James Thewlis
Language as the Medium: Multimodal Video Classification through text only
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Despite an exciting new wave of multimodal machine learning models, current approaches still struggle to interpret the complex contextual relationships between the different modalities present in videos. Going beyond existing methods that emphasize simple activities or objects, we propose a new model-agnostic approach for generating detailed textual descriptions that captures multimodal video information. Our method leverages the extensive knowledge learnt by large language models, such as GPT-3.5 or Llama2, to reason about textual descriptions of the visual and aural modalities, obtained from BLIP-2, Whisper and ImageBind. Without needing additional finetuning of video-text models or datasets, we demonstrate that available LLMs have the ability to use these multimodal textual descriptions as proxies for ``sight'' or ``hearing'' and perform zero-shot multimodal classification of videos in-context. Our evaluations on popular action recognition benchmarks, such as UCF-101 or Kinetics, show these context-rich descriptions can be successfully used in video understanding tasks. This method points towards a promising new research direction in multimodal classification, demonstrating how an interplay between textual, visual and auditory machine learning models can enable more holistic video understanding.
VTC: Improving Video-Text Retrieval with User Comments
Oct 19, 2022
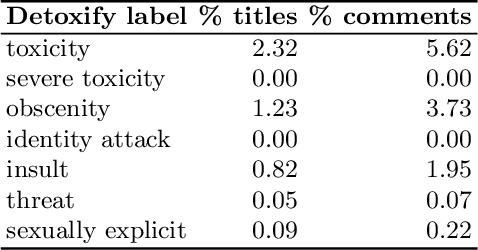
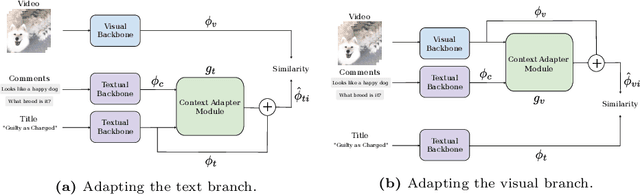
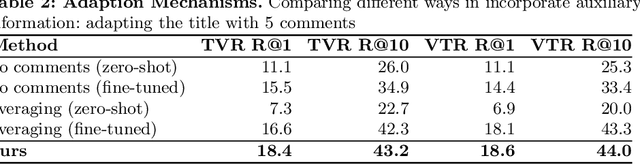
Abstract:Multi-modal retrieval is an important problem for many applications, such as recommendation and search. Current benchmarks and even datasets are often manually constructed and consist of mostly clean samples where all modalities are well-correlated with the content. Thus, current video-text retrieval literature largely focuses on video titles or audio transcripts, while ignoring user comments, since users often tend to discuss topics only vaguely related to the video. Despite the ubiquity of user comments online, there is currently no multi-modal representation learning datasets that includes comments. In this paper, we a) introduce a new dataset of videos, titles and comments; b) present an attention-based mechanism that allows the model to learn from sometimes irrelevant data such as comments; c) show that by using comments, our method is able to learn better, more contextualised, representations for image, video and audio representations. Project page: https://unitaryai.github.io/vtc-paper.
Unsupervised Learning of Landmarks by Descriptor Vector Exchange
Aug 18, 2019



Abstract:Equivariance to random image transformations is an effective method to learn landmarks of object categories, such as the eyes and the nose in faces, without manual supervision. However, this method does not explicitly guarantee that the learned landmarks are consistent with changes between different instances of the same object, such as different facial identities. In this paper, we develop a new perspective on the equivariance approach by noting that dense landmark detectors can be interpreted as local image descriptors equipped with invariance to intra-category variations. We then propose a direct method to enforce such an invariance in the standard equivariant loss. We do so by exchanging descriptor vectors between images of different object instances prior to matching them geometrically. In this manner, the same vectors must work regardless of the specific object identity considered. We use this approach to learn vectors that can simultaneously be interpreted as local descriptors and dense landmarks, combining the advantages of both. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that this approach can match, and in some cases surpass state-of-the-art performance amongst existing methods that learn landmarks without supervision. Code is available at www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/DVE/.
Slim DensePose: Thrifty Learning from Sparse Annotations and Motion Cues
Jun 13, 2019



Abstract:DensePose supersedes traditional landmark detectors by densely mapping image pixels to body surface coordinates. This power, however, comes at a greatly increased annotation time, as supervising the model requires to manually label hundreds of points per pose instance. In this work, we thus seek methods to significantly slim down the DensePose annotations, proposing more efficient data collection strategies. In particular, we demonstrate that if annotations are collected in video frames, their efficacy can be multiplied for free by using motion cues. To explore this idea, we introduce DensePose-Track, a dataset of videos where selected frames are annotated in the traditional DensePose manner. Then, building on geometric properties of the DensePose mapping, we use the video dynamic to propagate ground-truth annotations in time as well as to learn from Siamese equivariance constraints. Having performed exhaustive empirical evaluation of various data annotation and learning strategies, we demonstrate that doing so can deliver significantly improved pose estimation results over strong baselines. However, despite what is suggested by some recent works, we show that merely synthesizing motion patterns by applying geometric transformations to isolated frames is significantly less effective, and that motion cues help much more when they are extracted from videos.
Deep Industrial Espionage
Apr 01, 2019



Abstract:The theory of deep learning is now considered largely solved, and is well understood by researchers and influencers alike. To maintain our relevance, we therefore seek to apply our skills to under-explored, lucrative applications of this technology. To this end, we propose and Deep Industrial Espionage, an efficient end-to-end framework for industrial information propagation and productisation. Specifically, given a single image of a product or service, we aim to reverse-engineer, rebrand and distribute a copycat of the product at a profitable price-point to consumers in an emerging market---all within in a single forward pass of a Neural Network. Differently from prior work in machine perception which has been restricted to classifying, detecting and reasoning about object instances, our method offers tangible business value in a wide range of corporate settings. Our approach draws heavily on a promising recent arxiv paper until its original authors' names can no longer be read (we use felt tip pen). We then rephrase the anonymised paper, add the word "novel" to the title, and submit it a prestigious, closed-access espionage journal who assure us that someday, we will be entitled to some fraction of their extortionate readership fees.
Cross Pixel Optical Flow Similarity for Self-Supervised Learning
Jul 15, 2018



Abstract:We propose a novel method for learning convolutional neural image representations without manual supervision. We use motion cues in the form of optical flow, to supervise representations of static images. The obvious approach of training a network to predict flow from a single image can be needlessly difficult due to intrinsic ambiguities in this prediction task. We instead propose a much simpler learning goal: embed pixels such that the similarity between their embeddings matches that between their optical flow vectors. At test time, the learned deep network can be used without access to video or flow information and transferred to tasks such as image classification, detection, and segmentation. Our method, which significantly simplifies previous attempts at using motion for self-supervision, achieves state-of-the-art results in self-supervision using motion cues, competitive results for self-supervision in general, and is overall state of the art in self-supervised pretraining for semantic image segmentation, as demonstrated on standard benchmarks.
Substitute Teacher Networks: Learning with Almost No Supervision
Apr 01, 2018


Abstract:Learning through experience is time-consuming, inefficient and often bad for your cortisol levels. To address this problem, a number of recently proposed teacher-student methods have demonstrated the benefits of private tuition, in which a single model learns from an ensemble of more experienced tutors. Unfortunately, the cost of such supervision restricts good representations to a privileged minority. Unsupervised learning can be used to lower tuition fees, but runs the risk of producing networks that require extracurriculum learning to strengthen their CVs and create their own LinkedIn profiles. Inspired by the logo on a promotional stress ball at a local recruitment fair, we make the following three contributions. First, we propose a novel almost no supervision training algorithm that is effective, yet highly scalable in the number of student networks being supervised, ensuring that education remains affordable. Second, we demonstrate our approach on a typical use case: learning to bake, developing a method that tastily surpasses the current state of the art. Finally, we provide a rigorous quantitive analysis of our method, proving that we have access to a calculator. Our work calls into question the long-held dogma that life is the best teacher.
Unsupervised learning of object frames by dense equivariant image labelling
Nov 18, 2017



Abstract:One of the key challenges of visual perception is to extract abstract models of 3D objects and object categories from visual measurements, which are affected by complex nuisance factors such as viewpoint, occlusion, motion, and deformations. Starting from the recent idea of viewpoint factorization, we propose a new approach that, given a large number of images of an object and no other supervision, can extract a dense object-centric coordinate frame. This coordinate frame is invariant to deformations of the images and comes with a dense equivariant labelling neural network that can map image pixels to their corresponding object coordinates. We demonstrate the applicability of this method to simple articulated objects and deformable objects such as human faces, learning embeddings from random synthetic transformations or optical flow correspondences, all without any manual supervision.
Unsupervised learning of object landmarks by factorized spatial embeddings
Aug 06, 2017



Abstract:Learning automatically the structure of object categories remains an important open problem in computer vision. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised approach that can discover and learn landmarks in object categories, thus characterizing their structure. Our approach is based on factorizing image deformations, as induced by a viewpoint change or an object deformation, by learning a deep neural network that detects landmarks consistently with such visual effects. Furthermore, we show that the learned landmarks establish meaningful correspondences between different object instances in a category without having to impose this requirement explicitly. We assess the method qualitatively on a variety of object types, natural and man-made. We also show that our unsupervised landmarks are highly predictive of manually-annotated landmarks in face benchmark datasets, and can be used to regress these with a high degree of accuracy.
Fully-Trainable Deep Matching
Sep 12, 2016



Abstract:Deep Matching (DM) is a popular high-quality method for quasi-dense image matching. Despite its name, however, the original DM formulation does not yield a deep neural network that can be trained end-to-end via backpropagation. In this paper, we remove this limitation by rewriting the complete DM algorithm as a convolutional neural network. This results in a novel deep architecture for image matching that involves a number of new layer types and that, similar to recent networks for image segmentation, has a U-topology. We demonstrate the utility of the approach by improving the performance of DM by learning it end-to-end on an image matching task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge