José Jiménez-Luna
Improved motif-scaffolding with SE(3) flow matching
Jan 08, 2024Abstract:Protein design often begins with knowledge of a desired function from a motif which motif-scaffolding aims to construct a functional protein around. Recently, generative models have achieved breakthrough success in designing scaffolds for a diverse range of motifs. However, the generated scaffolds tend to lack structural diversity, which can hinder success in wet-lab validation. In this work, we extend FrameFlow, an SE(3) flow matching model for protein backbone generation, to perform motif-scaffolding with two complementary approaches. The first is motif amortization, in which FrameFlow is trained with the motif as input using a data augmentation strategy. The second is motif guidance, which performs scaffolding using an estimate of the conditional score from FrameFlow, and requires no additional training. Both approaches achieve an equivalent or higher success rate than previous state-of-the-art methods, with 2.5 times more structurally diverse scaffolds. Code: https://github.com/ microsoft/frame-flow.
Structure-based drug discovery with deep learning
Dec 26, 2022Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) in the form of deep learning bears promise for drug discovery and chemical biology, $\textit{e.g.}$, to predict protein structure and molecular bioactivity, plan organic synthesis, and design molecules $\textit{de novo}$. While most of the deep learning efforts in drug discovery have focused on ligand-based approaches, structure-based drug discovery has the potential to tackle unsolved challenges, such as affinity prediction for unexplored protein targets, binding-mechanism elucidation, and the rationalization of related chemical kinetic properties. Advances in deep learning methodologies and the availability of accurate predictions for protein tertiary structure advocate for a $\textit{renaissance}$ in structure-based approaches for drug discovery guided by AI. This review summarizes the most prominent algorithmic concepts in structure-based deep learning for drug discovery, and forecasts opportunities, applications, and challenges ahead.
Drug discovery with explainable artificial intelligence
Jul 02, 2020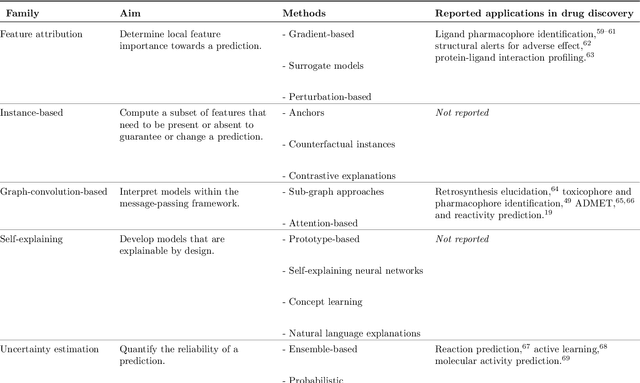
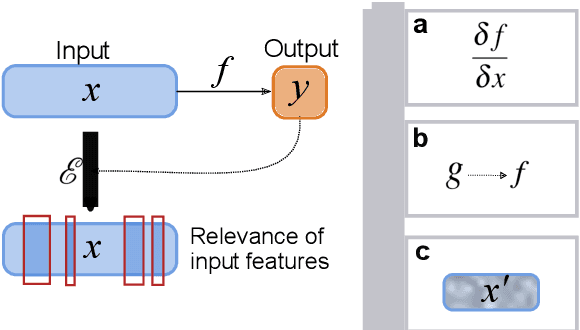
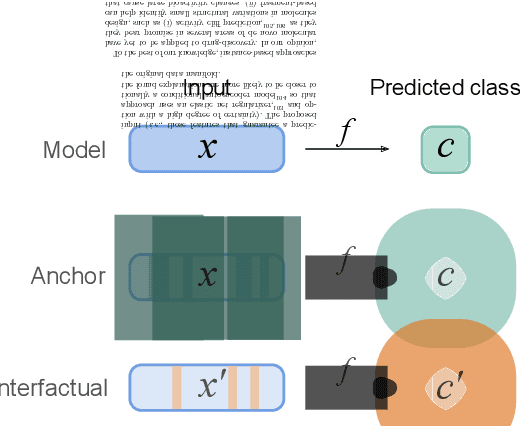
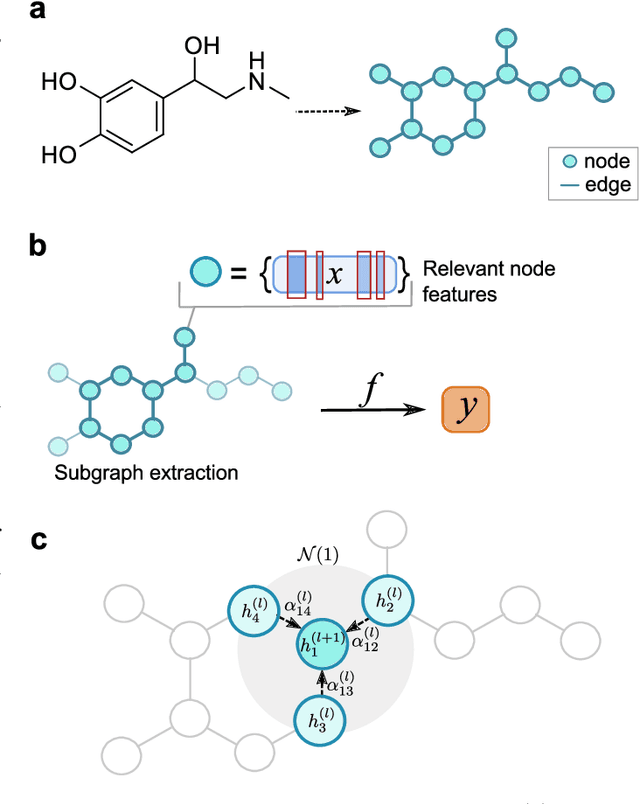
Abstract:Deep learning bears promise for drug discovery, including advanced image analysis, prediction of molecular structure and function, and automated generation of innovative chemical entities with bespoke properties. Despite the growing number of successful prospective applications, the underlying mathematical models often remain elusive to interpretation by the human mind. There is a demand for 'explainable' deep learning methods to address the need for a new narrative of the machine language of the molecular sciences. This review summarizes the most prominent algorithmic concepts of explainable artificial intelligence, and dares a forecast of the future opportunities, potential applications, and remaining challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge