Jeffrey Hu
Efficient Camera-Controlled Video Generation of Static Scenes via Sparse Diffusion and 3D Rendering
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Modern video generative models based on diffusion models can produce very realistic clips, but they are computationally inefficient, often requiring minutes of GPU time for just a few seconds of video. This inefficiency poses a critical barrier to deploying generative video in applications that require real-time interactions, such as embodied AI and VR/AR. This paper explores a new strategy for camera-conditioned video generation of static scenes: using diffusion-based generative models to generate a sparse set of keyframes, and then synthesizing the full video through 3D reconstruction and rendering. By lifting keyframes into a 3D representation and rendering intermediate views, our approach amortizes the generation cost across hundreds of frames while enforcing geometric consistency. We further introduce a model that predicts the optimal number of keyframes for a given camera trajectory, allowing the system to adaptively allocate computation. Our final method, SRENDER, uses very sparse keyframes for simple trajectories and denser ones for complex camera motion. This results in video generation that is more than 40 times faster than the diffusion-based baseline in generating 20 seconds of video, while maintaining high visual fidelity and temporal stability, offering a practical path toward efficient and controllable video synthesis.
gsplat: An Open-Source Library for Gaussian Splatting
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:gsplat is an open-source library designed for training and developing Gaussian Splatting methods. It features a front-end with Python bindings compatible with the PyTorch library and a back-end with highly optimized CUDA kernels. gsplat offers numerous features that enhance the optimization of Gaussian Splatting models, which include optimization improvements for speed, memory, and convergence times. Experimental results demonstrate that gsplat achieves up to 10% less training time and 4x less memory than the original implementation. Utilized in several research projects, gsplat is actively maintained on GitHub. Source code is available at https://github.com/nerfstudio-project/gsplat under Apache License 2.0. We welcome contributions from the open-source community.
Composition based oxidation state prediction of materials using deep learning
Nov 29, 2022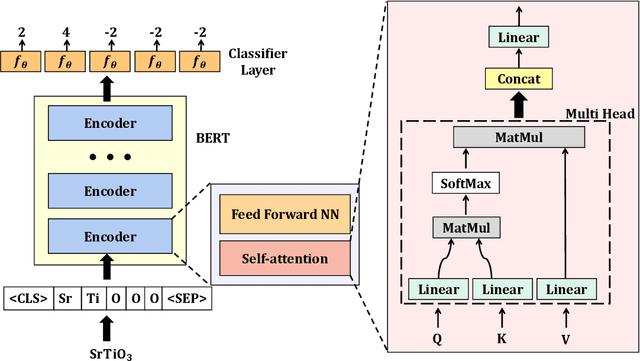
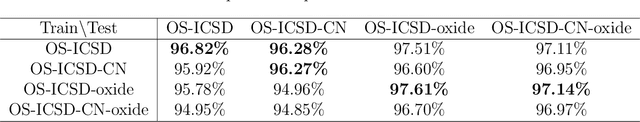
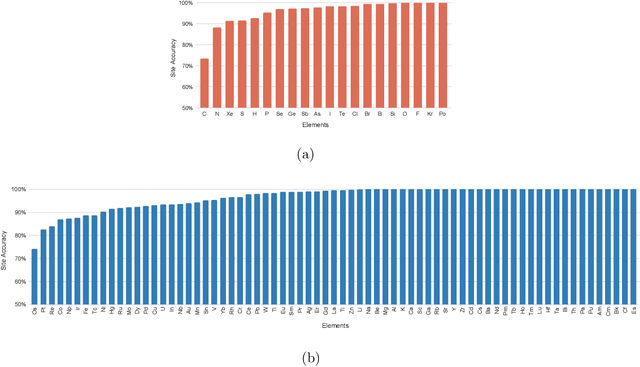
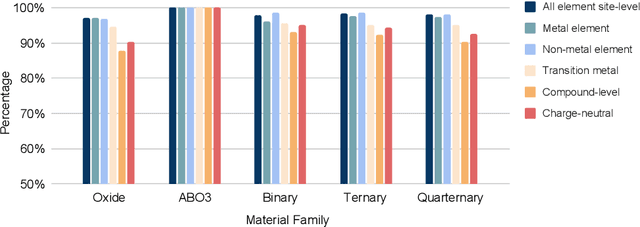
Abstract:Oxidation states are the charges of atoms after their ionic approximation of their bonds, which have been widely used in charge-neutrality verification, crystal structure determination, and reaction estimation. Currently only heuristic rules exist for guessing the oxidation states of a given compound with many exceptions. Recent work has developed machine learning models based on heuristic structural features for predicting the oxidation states of metal ions. However, composition based oxidation state prediction still remains elusive so far, which is more important in new material discovery for which the structures are not even available. This work proposes a novel deep learning based BERT transformer language model BERTOS for predicting the oxidation states of all elements of inorganic compounds given only their chemical composition. Our model achieves 96.82\% accuracy for all-element oxidation states prediction benchmarked on the cleaned ICSD dataset and achieves 97.61\% accuracy for oxide materials. We also demonstrate how it can be used to conduct large-scale screening of hypothetical material compositions for materials discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge