Kaitong Cai
Why Keep Your Doubts to Yourself? Trading Visual Uncertainties in Multi-Agent Bandit Systems
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) enable powerful multi-agent systems, but scaling them is economically unsustainable: coordinating heterogeneous agents under information asymmetry often spirals costs. Existing paradigms, such as Mixture-of-Agents and knowledge-based routers, rely on heuristic proxies that ignore costs and collapse uncertainty structure, leading to provably suboptimal coordination. We introduce Agora, a framework that reframes coordination as a decentralized market for uncertainty. Agora formalizes epistemic uncertainty into a structured, tradable asset (perceptual, semantic, inferential), and enforces profitability-driven trading among agents based on rational economic rules. A market-aware broker, extending Thompson Sampling, initiates collaboration and guides the system toward cost-efficient equilibria. Experiments on five multimodal benchmarks (MMMU, MMBench, MathVision, InfoVQA, CC-OCR) show that Agora outperforms strong VLMs and heuristic multi-agent strategies, e.g., achieving +8.5% accuracy over the best baseline on MMMU while reducing cost by over 3x. These results establish market-based coordination as a principled and scalable paradigm for building economically viable multi-agent visual intelligence systems.
Self-Rewarded Multimodal Coherent Reasoning Across Diverse Visual Domains
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Multimodal LLMs often produce fluent yet unreliable reasoning, exhibiting weak step-to-step coherence and insufficient visual grounding, largely because existing alignment approaches supervise only the final answer while ignoring the reliability of the intermediate reasoning process. We introduce SR-MCR, a lightweight and label-free framework that aligns reasoning by exploiting intrinsic process signals derived directly from model outputs. Five self-referential cues -- semantic alignment, lexical fidelity, non-redundancy, visual grounding, and step consistency -- are integrated into a normalized, reliability-weighted reward that provides fine-grained process-level guidance. A critic-free GRPO objective, enhanced with a confidence-aware cooling mechanism, further stabilizes training and suppresses trivial or overly confident generations. Built on Qwen2.5-VL, SR-MCR improves both answer accuracy and reasoning coherence across a broad set of visual benchmarks; among open-source models of comparable size, SR-MCR-7B achieves state-of-the-art performance with an average accuracy of 81.4%. Ablation studies confirm the independent contributions of each reward term and the cooling module.
CoAgent: Collaborative Planning and Consistency Agent for Coherent Video Generation
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Maintaining narrative coherence and visual consistency remains a central challenge in open-domain video generation. Existing text-to-video models often treat each shot independently, resulting in identity drift, scene inconsistency, and unstable temporal structure. We propose CoAgent, a collaborative and closed-loop framework for coherent video generation that formulates the process as a plan-synthesize-verify pipeline. Given a user prompt, style reference, and pacing constraints, a Storyboard Planner decomposes the input into structured shot-level plans with explicit entities, spatial relations, and temporal cues. A Global Context Manager maintains entity-level memory to preserve appearance and identity consistency across shots. Each shot is then generated by a Synthesis Module under the guidance of a Visual Consistency Controller, while a Verifier Agent evaluates intermediate results using vision-language reasoning and triggers selective regeneration when inconsistencies are detected. Finally, a pacing-aware editor refines temporal rhythm and transitions to match the desired narrative flow. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CoAgent significantly improves coherence, visual consistency, and narrative quality in long-form video generation.
RevFFN: Memory-Efficient Full-Parameter Fine-Tuning of Mixture-of-Experts LLMs with Reversible Blocks
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Full parameter fine tuning is a key technique for adapting large language models (LLMs) to downstream tasks, but it incurs substantial memory overhead due to the need to cache extensive intermediate activations for backpropagation. This bottleneck makes full fine tuning of contemporary large scale LLMs challenging in practice. Existing distributed training frameworks such as DeepSpeed alleviate this issue using techniques like ZeRO and FSDP, which rely on multi GPU memory or CPU offloading, but often require additional hardware resources and reduce training speed. We introduce RevFFN, a memory efficient fine tuning paradigm for mixture of experts (MoE) LLMs. RevFFN employs carefully designed reversible Transformer blocks that allow reconstruction of layer input activations from outputs during backpropagation, eliminating the need to store most intermediate activations in memory. While preserving the expressive capacity of MoE architectures, this approach significantly reduces peak memory consumption for full parameter fine tuning. As a result, RevFFN enables efficient full fine tuning on a single consumer grade or server grade GPU.
SirenPose: Dynamic Scene Reconstruction via Geometric Supervision
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:We introduce SirenPose, a geometry-aware loss formulation that integrates the periodic activation properties of sinusoidal representation networks with keypoint-based geometric supervision, enabling accurate and temporally consistent reconstruction of dynamic 3D scenes from monocular videos. Existing approaches often struggle with motion fidelity and spatiotemporal coherence in challenging settings involving fast motion, multi-object interaction, occlusion, and rapid scene changes. SirenPose incorporates physics inspired constraints to enforce coherent keypoint predictions across both spatial and temporal dimensions, while leveraging high frequency signal modeling to capture fine grained geometric details. We further expand the UniKPT dataset to 600,000 annotated instances and integrate graph neural networks to model keypoint relationships and structural correlations. Extensive experiments on benchmarks including Sintel, Bonn, and DAVIS demonstrate that SirenPose consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods. On DAVIS, SirenPose achieves a 17.8 percent reduction in FVD, a 28.7 percent reduction in FID, and a 6.0 percent improvement in LPIPS compared to MoSCA. It also improves temporal consistency, geometric accuracy, user score, and motion smoothness. In pose estimation, SirenPose outperforms Monst3R with lower absolute trajectory error as well as reduced translational and rotational relative pose error, highlighting its effectiveness in handling rapid motion, complex dynamics, and physically plausible reconstruction.
FlashVLM: Text-Guided Visual Token Selection for Large Multimodal Models
Dec 23, 2025



Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) typically process hundreds or thousands of visual tokens per image or video frame, incurring quadratic attention cost and substantial redundancy. Existing token reduction methods often ignore the textual query or rely on deep attention maps, whose instability under aggressive pruning leads to degraded semantic alignment. We propose FlashVLM, a text guided visual token selection framework that dynamically adapts visual inputs to the query. Instead of relying on noisy attention weights, FlashVLM computes an explicit cross modal similarity between projected image tokens and normalized text embeddings in the language model space. This extrinsic relevance is fused with intrinsic visual saliency using log domain weighting and temperature controlled sharpening. In addition, a diversity preserving partition retains a minimal yet representative set of background tokens to maintain global context. Under identical token budgets and evaluation protocols, FlashVLM achieves beyond lossless compression, slightly surpassing the unpruned baseline while pruning up to 77.8 percent of visual tokens on LLaVA 1.5, and maintaining 92.8 percent accuracy even under 94.4 percent compression. Extensive experiments on 14 image and video benchmarks demonstrate that FlashVLM delivers state of the art efficiency performance trade offs while maintaining strong robustness and generalization across mainstream VLMs.
PTTA: A Pure Text-to-Animation Framework for High-Quality Creation
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Traditional animation production involves complex pipelines and significant manual labor cost. While recent video generation models such as Sora, Kling, and CogVideoX achieve impressive results on natural video synthesis, they exhibit notable limitations when applied to animation generation. Recent efforts, such as AniSora, demonstrate promising performance by fine-tuning image-to-video models for animation styles, yet analogous exploration in the text-to-video setting remains limited. In this work, we present PTTA, a pure text-to-animation framework for high-quality animation creation. We first construct a small-scale but high-quality paired dataset of animation videos and textual descriptions. Building upon the pretrained text-to-video model HunyuanVideo, we perform fine-tuning to adapt it to animation-style generation. Extensive visual evaluations across multiple dimensions show that the proposed approach consistently outperforms comparable baselines in animation video synthesis.
LLM-CAS: Dynamic Neuron Perturbation for Real-Time Hallucination Correction
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often generate hallucinated content that lacks factual or contextual grounding, limiting their reliability in critical applications. Existing approaches such as supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning from human feedback are data intensive and computationally expensive, while static parameter editing methods struggle with context dependent errors and catastrophic forgetting. We propose LLM-CAS, a framework that formulates real-time hallucination correction as a hierarchical reinforcement learning problem. LLM-CAS trains an agent to learn a policy that dynamically selects temporary neuron perturbations during inference based on the current context. Unlike prior dynamic approaches that rely on heuristic or predefined adjustments, this policy driven mechanism enables adaptive and fine grained correction without permanent parameter modification. Experiments across multiple language models demonstrate that LLM-CAS consistently improves factual accuracy, achieving gains of 10.98 percentage points on StoryCloze, 2.71 points on TriviaQA, and 2.06 points on the MC1 score of TruthfulQA. These results outperform both static editing methods such as ITI and CAA and the dynamic SADI framework. Overall, LLM-CAS provides an efficient and context aware solution for improving the reliability of LLMs, with promising potential for future multimodal extensions.
STORM: Search-Guided Generative World Models for Robotic Manipulation
Dec 20, 2025



Abstract:We present STORM (Search-Guided Generative World Models), a novel framework for spatio-temporal reasoning in robotic manipulation that unifies diffusion-based action generation, conditional video prediction, and search-based planning. Unlike prior Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models that rely on abstract latent dynamics or delegate reasoning to language components, STORM grounds planning in explicit visual rollouts, enabling interpretable and foresight-driven decision-making. A diffusion-based VLA policy proposes diverse candidate actions, a generative video world model simulates their visual and reward outcomes, and Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) selectively refines plans through lookahead evaluation. Experiments on the SimplerEnv manipulation benchmark demonstrate that STORM achieves a new state-of-the-art average success rate of 51.0 percent, outperforming strong baselines such as CogACT. Reward-augmented video prediction substantially improves spatio-temporal fidelity and task relevance, reducing Frechet Video Distance by over 75 percent. Moreover, STORM exhibits robust re-planning and failure recovery behavior, highlighting the advantages of search-guided generative world models for long-horizon robotic manipulation.
MM-CoT:A Benchmark for Probing Visual Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Multimodal Models
Dec 09, 2025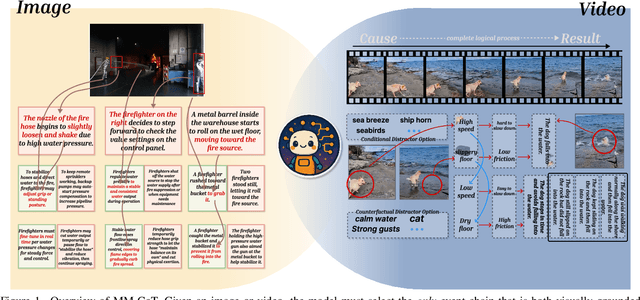
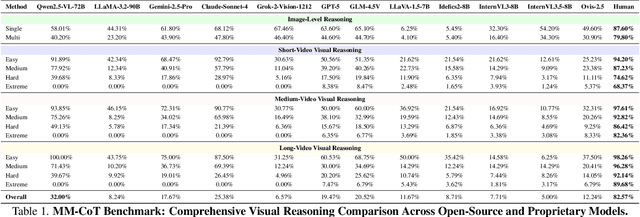
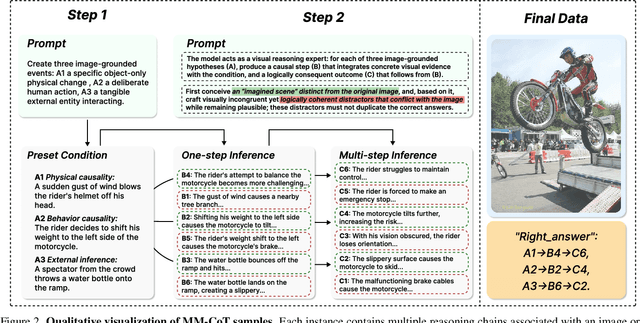
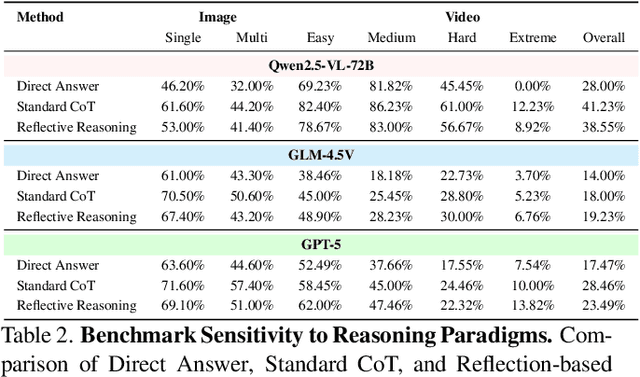
Abstract:The ability to perform Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning marks a major milestone for multimodal models (MMs), enabling them to solve complex visual reasoning problems. Yet a critical question remains: is such reasoning genuinely grounded in visual evidence and logically coherent? Existing benchmarks emphasize generation but neglect verification, i.e., the capacity to assess whether a reasoning chain is both visually consistent and logically valid. To fill this gap, we introduce MM-CoT, a diagnostic benchmark specifically designed to probe the visual grounding and logical coherence of CoT reasoning in MMs. Instead of generating free-form explanations, models must select the sole event chain that satisfies two orthogonal constraints: (i) visual consistency, ensuring all steps are anchored in observable evidence, and (ii) logical coherence, ensuring causal and commonsense validity. Adversarial distractors are engineered to violate one of these constraints, exposing distinct reasoning failures. We evaluate leading vision-language models on MM-CoT and find that even the most advanced systems struggle, revealing a sharp discrepancy between generative fluency and true reasoning fidelity. MM-CoT shows low correlation with existing benchmarks, confirming that it measures a unique combination of visual grounding and logical reasoning. This benchmark provides a foundation for developing future models that reason not just plausibly, but faithfully and coherently within the visual world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge