Kaihao Guo
Knowledge Graph Enhanced Event Extraction in Financial Documents
Sep 06, 2021



Abstract:Event extraction is a classic task in natural language processing with wide use in handling large amount of yet rapidly growing financial, legal, medical, and government documents which often contain multiple events with their elements scattered and mixed across the documents, making the problem much more difficult. Though the underlying relations between event elements to be extracted provide helpful contextual information, they are somehow overlooked in prior studies. We showcase the enhancement to this task brought by utilizing the knowledge graph that captures entity relations and their attributes. We propose a first event extraction framework that embeds a knowledge graph through a Graph Neural Network and integrates the embedding with regular features, all at document-level. Specifically, for extracting events from Chinese financial announcements, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 5.3% in F1-score.
Graph Neural Network Based VC Investment Success Prediction
May 25, 2021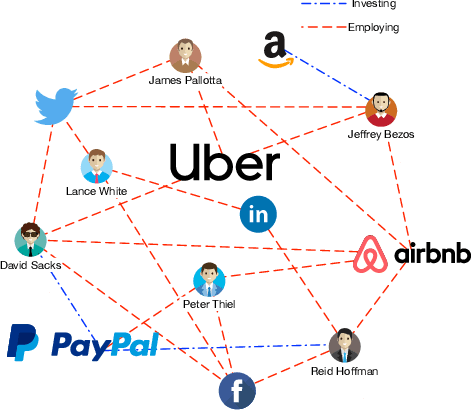
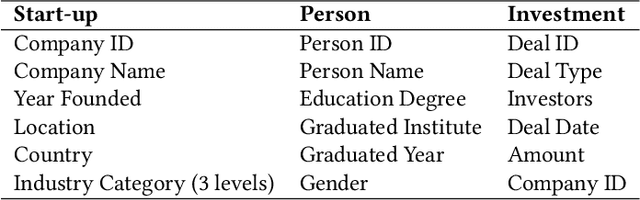
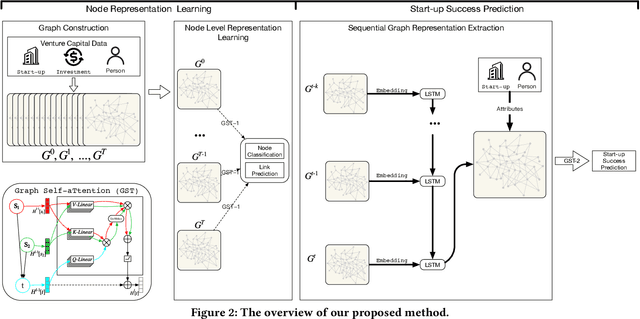
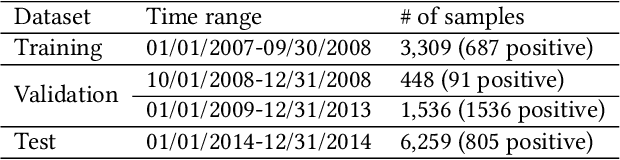
Abstract:Predicting the start-ups that will eventually succeed is essentially important for the venture capital business and worldwide policy makers, especially at an early stage such that rewards can possibly be exponential. Though various empirical studies and data-driven modeling work have been done, the predictive power of the complex networks of stakeholders including venture capital investors, start-ups, and start-ups' managing members has not been thoroughly explored. We design an incremental representation learning mechanism and a sequential learning model, utilizing the network structure together with the rich attributes of the nodes. In general, our method achieves the state-of-the-art prediction performance on a comprehensive dataset of global venture capital investments and surpasses human investors by large margins. Specifically, it excels at predicting the outcomes for start-ups in industries such as healthcare and IT. Meanwhile, we shed light on impacts on start-up success from observable factors including gender, education, and networking, which can be of value for practitioners as well as policy makers when they screen ventures of high growth potentials.
Learning Numeral Embeddings
Jan 11, 2020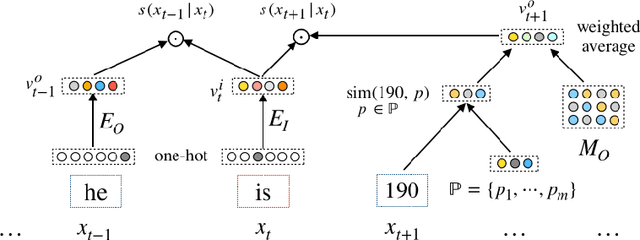
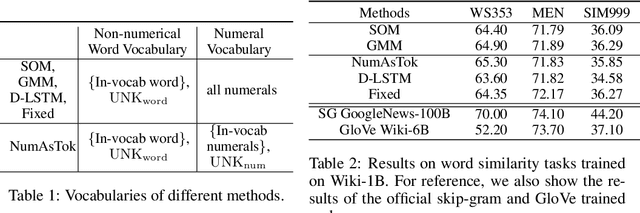
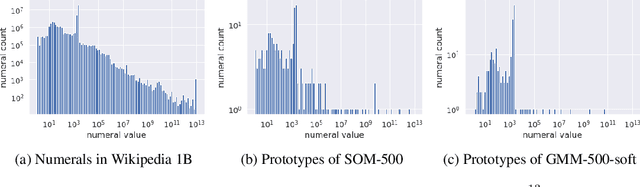
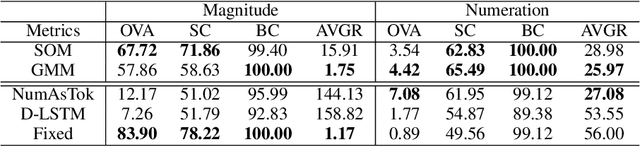
Abstract:Word embedding is an essential building block for deep learning methods for natural language processing. Although word embedding has been extensively studied over the years, the problem of how to effectively embed numerals, a special subset of words, is still underexplored. Existing word embedding methods do not learn numeral embeddings well because there are an infinite number of numerals and their individual appearances in training corpora are highly scarce. In this paper, we propose two novel numeral embedding methods that can handle the out-of-vocabulary (OOV) problem for numerals. We first induce a finite set of prototype numerals using either a self-organizing map or a Gaussian mixture model. We then represent the embedding of a numeral as a weighted average of the prototype number embeddings. Numeral embeddings represented in this manner can be plugged into existing word embedding learning approaches such as skip-gram for training. We evaluated our methods and showed its effectiveness on four intrinsic and extrinsic tasks: word similarity, embedding numeracy, numeral prediction, and sequence labeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge