Jingtian Hu
Subwavelength Imaging using a Solid-Immersion Diffractive Optical Processor
Jan 17, 2024Abstract:Phase imaging is widely used in biomedical imaging, sensing, and material characterization, among other fields. However, direct imaging of phase objects with subwavelength resolution remains a challenge. Here, we demonstrate subwavelength imaging of phase and amplitude objects based on all-optical diffractive encoding and decoding. To resolve subwavelength features of an object, the diffractive imager uses a thin, high-index solid-immersion layer to transmit high-frequency information of the object to a spatially-optimized diffractive encoder, which converts/encodes high-frequency information of the input into low-frequency spatial modes for transmission through air. The subsequent diffractive decoder layers (in air) are jointly designed with the encoder using deep-learning-based optimization, and communicate with the encoder layer to create magnified images of input objects at its output, revealing subwavelength features that would otherwise be washed away due to diffraction limit. We demonstrate that this all-optical collaboration between a diffractive solid-immersion encoder and the following decoder layers in air can resolve subwavelength phase and amplitude features of input objects in a highly compact design. To experimentally demonstrate its proof-of-concept, we used terahertz radiation and developed a fabrication method for creating monolithic multi-layer diffractive processors. Through these monolithically fabricated diffractive encoder-decoder pairs, we demonstrated phase-to-intensity transformations and all-optically reconstructed subwavelength phase features of input objects by directly transforming them into magnified intensity features at the output. This solid-immersion-based diffractive imager, with its compact and cost-effective design, can find wide-ranging applications in bioimaging, endoscopy, sensing and materials characterization.
Universal Polarization Transformations: Spatial programming of polarization scattering matrices using a deep learning-designed diffractive polarization transformer
Apr 12, 2023Abstract:We demonstrate universal polarization transformers based on an engineered diffractive volume, which can synthesize a large set of arbitrarily-selected, complex-valued polarization scattering matrices between the polarization states at different positions within its input and output field-of-views (FOVs). This framework comprises 2D arrays of linear polarizers with diverse angles, which are positioned between isotropic diffractive layers, each containing tens of thousands of diffractive features with optimizable transmission coefficients. We demonstrate that, after its deep learning-based training, this diffractive polarization transformer could successfully implement N_i x N_o = 10,000 different spatially-encoded polarization scattering matrices with negligible error within a single diffractive volume, where N_i and N_o represent the number of pixels in the input and output FOVs, respectively. We experimentally validated this universal polarization transformation framework in the terahertz part of the spectrum by fabricating wire-grid polarizers and integrating them with 3D-printed diffractive layers to form a physical polarization transformer operating at 0.75 mm wavelength. Through this set-up, we demonstrated an all-optical polarization permutation operation of spatially-varying polarization fields, and simultaneously implemented distinct spatially-encoded polarization scattering matrices between the input and output FOVs of a compact diffractive processor that axially spans 200 wavelengths. This framework opens up new avenues for developing novel optical devices for universal polarization control, and may find various applications in, e.g., remote sensing, medical imaging, security, material inspection and machine vision.
To image, or not to image: Class-specific diffractive cameras with all-optical erasure of undesired objects
May 26, 2022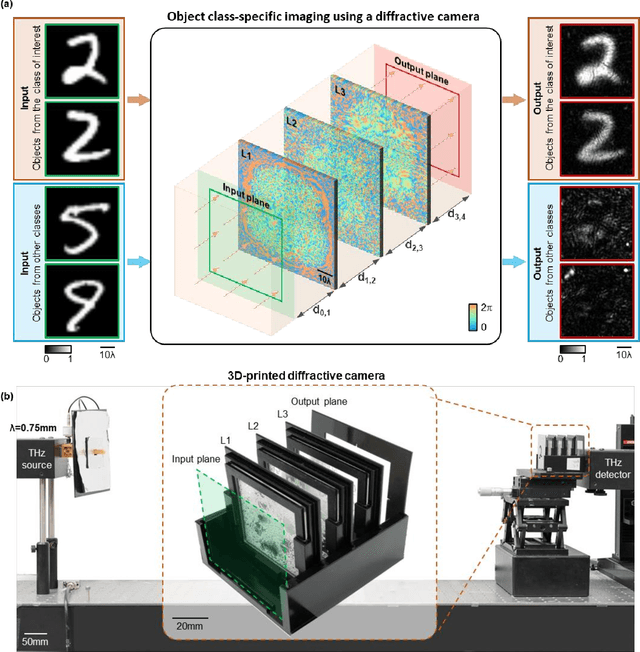
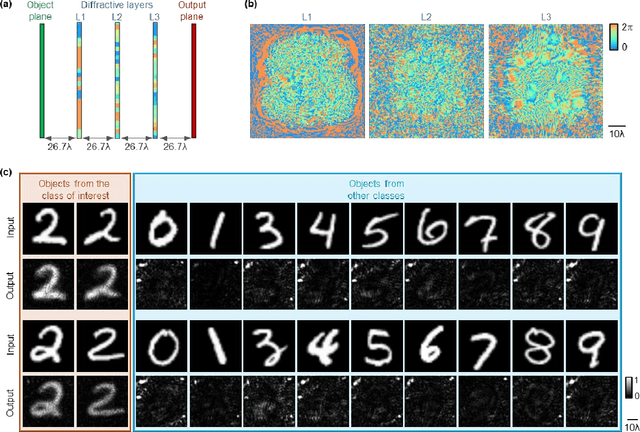
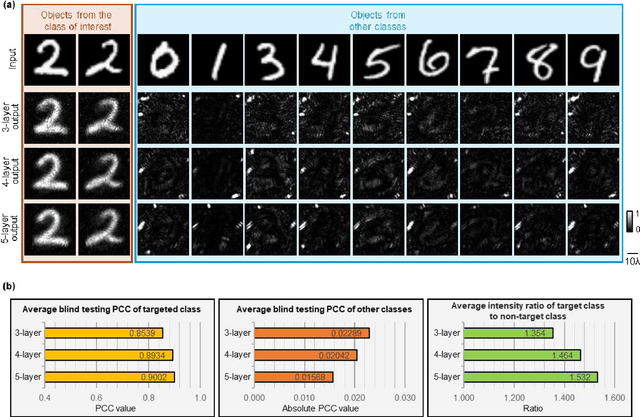
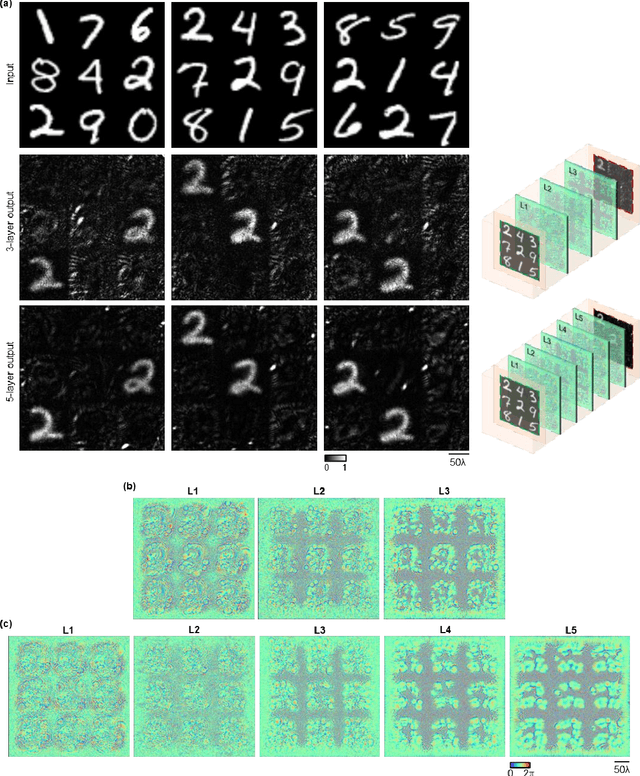
Abstract:Privacy protection is a growing concern in the digital era, with machine vision techniques widely used throughout public and private settings. Existing methods address this growing problem by, e.g., encrypting camera images or obscuring/blurring the imaged information through digital algorithms. Here, we demonstrate a camera design that performs class-specific imaging of target objects with instantaneous all-optical erasure of other classes of objects. This diffractive camera consists of transmissive surfaces structured using deep learning to perform selective imaging of target classes of objects positioned at its input field-of-view. After their fabrication, the thin diffractive layers collectively perform optical mode filtering to accurately form images of the objects that belong to a target data class or group of classes, while instantaneously erasing objects of the other data classes at the output field-of-view. Using the same framework, we also demonstrate the design of class-specific permutation cameras, where the objects of a target data class are pixel-wise permuted for all-optical class-specific encryption, while the other objects are irreversibly erased from the output image. The success of class-specific diffractive cameras was experimentally demonstrated using terahertz (THz) waves and 3D-printed diffractive layers that selectively imaged only one class of the MNIST handwritten digit dataset, all-optically erasing the other handwritten digits. This diffractive camera design can be scaled to different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, including, e.g., the visible and infrared wavelengths, to provide transformative opportunities for privacy-preserving digital cameras and task-specific data-efficient imaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge