Jiacheng Zuo
VLM-C4L: Continual Core Dataset Learning with Corner Case Optimization via Vision-Language Models for Autonomous Driving
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:With the widespread adoption and deployment of autonomous driving, handling complex environments has become an unavoidable challenge. Due to the scarcity and diversity of extreme scenario datasets, current autonomous driving models struggle to effectively manage corner cases. This limitation poses a significant safety risk, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), autonomous vehicle systems have been involved in hundreds of reported crashes annually in the United States, occurred in corner cases like sun glare and fog, which caused a few fatal accident. Furthermore, in order to consistently maintain a robust and reliable autonomous driving system, it is essential for models not only to perform well on routine scenarios but also to adapt to newly emerging scenarios, especially those corner cases that deviate from the norm. This requires a learning mechanism that incrementally integrates new knowledge without degrading previously acquired capabilities. However, to the best of our knowledge, no existing continual learning methods have been proposed to ensure consistent and scalable corner case learning in autonomous driving. To address these limitations, we propose VLM-C4L, a continual learning framework that introduces Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to dynamically optimize and enhance corner case datasets, and VLM-C4L combines VLM-guided high-quality data extraction with a core data replay strategy, enabling the model to incrementally learn from diverse corner cases while preserving performance on previously routine scenarios, thus ensuring long-term stability and adaptability in real-world autonomous driving. We evaluate VLM-C4L on large-scale real-world autonomous driving datasets, including Waymo and the corner case dataset CODA.
CoT-VLM4Tar: Chain-of-Thought Guided Vision-Language Models for Traffic Anomaly Resolution
Mar 03, 2025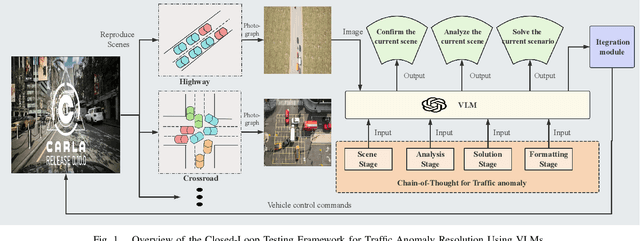
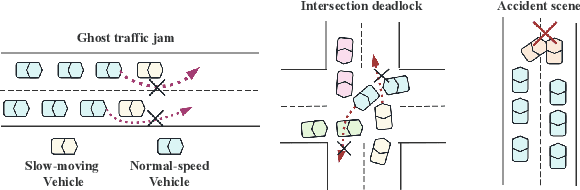
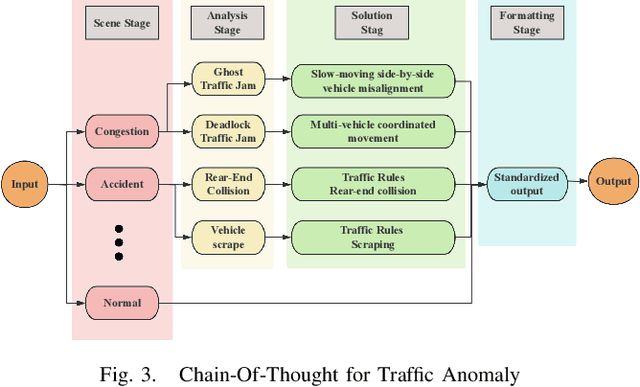
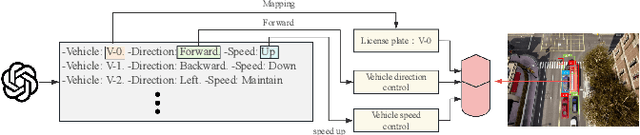
Abstract:With the acceleration of urbanization, modern urban traffic systems are becoming increasingly complex, leading to frequent traffic anomalies. These anomalies encompass not only common traffic jams but also more challenging issues such as phantom traffic jams, intersection deadlocks, and accident liability analysis, which severely impact traffic flow, vehicular safety, and overall transportation efficiency. Currently, existing solutions primarily rely on manual intervention by traffic police or artificial intelligence-based detection systems. However, these methods often suffer from response delays and inconsistent management due to inadequate resources, while AI detection systems, despite enhancing efficiency to some extent, still struggle to handle complex traffic anomalies in a real-time and precise manner. To address these issues, we propose CoT-VLM4Tar: (Chain of Thought Visual-Language Model for Traffic Anomaly Resolution), this innovative approach introduces a new chain-of-thought to guide the VLM in analyzing, reasoning, and generating solutions for traffic anomalies with greater reasonable and effective solution, and to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of our method, we developed a closed-loop testing framework based on the CARLA simulator. Furthermore, to ensure seamless integration of the solutions generated by the VLM with the CARLA simulator, we implement an itegration module that converts these solutions into executable commands. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of VLM in the resolution of real-time traffic anomalies, providing a proof-of-concept for its integration into autonomous traffic management systems.
RALAD: Bridging the Real-to-Sim Domain Gap in Autonomous Driving with Retrieval-Augmented Learning
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:In the pursuit of robust autonomous driving systems, models trained on real-world datasets often struggle to adapt to new environments, particularly when confronted with corner cases such as extreme weather conditions. Collecting these corner cases in the real world is non-trivial, which necessitates the use of simulators for validation. However,the high computational cost and the domain gap in data distribution have hindered the seamless transition between real and simulated driving scenarios. To tackle this challenge, we propose Retrieval-Augmented Learning for Autonomous Driving (RALAD), a novel framework designed to bridge the real-to-sim gap at a low cost. RALAD features three primary designs, including (1) domain adaptation via an enhanced Optimal Transport (OT) method that accounts for both individual and grouped image distances, (2) a simple and unified framework that can be applied to various models, and (3) efficient fine-tuning techniques that freeze the computationally expensive layers while maintaining robustness. Experimental results demonstrate that RALAD compensates for the performance degradation in simulated environments while maintaining accuracy in real-world scenarios across three different models. Taking Cross View as an example, the mIOU and mAP metrics in real-world scenarios remain stable before and after RALAD fine-tuning, while in simulated environments,the mIOU and mAP metrics are improved by 10.30% and 12.29%, respectively. Moreover, the re-training cost of our approach is reduced by approximately 88.1%. Our code is available at https://github.com/JiachengZuo/RALAD.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge