Junyuan Lin
Narrative Analysis of True Crime Podcasts With Knowledge Graph-Augmented Large Language Models
Nov 01, 2024
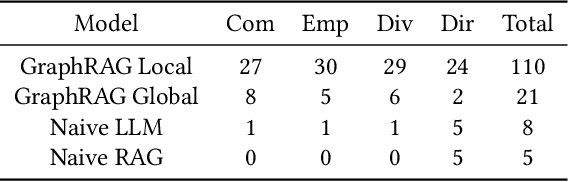
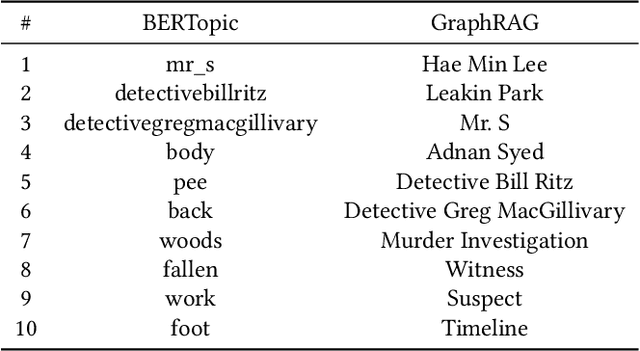
Abstract:Narrative data spans all disciplines and provides a coherent model of the world to the reader or viewer. Recent advancement in machine learning and Large Language Models (LLMs) have enable great strides in analyzing natural language. However, Large language models (LLMs) still struggle with complex narrative arcs as well as narratives containing conflicting information. Recent work indicates LLMs augmented with external knowledge bases can improve the accuracy and interpretability of the resulting models. In this work, we analyze the effectiveness of applying knowledge graphs (KGs) in understanding true-crime podcast data from both classical Natural Language Processing (NLP) and LLM approaches. We directly compare KG-augmented LLMs (KGLLMs) with classical methods for KG construction, topic modeling, and sentiment analysis. Additionally, the KGLLM allows us to query the knowledge base in natural language and test its ability to factually answer questions. We examine the robustness of the model to adversarial prompting in order to test the model's ability to deal with conflicting information. Finally, we apply classical methods to understand more subtle aspects of the text such as the use of hearsay and sentiment in narrative construction and propose future directions. Our results indicate that KGLLMs outperform LLMs on a variety of metrics, are more robust to adversarial prompts, and are more capable of summarizing the text into topics.
An Analysis of COVID-19 Knowledge Graph Construction and Applications
Oct 10, 2021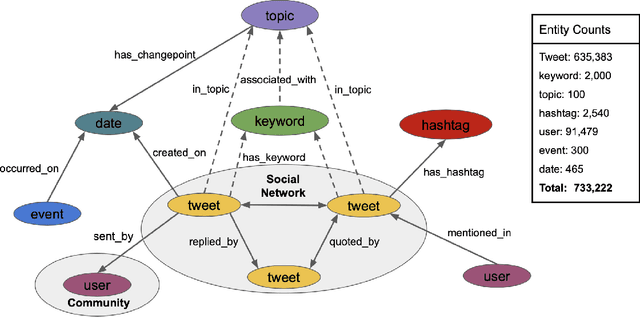
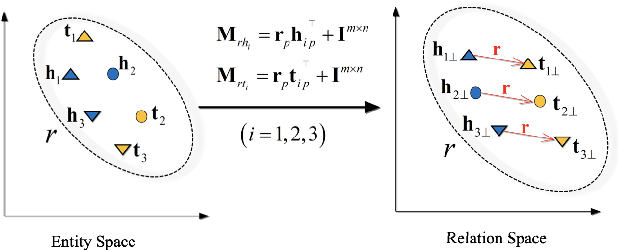
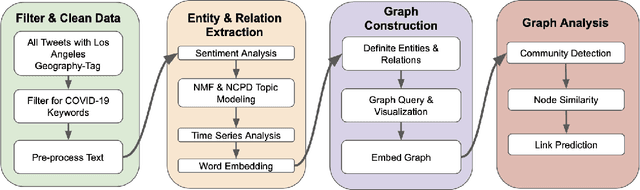
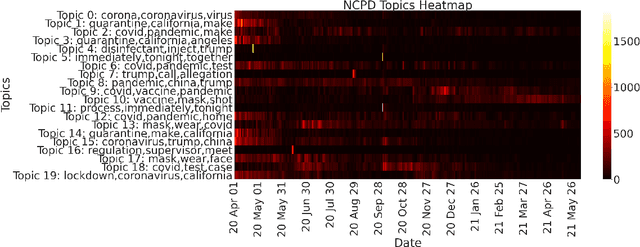
Abstract:The construction and application of knowledge graphs have seen a rapid increase across many disciplines in recent years. Additionally, the problem of uncovering relationships between developments in the COVID-19 pandemic and social media behavior is of great interest to researchers hoping to curb the spread of the disease. In this paper we present a knowledge graph constructed from COVID-19 related tweets in the Los Angeles area, supplemented with federal and state policy announcements and disease spread statistics. By incorporating dates, topics, and events as entities, we construct a knowledge graph that describes the connections between these useful information. We use natural language processing and change point analysis to extract tweet-topic, tweet-date, and event-date relations. Further analysis on the constructed knowledge graph provides insight into how tweets reflect public sentiments towards COVID-19 related topics and how changes in these sentiments correlate with real-world events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge