Jusheng Zhang
Rational ANOVA Networks
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Deep neural networks typically treat nonlinearities as fixed primitives (e.g., ReLU), limiting both interpretability and the granularity of control over the induced function class. While recent additive models (like KANs) attempt to address this using splines, they often suffer from computational inefficiency and boundary instability. We propose the Rational-ANOVA Network (RAN), a foundational architecture grounded in functional ANOVA decomposition and Padé-style rational approximation. RAN models f(x) as a composition of main effects and sparse pairwise interactions, where each component is parameterized by a stable, learnable rational unit. Crucially, we enforce a strictly positive denominator, which avoids poles and numerical instability while capturing sharp transitions and near-singular behaviors more efficiently than polynomial bases. This ANOVA structure provides an explicit low-order interaction bias for data efficiency and interpretability, while the rational parameterization significantly improves extrapolation. Across controlled function benchmarks and vision classification tasks (e.g., CIFAR-10) under matched parameter and compute budgets, RAN matches or surpasses parameter-matched MLPs and learnable-activation baselines, with better stability and throughput. Code is available at https://github.com/jushengzhang/Rational-ANOVA-Networks.git.
Why Keep Your Doubts to Yourself? Trading Visual Uncertainties in Multi-Agent Bandit Systems
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) enable powerful multi-agent systems, but scaling them is economically unsustainable: coordinating heterogeneous agents under information asymmetry often spirals costs. Existing paradigms, such as Mixture-of-Agents and knowledge-based routers, rely on heuristic proxies that ignore costs and collapse uncertainty structure, leading to provably suboptimal coordination. We introduce Agora, a framework that reframes coordination as a decentralized market for uncertainty. Agora formalizes epistemic uncertainty into a structured, tradable asset (perceptual, semantic, inferential), and enforces profitability-driven trading among agents based on rational economic rules. A market-aware broker, extending Thompson Sampling, initiates collaboration and guides the system toward cost-efficient equilibria. Experiments on five multimodal benchmarks (MMMU, MMBench, MathVision, InfoVQA, CC-OCR) show that Agora outperforms strong VLMs and heuristic multi-agent strategies, e.g., achieving +8.5% accuracy over the best baseline on MMMU while reducing cost by over 3x. These results establish market-based coordination as a principled and scalable paradigm for building economically viable multi-agent visual intelligence systems.
ResAgent: Entropy-based Prior Point Discovery and Visual Reasoning for Referring Expression Segmentation
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Referring Expression Segmentation (RES) is a core vision-language segmentation task that enables pixel-level understanding of targets via free-form linguistic expressions, supporting critical applications such as human-robot interaction and augmented reality. Despite the progress of Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based approaches, existing RES methods still suffer from two key limitations: first, the coarse bounding boxes from MLLMs lead to redundant or non-discriminative point prompts; second, the prevalent reliance on textual coordinate reasoning is unreliable, as it fails to distinguish targets from visually similar distractors. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{\model}, a novel RES framework integrating \textbf{E}ntropy-\textbf{B}ased Point \textbf{D}iscovery (\textbf{EBD}) and \textbf{V}ision-\textbf{B}ased \textbf{R}easoning (\textbf{VBR}). Specifically, EBD identifies high-information candidate points by modeling spatial uncertainty within coarse bounding boxes, treating point selection as an information maximization process. VBR verifies point correctness through joint visual-semantic alignment, abandoning text-only coordinate inference for more robust validation. Built on these components, \model implements a coarse-to-fine workflow: bounding box initialization, entropy-guided point discovery, vision-based validation, and mask decoding. Extensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets (RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, RefCOCOg, and ReasonSeg) demonstrate that \model achieves new state-of-the-art performance across all four benchmarks, highlighting its effectiveness in generating accurate and semantically grounded segmentation masks with minimal prompts.
3D-Agent:Tri-Modal Multi-Agent Collaboration for Scalable 3D Object Annotation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Driven by applications in autonomous driving robotics and augmented reality 3D object annotation presents challenges beyond 2D annotation including spatial complexity occlusion and viewpoint inconsistency Existing approaches based on single models often struggle to address these issues effectively We propose Tri MARF a novel framework that integrates tri modal inputs including 2D multi view images textual descriptions and 3D point clouds within a multi agent collaborative architecture to enhance large scale 3D annotation Tri MARF consists of three specialized agents a vision language model agent for generating multi view descriptions an information aggregation agent for selecting optimal descriptions and a gating agent that aligns textual semantics with 3D geometry for refined captioning Extensive experiments on Objaverse LVIS Objaverse XL and ABO demonstrate that Tri MARF substantially outperforms existing methods achieving a CLIPScore of 88 point 7 compared to prior state of the art methods retrieval accuracy of 45 point 2 and 43 point 8 on ViLT R at 5 and a throughput of up to 12000 objects per hour on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU
FlashVLM: Text-Guided Visual Token Selection for Large Multimodal Models
Dec 23, 2025



Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) typically process hundreds or thousands of visual tokens per image or video frame, incurring quadratic attention cost and substantial redundancy. Existing token reduction methods often ignore the textual query or rely on deep attention maps, whose instability under aggressive pruning leads to degraded semantic alignment. We propose FlashVLM, a text guided visual token selection framework that dynamically adapts visual inputs to the query. Instead of relying on noisy attention weights, FlashVLM computes an explicit cross modal similarity between projected image tokens and normalized text embeddings in the language model space. This extrinsic relevance is fused with intrinsic visual saliency using log domain weighting and temperature controlled sharpening. In addition, a diversity preserving partition retains a minimal yet representative set of background tokens to maintain global context. Under identical token budgets and evaluation protocols, FlashVLM achieves beyond lossless compression, slightly surpassing the unpruned baseline while pruning up to 77.8 percent of visual tokens on LLaVA 1.5, and maintaining 92.8 percent accuracy even under 94.4 percent compression. Extensive experiments on 14 image and video benchmarks demonstrate that FlashVLM delivers state of the art efficiency performance trade offs while maintaining strong robustness and generalization across mainstream VLMs.
HybridToken-VLM: Hybrid Token Compression for Vision-Language Models
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have transformed multimodal reasoning, but feeding hundreds of visual patch tokens into LLMs incurs quadratic computational costs, straining memory and context windows. Traditional approaches face a trade-off: continuous compression dilutes high-level semantics such as object identities, while discrete quantization loses fine-grained details such as textures. We introduce HTC-VLM, a hybrid framework that disentangles semantics and appearance through dual channels, i.e., a continuous pathway for fine-grained details via ViT patches and a discrete pathway for symbolic anchors using MGVQ quantization projected to four tokens. These are fused into a 580-token hybrid sequence and compressed into a single voco token via a disentanglement attention mask and bottleneck, ensuring efficient and grounded representations. HTC-VLM achieves an average performance retention of 87.2 percent across seven benchmarks (GQA, VQAv2, MMBench, MME, POPE, SEED-Bench, ScienceQA-Image), outperforming the leading continuous baseline at 81.0 percent with a 580-to-1 compression ratio. Attention analyses show that the compressed token prioritizes the discrete anchor, validating its semantic guidance. Our work demonstrates that a minimalist hybrid design can resolve the efficiency-fidelity dilemma and advance scalable VLMs.
MM-CoT:A Benchmark for Probing Visual Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Multimodal Models
Dec 09, 2025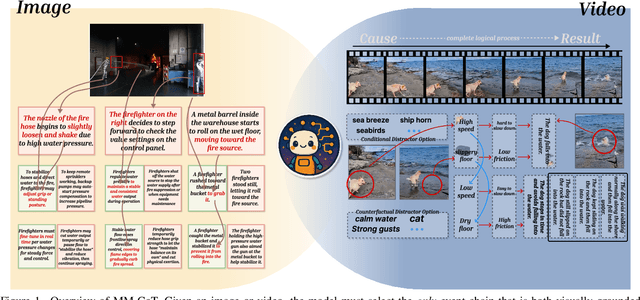
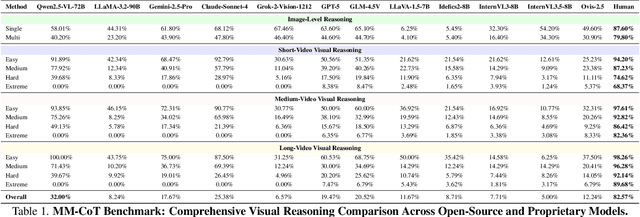
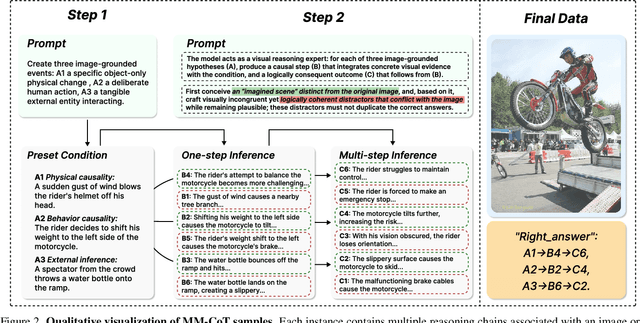
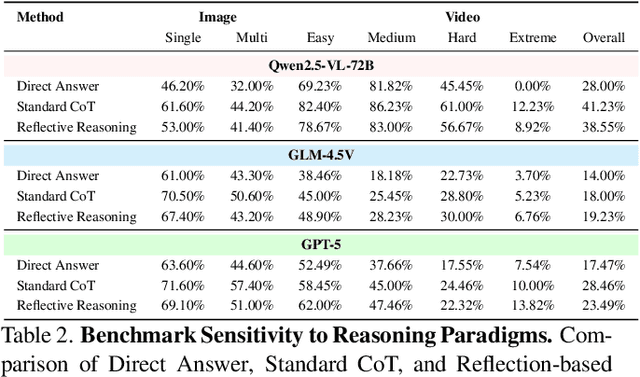
Abstract:The ability to perform Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning marks a major milestone for multimodal models (MMs), enabling them to solve complex visual reasoning problems. Yet a critical question remains: is such reasoning genuinely grounded in visual evidence and logically coherent? Existing benchmarks emphasize generation but neglect verification, i.e., the capacity to assess whether a reasoning chain is both visually consistent and logically valid. To fill this gap, we introduce MM-CoT, a diagnostic benchmark specifically designed to probe the visual grounding and logical coherence of CoT reasoning in MMs. Instead of generating free-form explanations, models must select the sole event chain that satisfies two orthogonal constraints: (i) visual consistency, ensuring all steps are anchored in observable evidence, and (ii) logical coherence, ensuring causal and commonsense validity. Adversarial distractors are engineered to violate one of these constraints, exposing distinct reasoning failures. We evaluate leading vision-language models on MM-CoT and find that even the most advanced systems struggle, revealing a sharp discrepancy between generative fluency and true reasoning fidelity. MM-CoT shows low correlation with existing benchmarks, confirming that it measures a unique combination of visual grounding and logical reasoning. This benchmark provides a foundation for developing future models that reason not just plausibly, but faithfully and coherently within the visual world.
3DAlign-DAER: Dynamic Attention Policy and Efficient Retrieval Strategy for Fine-grained 3D-Text Alignment at Scale
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Despite recent advancements in 3D-text cross-modal alignment, existing state-of-the-art methods still struggle to align fine-grained textual semantics with detailed geometric structures, and their alignment performance degrades significantly when scaling to large-scale 3D databases. To overcome this limitation, we introduce 3DAlign-DAER, a unified framework designed to align text and 3D geometry via the proposed dynamic attention policy and the efficient retrieval strategy, capturing subtle correspondences for diverse cross-modal retrieval and classification tasks. Specifically, during the training, our proposed dynamic attention policy (DAP) employs the Hierarchical Attention Fusion (HAF) module to represent the alignment as learnable fine-grained token-to-point attentions. To optimize these attentions across different tasks and geometric hierarchies, our DAP further exploits the Monte Carlo tree search to dynamically calibrate HAF attention weights via a hybrid reward signal and further enhances the alignment between textual descriptions and local 3D geometry. During the inference, our 3DAlign-DAER introduces an Efficient Retrieval Strategy (ERS) to leverage efficient hierarchical searching in the large-scale embedding spaces, outperforming traditional methods (e.g., KNN) in accuracy and efficiency. Furthermore, to facilitate text-3D alignment research and train our 3DAlign-DAER, we construct Align3D-2M, a large-scale dataset featuring 2M text-3D pairs, to provide sufficient fine-grained cross-modal annotations. Extensive and comprehensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our 3DAlign-DAER on diverse benchmarks. We will release our codes, models, and datasets.
Cost-Effective Communication: An Auction-based Method for Language Agent Interaction
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent systems (MAS) built on large language models (LLMs) often suffer from inefficient "free-for-all" communication, leading to exponential token costs and low signal-to-noise ratios that hinder their practical deployment. We challenge the notion that more communication is always beneficial, hypothesizing instead that the core issue is the absence of resource rationality. We argue that "free" communication, by ignoring the principle of scarcity, inherently breeds inefficiency and unnecessary expenses. To address this, we introduce the Dynamic Auction-based Language Agent (DALA), a novel framework that treats communication bandwidth as a scarce and tradable resource. Specifically, our DALA regards inter-agent communication as a centralized auction, where agents learn to bid for the opportunity to speak based on the predicted value density of their messages. Thus, our DALA intrinsically encourages agents to produce concise, informative messages while filtering out low-value communication. Extensive and comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our economically-driven DALA achieves new state-of-the-art performance across seven challenging reasoning benchmarks, including 84.32% on MMLU and a 91.21% pass@1 rate on HumanEval. Note that this is accomplished with remarkable efficiency, i.e., our DALA uses only 6.25 million tokens, a fraction of the resources consumed by current state-of-the-art methods on GSM8K. Further analysis reveals that our DALA cultivates the emergent skill of strategic silence, effectively adapting its communication strategies from verbosity to silence in a dynamical manner via resource constraints.
Understanding Hardness of Vision-Language Compositionality from A Token-level Causal Lens
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) delivers strong cross modal generalization by aligning images and texts in a shared embedding space, yet it persistently fails at compositional reasoning over objects, attributes, and relations often behaving like a bag-of-words matcher. Prior causal accounts typically model text as a single vector, obscuring token-level structure and leaving core phenomena-such as prompt sensitivity and failures on hard negatives unexplained. We address this gap with a token-aware causal representation learning (CRL) framework grounded in a sequential, language-token SCM. Our theory extends block identifiability to tokenized text, proving that CLIP's contrastive objective can recover the modal-invariant latent variable under both sentence-level and token-level SCMs. Crucially, token granularity yields the first principled explanation of CLIP's compositional brittleness: composition nonidentifiability. We show the existence of pseudo-optimal text encoders that achieve perfect modal-invariant alignment yet are provably insensitive to SWAP, REPLACE, and ADD operations over atomic concepts, thereby failing to distinguish correct captions from hard negatives despite optimizing the same training objective as true-optimal encoders. The analysis further links language-side nonidentifiability to visual-side failures via the modality gap and shows how iterated composition operators compound hardness, motivating improved negative mining strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge