Jungwoo Lim
Post-hoc Utterance Refining Method by Entity Mining for Faithful Knowledge Grounded Conversations
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Despite the striking advances in recent language generation performance, model-generated responses have suffered from the chronic problem of hallucinations that are either untrue or unfaithful to a given source. Especially in the task of knowledge grounded conversation, the models are required to generate informative responses, but hallucinated utterances lead to miscommunication. In particular, entity-level hallucination that causes critical misinformation and undesirable conversation is one of the major concerns. To address this issue, we propose a post-hoc refinement method called REM. It aims to enhance the quality and faithfulness of hallucinated utterances by refining them based on the source knowledge. If the generated utterance has a low source-faithfulness score with the given knowledge, REM mines the key entities in the knowledge and implicitly uses them for refining the utterances. We verify that our method reduces entity hallucination in the utterance. Also, we show the adaptability and efficacy of REM with extensive experiments and generative results. Our code is available at https://github.com/YOONNAJANG/REM.
You Truly Understand What I Need: Intellectual and Friendly Dialogue Agents grounding Knowledge and Persona
Jan 06, 2023



Abstract:To build a conversational agent that interacts fluently with humans, previous studies blend knowledge or personal profile into the pre-trained language model. However, the model that considers knowledge and persona at the same time is still limited, leading to hallucination and a passive way of using personas. We propose an effective dialogue agent that grounds external knowledge and persona simultaneously. The agent selects the proper knowledge and persona to use for generating the answers with our candidate scoring implemented with a poly-encoder. Then, our model generates the utterance with lesser hallucination and more engagingness utilizing retrieval augmented generation with knowledge-persona enhanced query. We conduct experiments on the persona-knowledge chat and achieve state-of-the-art performance in grounding and generation tasks on the automatic metrics. Moreover, we validate the answers from the models regarding hallucination and engagingness through human evaluation and qualitative results. We show our retriever's effectiveness in extracting relevant documents compared to the other previous retrievers, along with the comparison of multiple candidate scoring methods. Code is available at https://github.com/dlawjddn803/INFO
GRASP: Guiding model with RelAtional Semantics using Prompt
Aug 29, 2022



Abstract:The dialogue-based relation extraction (DialogRE) task aims to predict the relations between argument pairs that appear in dialogue. Most previous studies utilize fine-tuning pre-trained language models (PLMs) only with extensive features to supplement the low information density of the dialogue by multiple speakers. To effectively exploit inherent knowledge of PLMs without extra layers and consider scattered semantic cues on the relation between the arguments, we propose a Guiding model with RelAtional Semantics using Prompt (GRASP). We adopt a prompt-based fine-tuning approach and capture relational semantic clues of a given dialogue with 1) an argument-aware prompt marker strategy and 2) the relational clue detection task. In the experiments, GRASP achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of both F1 and F1c scores on a DialogRE dataset even though our method only leverages PLMs without adding any extra layers.
Call for Customized Conversation: Customized Conversation Grounding Persona and Knowledge
Dec 16, 2021
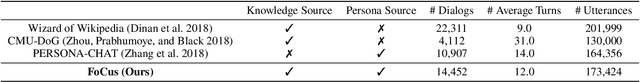

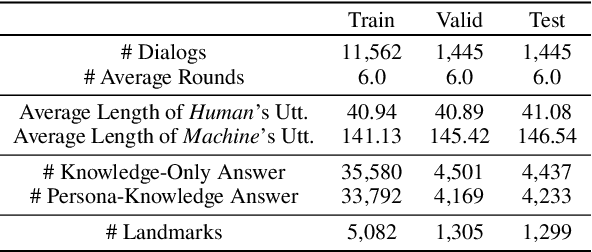
Abstract:Humans usually have conversations by making use of prior knowledge about a topic and background information of the people whom they are talking to. However, existing conversational agents and datasets do not consider such comprehensive information, and thus they have a limitation in generating the utterances where the knowledge and persona are fused properly. To address this issue, we introduce a call For Customized conversation (FoCus) dataset where the customized answers are built with the user's persona and Wikipedia knowledge. To evaluate the abilities to make informative and customized utterances of pre-trained language models, we utilize BART and GPT-2 as well as transformer-based models. We assess their generation abilities with automatic scores and conduct human evaluations for qualitative results. We examine whether the model reflects adequate persona and knowledge with our proposed two sub-tasks, persona grounding (PG) and knowledge grounding (KG). Moreover, we show that the utterances of our data are constructed with the proper knowledge and persona through grounding quality assessment.
I Know What You Asked: Graph Path Learning using AMR for Commonsense Reasoning
Nov 06, 2020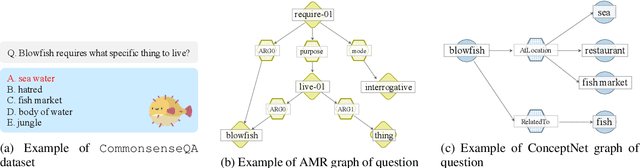
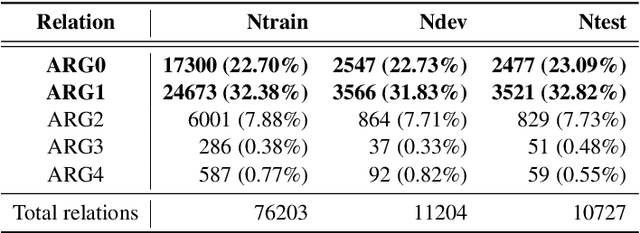
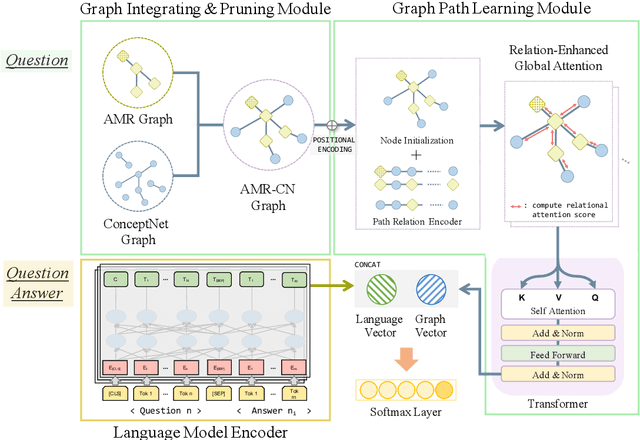
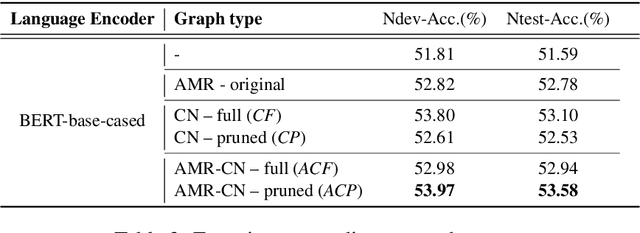
Abstract:CommonsenseQA is a task in which a correct answer is predicted through commonsense reasoning with pre-defined knowledge. Most previous works have aimed to improve the performance with distributed representation without considering the process of predicting the answer from the semantic representation of the question. To shed light upon the semantic interpretation of the question, we propose an AMR-ConceptNet-Pruned (ACP) graph. The ACP graph is pruned from a full integrated graph encompassing Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) graph generated from input questions and an external commonsense knowledge graph, ConceptNet (CN). Then the ACP graph is exploited to interpret the reasoning path as well as to predict the correct answer on the CommonsenseQA task. This paper presents the manner in which the commonsense reasoning process can be interpreted with the relations and concepts provided by the ACP graph. Moreover, ACP-based models are shown to outperform the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge