José Alberto Benítez-Andrades
Classification of Psychiatry Clinical Notes by Diagnosis: A Deep Learning and Machine Learning Approach
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:The classification of clinical notes into specific diagnostic categories is critical in healthcare, especially for mental health conditions like Anxiety and Adjustment Disorder. In this study, we compare the performance of various Artificial Intelligence models, including both traditional Machine Learning approaches (Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, K-nearest neighbors, Decision Tree, and eXtreme Gradient Boost) and Deep Learning models (DistilBERT and SciBERT), to classify clinical notes into these two diagnoses. Additionally, we implemented three oversampling strategies: No Oversampling, Random Oversampling, and Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE), to assess their impact on model performance. Hyperparameter tuning was also applied to optimize model accuracy. Our results indicate that oversampling techniques had minimal impact on model performance overall. The only exception was SMOTE, which showed a positive effect specifically with BERT-based models. However, hyperparameter optimization significantly improved accuracy across the models, enhancing their ability to generalize and perform on the dataset. The Decision Tree and eXtreme Gradient Boost models achieved the highest accuracy among machine learning approaches, both reaching 96%, while the DistilBERT and SciBERT models also attained 96% accuracy in the deep learning category. These findings underscore the importance of hyperparameter tuning in maximizing model performance. This study contributes to the ongoing research on AI-assisted diagnostic tools in mental health by providing insights into the efficacy of different model architectures and data balancing methods.
TEDNet: Twin Encoder Decoder Neural Network for 2D Camera and LiDAR Road Detection
May 14, 2024Abstract:Robust road surface estimation is required for autonomous ground vehicles to navigate safely. Despite it becoming one of the main targets for autonomous mobility researchers in recent years, it is still an open problem in which cameras and LiDAR sensors have demonstrated to be adequate to predict the position, size and shape of the road a vehicle is driving on in different environments. In this work, a novel Convolutional Neural Network model is proposed for the accurate estimation of the roadway surface. Furthermore, an ablation study has been conducted to investigate how different encoding strategies affect model performance, testing 6 slightly different neural network architectures. Our model is based on the use of a Twin Encoder-Decoder Neural Network (TEDNet) for independent camera and LiDAR feature extraction, and has been trained and evaluated on the Kitti-Road dataset. Bird's Eye View projections of the camera and LiDAR data are used in this model to perform semantic segmentation on whether each pixel belongs to the road surface. The proposed method performs among other state-of-the-art methods and operates at the same frame-rate as the LiDAR and cameras, so it is adequate for its use in real-time applications.
* Source code: https://github.com/martin-bayon/TEDNet
Application of Machine Learning Algorithms in Classifying Postoperative Success in Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: A Comprehensive Study
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:Objectives: Metabolic Bariatric Surgery (MBS) is a critical intervention for patients living with obesity and related health issues. Accurate classification and prediction of patient outcomes are vital for optimizing treatment strategies. This study presents a novel machine learning approach to classify patients in the context of metabolic bariatric surgery, providing insights into the efficacy of different models and variable types. Methods: Various machine learning models, including GaussianNB, ComplementNB, KNN, Decision Tree, KNN with RandomOverSampler, and KNN with SMOTE, were applied to a dataset of 73 patients. The dataset, comprising psychometric, socioeconomic, and analytical variables, was analyzed to determine the most efficient predictive model. The study also explored the impact of different variable groupings and oversampling techniques. Results: Experimental results indicate average accuracy values as high as 66.7% for the best model. Enhanced versions of KNN and Decision Tree, along with variations of KNN such as RandomOverSampler and SMOTE, yielded the best results. Conclusions: The study unveils a promising avenue for classifying patients in the realm of metabolic bariatric surgery. The results underscore the importance of selecting appropriate variables and employing diverse approaches to achieve optimal performance. The developed system holds potential as a tool to assist healthcare professionals in decision-making, thereby enhancing metabolic bariatric surgery outcomes. These findings lay the groundwork for future collaboration between hospitals and healthcare entities to improve patient care through the utilization of machine learning algorithms. Moreover, the findings suggest room for improvement, potentially achievable with a larger dataset and careful parameter tuning.
Enhancing ASD detection accuracy: a combined approach of machine learning and deep learning models with natural language processing
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Purpose: Our study explored the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to diagnose autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It focused on machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) to detect ASD from text inputs on social media, addressing challenges in traditional ASD diagnosis. Methods: We used natural language processing (NLP), ML, and DL models (including decision trees, XGB, KNN, RNN, LSTM, Bi-LSTM, BERT, and BERTweet) to analyze 404,627 tweets, classifying them based on ASD or non-ASD authors. A subset of 90,000 tweets was used for model training and testing. Results: Our AI models showed high accuracy, with an 88% success rate in identifying texts from individuals with ASD. Conclusion: The study demonstrates AI's potential in improving ASD diagnosis, especially in children, highlighting the importance of early detection.
Evaluation of Country Dietary Habits Using Machine Learning Techniques in Relation to Deaths from COVID-19
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:COVID-19 disease has affected almost every country in the world. The large number of infected people and the different mortality rates between countries has given rise to many hypotheses about the key points that make the virus so lethal in some places. In this study, the eating habits of 170 countries were evaluated in order to find correlations between these habits and mortality rates caused by COVID-19 using machine learning techniques that group the countries together according to the different distribution of fat, energy, and protein across 23 different types of food, as well as the amount ingested in kilograms. Results shown how obesity and the high consumption of fats appear in countries with the highest death rates, whereas countries with a lower rate have a higher level of cereal consumption accompanied by a lower total average intake of kilocalories.
Detection of the most influential variables for preventing postpartum urinary incontinence using machine learning techniques
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Background: Postpartum urinary incontinence (PUI) is a common issue among postnatal women. Previous studies identified potential related variables, but lacked analysis on certain intrinsic and extrinsic patient variables during pregnancy. Objective: The study aims to evaluate the most influential variables in PUI using machine learning, focusing on intrinsic, extrinsic, and combined variable groups. Methods: Data from 93 pregnant women were analyzed using machine learning and oversampling techniques. Four key variables were predicted: occurrence, frequency, intensity of urinary incontinence, and stress urinary incontinence. Results: Models using extrinsic variables were most accurate, with 70% accuracy for urinary incontinence, 77% for frequency, 71% for intensity, and 93% for stress urinary incontinence. Conclusions: The study highlights extrinsic variables as significant predictors of PUI issues. This suggests that PUI prevention might be achievable through healthy habits during pregnancy, although further research is needed for confirmation.
A Web-Based Tool for Automatic Data Collection, Curation, and Visualization of Complex Healthcare Survey Studies including Social Network Analysis
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:There is a great concern nowadays regarding alcohol consumption and drug abuse, especially in young people. Analyzing the social environment where these adolescents are immersed, as well as a series of measures determining the alcohol abuse risk or personal situation and perception using a number of questionnaires like AUDIT, FAS, KIDSCREEN, and others, it is possible to gain insight into the current situation of a given individual regarding his/her consumption behavior. But this analysis, in order to be achieved, requires the use of tools that can ease the process of questionnaire creation, data gathering, curation and representation, and later analysis and visualization to the user. This research presents the design and construction of a web-based platform able to facilitate each of the mentioned processes by integrating the different phases into an intuitive system with a graphical user interface that hides the complexity underlying each of the questionnaires and techniques used and presenting the results in a flexible and visual way, avoiding any manual handling of data during the process. Advantages of this approach are shown and compared to the previous situation where some of the tasks were accomplished by time consuming and error prone manipulations of data.
Implementing local-explainability in Gradient Boosting Trees: Feature Contribution
Feb 14, 2024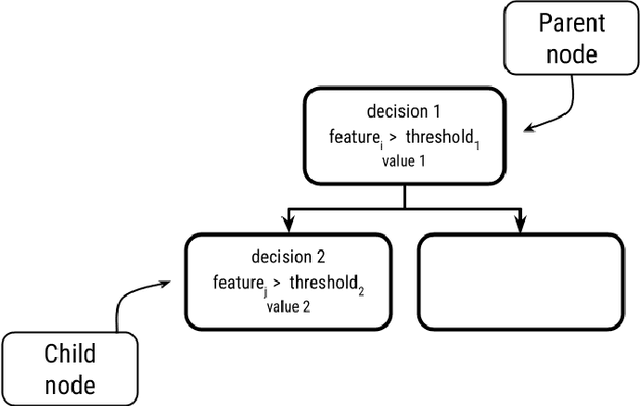
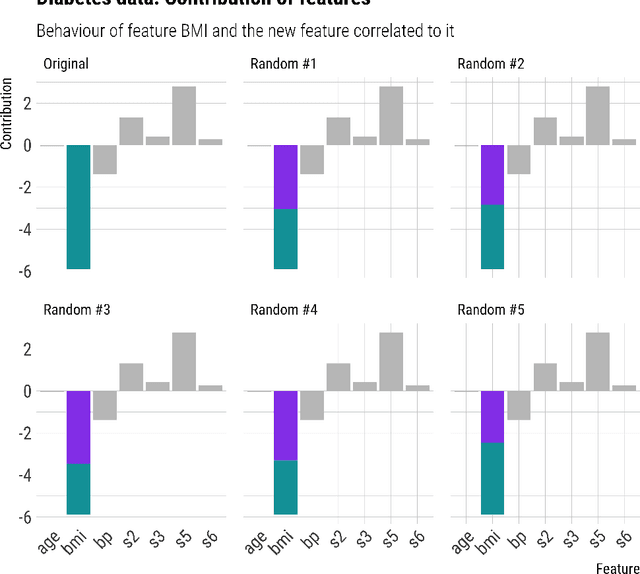
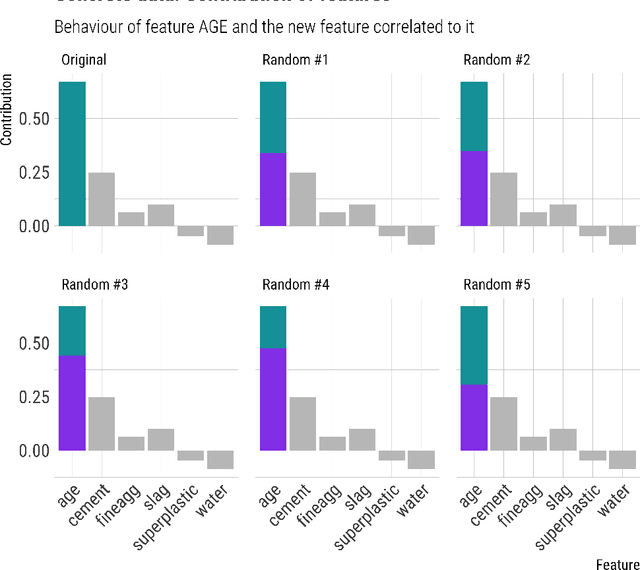
Abstract:Gradient Boost Decision Trees (GBDT) is a powerful additive model based on tree ensembles. Its nature makes GBDT a black-box model even though there are multiple explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) models obtaining information by reinterpreting the model globally and locally. Each tree of the ensemble is a transparent model itself but the final outcome is the result of a sum of these trees and it is not easy to clarify. In this paper, a feature contribution method for GBDT is developed. The proposed method takes advantage of the GBDT architecture to calculate the contribution of each feature using the residue of each node. This algorithm allows to calculate the sequence of node decisions given a prediction. Theoretical proofs and multiple experiments have been carried out to demonstrate the performance of our method which is not only a local explicability model for the GBDT algorithm but also a unique option that reflects GBDTs internal behavior. The proposal is aligned to the contribution of characteristics having impact in some artificial intelligence problems such as ethical analysis of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and comply with the new European laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) about the right to explain and nondiscrimination.
Social network analysis for personalized characterization and risk assessment of alcohol use disorders in adolescents using semantic technologies
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is a major concern for public health organizations worldwide, especially as regards the adolescent population. The consumption of alcohol in adolescents is known to be influenced by seeing friends and even parents drinking alcohol. Building on this fact, a number of studies into alcohol consumption among adolescents have made use of Social Network Analysis (SNA) techniques to study the different social networks (peers, friends, family, etc.) with whom the adolescent is involved. These kinds of studies need an initial phase of data gathering by means of questionnaires and a subsequent analysis phase using the SNA techniques. The process involves a number of manual data handling stages that are time consuming and error-prone. The use of knowledge engineering techniques (including the construction of a domain ontology) to represent the information, allows the automation of all the activities, from the initial data collection to the results of the SNA study. This paper shows how a knowledge model is constructed, and compares the results obtained using the traditional method with this, fully automated model, detailing the main advantages of the latter. In the case of the SNA analysis, the validity of the results obtained with the knowledge engineering approach are compared to those obtained manually using the UCINET, Cytoscape, Pajek and Gephi to test the accuracy of the knowledge model.
A Semantic Social Network Analysis Tool for Sensitivity Analysis and What-If Scenario Testing in Alcohol Consumption Studies
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Social Network Analysis (SNA) is a set of techniques developed in the field of social and behavioral sciences research, in order to characterize and study the social relationships that are established among a set of individuals. When building a social network for performing an SNA analysis, an initial process of data gathering is achieved in order to extract the characteristics of the individuals and their relationships. This is usually done by completing a questionnaire containing different types of questions that will be later used to obtain the SNA measures needed to perform the study. There are, then, a great number of different possible network generating questions and also many possibilities for mapping the responses to the corresponding characteristics and relationships. Many variations may be introduced into these questions (the way they are posed, the weights given to each of the responses, etc.) that may have an effect on the resulting networks. All these different variations are difficult to achieve manually, because the process is time-consuming and error prone. The tool described in this paper uses semantic knowledge representation techniques in order to facilitate this kind of sensitivity studies. The base of the tool is a conceptual structure, called "ontology" that is able to represent the different concepts and their definitions. The tool is compared to other similar ones, and the advantages of the approach are highlighted, giving some particular examples from an ongoing SNA study about alcohol consumption habits in adolescents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge