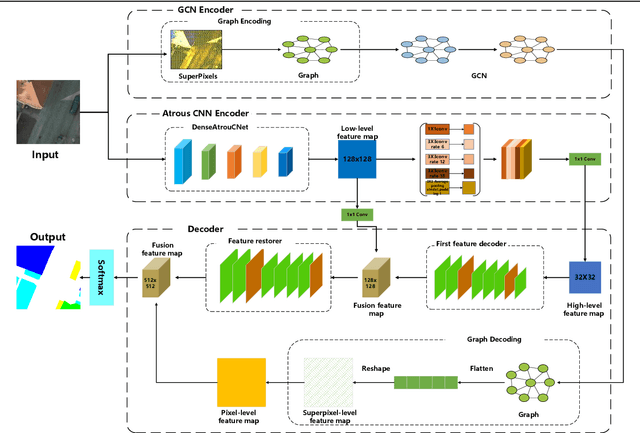
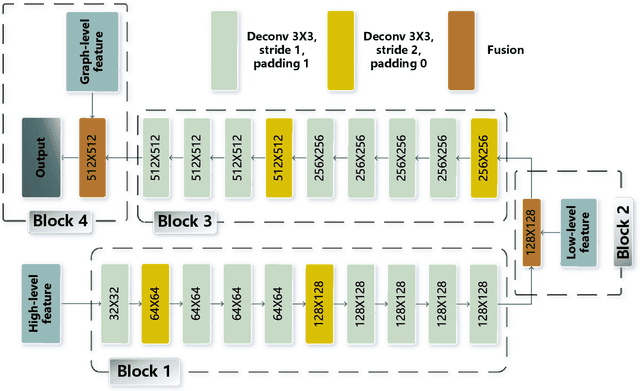
Abstract:For semantic segmentation of remote sensing images (RSI), trade-off between representation power and location accuracy is quite important. How to get the trade-off effectively is an open question, where current approaches of utilizing attention schemes or very deep models result in complex models with large memory consumption. Compared with the popularly-used convolutional neural network (CNN) with fixed square kernels, graph convolutional network (GCN) can explicitly utilize correlations between adjacent land covers and conduct flexible convolution on arbitrarily irregular image regions. However, the problems of large variations of target scales and blurred boundary cannot be easily solved by GCN, while densely connected atrous convolution network (DenseAtrousCNet) with multi-scale atrous convolution can expand the receptive fields and obtain image global information. Inspired by the advantages of both GCN and Atrous CNN, a two-stream deep neural network for semantic segmentation of RSI (RSI-Net) is proposed in this paper to obtain improved performance through modeling and propagating spatial contextual structure effectively and a novel decoding scheme with image-level and graph-level combination. Extensive experiments are implemented on the Vaihingen, Potsdam and Gaofen RSI datasets, where the comparison results demonstrate the superior performance of RSI-Net in terms of overall accuracy, F1 score and kappa coefficient when compared with six state-of-the-art RSI semantic segmentation methods.
CSC-Unet: A Novel Convolutional Sparse Coding Strategy based Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation
Aug 01, 2021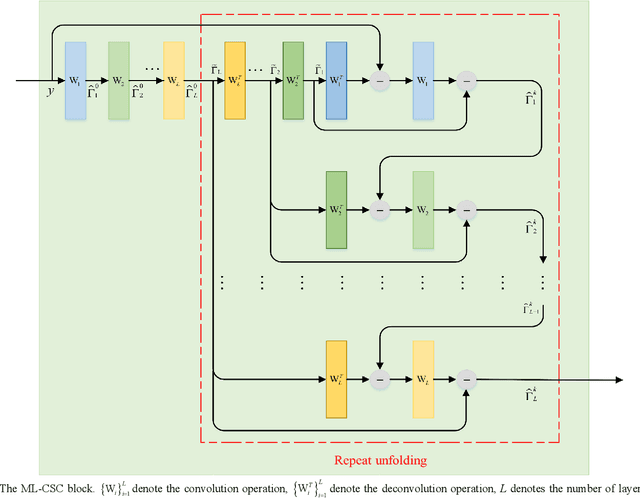
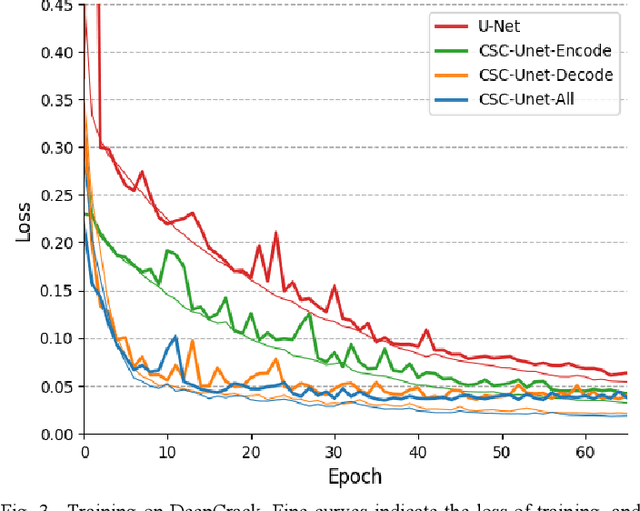
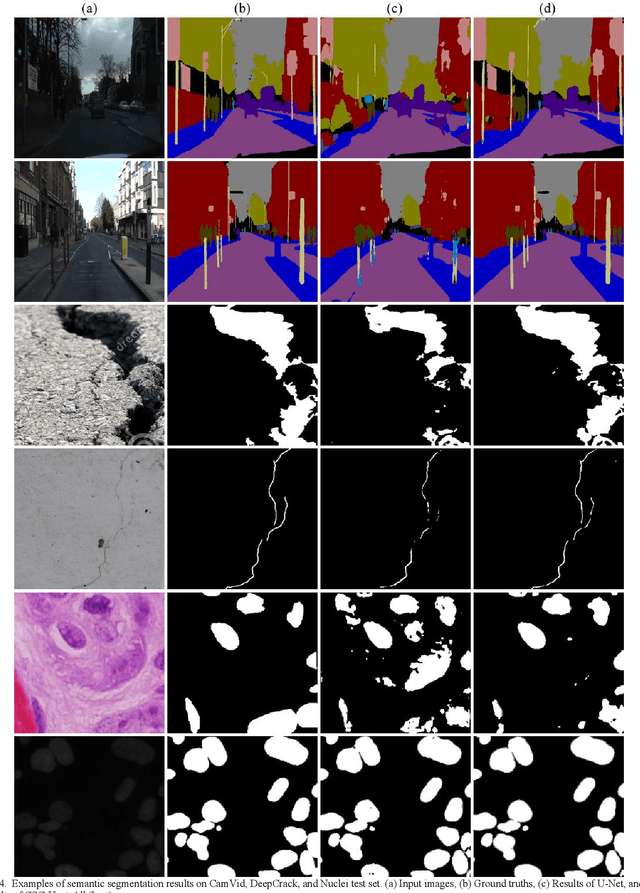
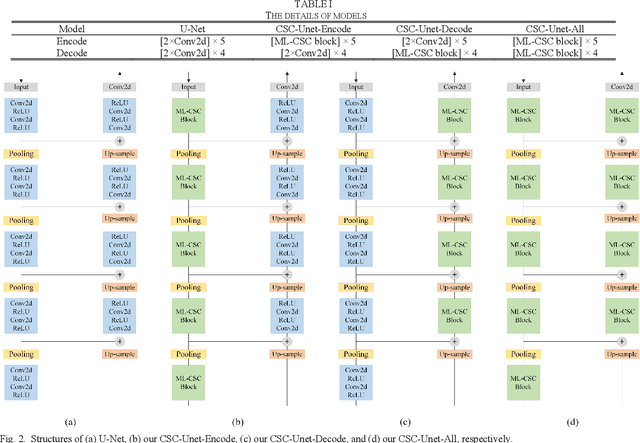
Abstract:It is a challenging task to accurately perform semantic segmentation due to the complexity of real picture scenes. Many semantic segmentation methods based on traditional deep learning insufficiently captured the semantic and appearance information of images, which put limit on their generality and robustness for various application scenes. In this paper, we proposed a novel strategy that reformulated the popularly-used convolution operation to multi-layer convolutional sparse coding block to ease the aforementioned deficiency. This strategy can be possibly used to significantly improve the segmentation performance of any semantic segmentation model that involves convolutional operations. To prove the effectiveness of our idea, we chose the widely-used U-Net model for the demonstration purpose, and we designed CSC-Unet model series based on U-Net. Through extensive analysis and experiments, we provided credible evidence showing that the multi-layer convolutional sparse coding block enables semantic segmentation model to converge faster, can extract finer semantic and appearance information of images, and improve the ability to recover spatial detail information. The best CSC-Unet model significantly outperforms the results of the original U-Net on three public datasets with different scenarios, i.e., 87.14% vs. 84.71% on DeepCrack dataset, 68.91% vs. 67.09% on Nuclei dataset, and 53.68% vs. 48.82% on CamVid dataset, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge