Jake Vasilakes
SCRum-9: Multilingual Stance Classification over Rumours on Social Media
May 25, 2025Abstract:We introduce SCRum-9, a multilingual dataset for Rumour Stance Classification, containing 7,516 tweet-reply pairs from X. SCRum-9 goes beyond existing stance classification datasets by covering more languages (9), linking examples to more fact-checked claims (2.1k), and including complex annotations from multiple annotators to account for intra- and inter-annotator variability. Annotations were made by at least three native speakers per language, totalling around 405 hours of annotation and 8,150 dollars in compensation. Experiments on SCRum-9 show that it is a challenging benchmark for both state-of-the-art LLMs (e.g. Deepseek) as well as fine-tuned pre-trained models, motivating future work in this area.
Efficient Annotator Reliablity Assessment with EffiARA
Apr 01, 2025


Abstract:Data annotation is an essential component of the machine learning pipeline; it is also a costly and time-consuming process. With the introduction of transformer-based models, annotation at the document level is increasingly popular; however, there is no standard framework for structuring such tasks. The EffiARA annotation framework is, to our knowledge, the first project to support the whole annotation pipeline, from understanding the resources required for an annotation task to compiling the annotated dataset and gaining insights into the reliability of individual annotators as well as the dataset as a whole. The framework's efficacy is supported by two previous studies: one improving classification performance through annotator-reliability-based soft label aggregation and sample weighting, and the other increasing the overall agreement among annotators through removing identifying and replacing an unreliable annotator. This work introduces the EffiARA Python package and its accompanying webtool, which provides an accessible graphical user interface for the system. We open-source the EffiARA Python package at https://github.com/MiniEggz/EffiARA and the webtool is publicly accessible at https://effiara.gate.ac.uk.
Subjective Logic Encodings
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:Many existing approaches for learning from labeled data assume the existence of gold-standard labels. According to these approaches, inter-annotator disagreement is seen as noise to be removed, either through refinement of annotation guidelines, label adjudication, or label filtering. However, annotator disagreement can rarely be totally eradicated, especially on more subjective tasks such as sentiment analysis or hate speech detection where disagreement is natural. Therefore, a new approach to learning from labeled data, called data perspectivism, seeks to leverage inter-annotator disagreement to learn models that stay true to the inherent uncertainty of the task by treating annotations as opinions of the annotators, rather than gold-standard facts. Despite this conceptual grounding, existing methods under data perspectivism are limited to using disagreement as the sole source of annotation uncertainty. To expand the possibilities of data perspectivism, we introduce Subjective Logic Encodings (SLEs), a flexible framework for constructing classification targets that explicitly encodes annotations as opinions of the annotators. Based on Subjective Logic Theory, SLEs encode labels as Dirichlet distributions and provide principled methods for encoding and aggregating various types of annotation uncertainty -- annotator confidence, reliability, and disagreement -- into the targets. We show that SLEs are a generalization of other types of label encodings as well as how to estimate models to predict SLEs using a distribution matching objective.
Learning Disentangled Representations of Negation and Uncertainty
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:Negation and uncertainty modeling are long-standing tasks in natural language processing. Linguistic theory postulates that expressions of negation and uncertainty are semantically independent from each other and the content they modify. However, previous works on representation learning do not explicitly model this independence. We therefore attempt to disentangle the representations of negation, uncertainty, and content using a Variational Autoencoder. We find that simply supervising the latent representations results in good disentanglement, but auxiliary objectives based on adversarial learning and mutual information minimization can provide additional disentanglement gains.
An Empirical Study of UMLS Concept Extraction from Clinical Notes using Boolean Combination Ensembles
Aug 04, 2021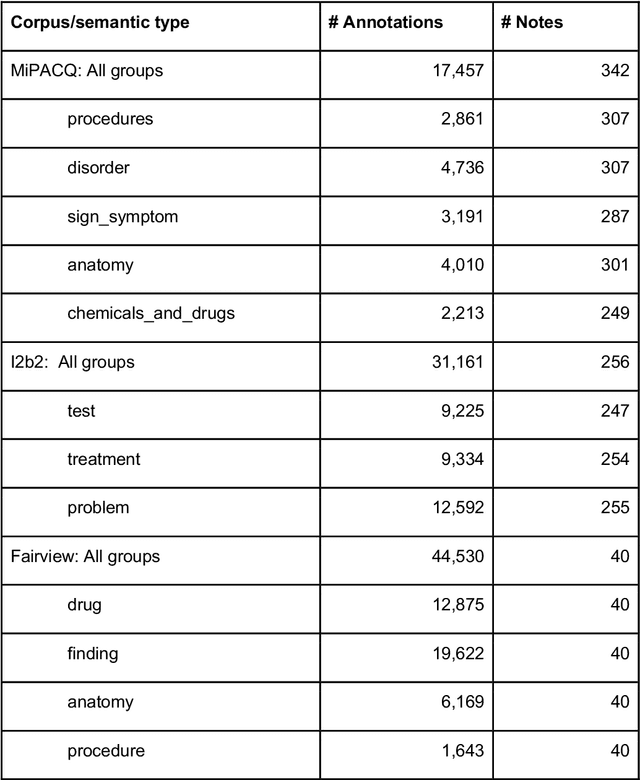
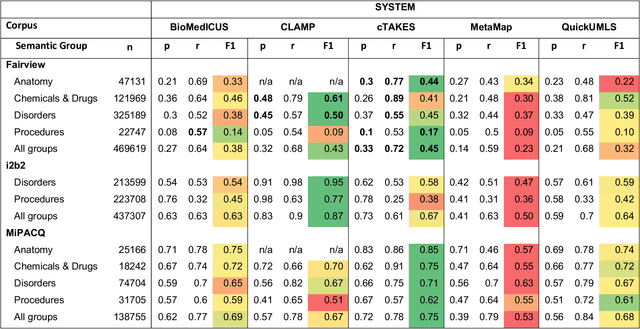
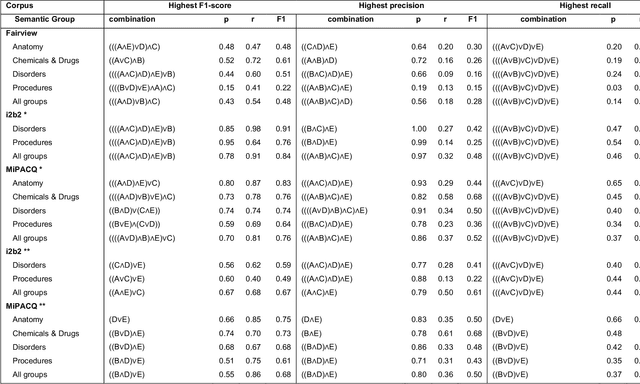
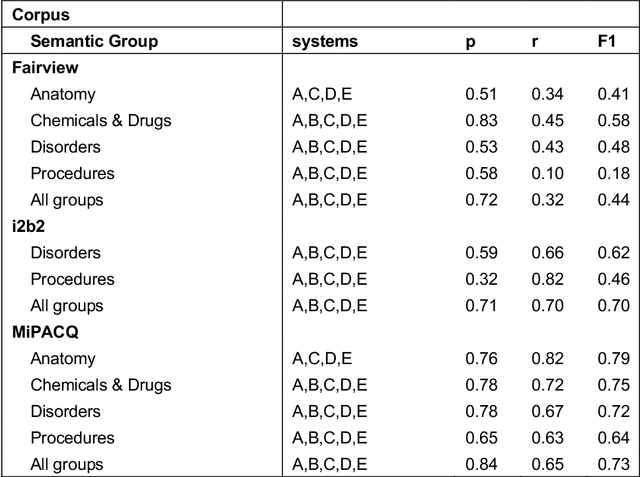
Abstract:Our objective in this study is to investigate the behavior of Boolean operators on combining annotation output from multiple Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems across multiple corpora and to assess how filtering by aggregation of Unified Medical Language System (UMLS) Metathesaurus concepts affects system performance for Named Entity Recognition (NER) of UMLS concepts. We used three corpora annotated for UMLS concepts: 2010 i2b2 VA challenge set (31,161 annotations), Multi-source Integrated Platform for Answering Clinical Questions (MiPACQ) corpus (17,457 annotations including UMLS concept unique identifiers), and Fairview Health Services corpus (44,530 annotations). Our results showed that for UMLS concept matching, Boolean ensembling of the MiPACQ corpus trended towards higher performance over individual systems. Use of an approximate grid-search can help optimize the precision-recall tradeoff and can provide a set of heuristics for choosing an optimal set of ensembles.
Discovering novel drug-supplement interactions using a dietary supplements knowledge graph generated from the biomedical literature
Jun 24, 2021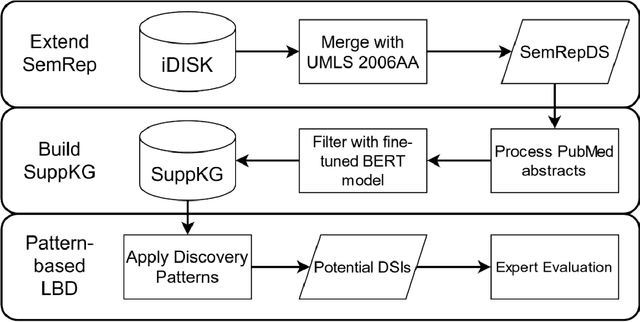
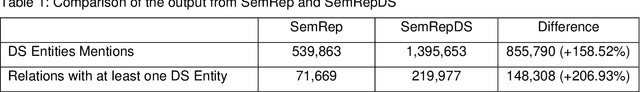
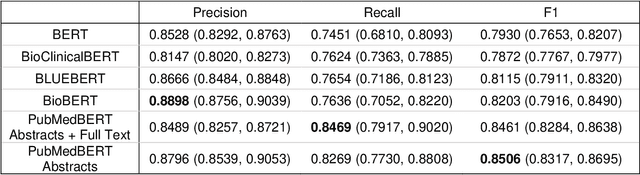
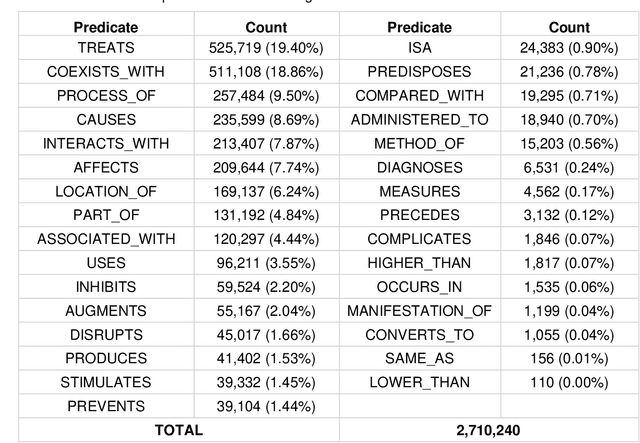
Abstract:OBJECTIVE: Leverage existing biomedical NLP tools and DS domain terminology to produce a novel and comprehensive knowledge graph containing dietary supplement (DS) information for discovering interactions between DS and drugs, or Drug-Supplement Interactions (DSI). MATERIALS AND METHODS: We created SemRepDS (an extension of SemRep), capable of extracting semantic relations from abstracts by leveraging a DS-specific terminology (iDISK) containing 28,884 DS terms not found in the UMLS. PubMed abstracts were processed using SemRepDS to generate semantic relations, which were then filtered using a PubMedBERT-based model to remove incorrect relations before generating our knowledge graph (SuppKG). Two pathways are used to identify potential DS-Drug interactions which are then evaluated by medical professionals for mechanistic plausibility. RESULTS: Comparison analysis found that SemRepDS returned 206.9% more DS relations and 158.5% more DS entities than SemRep. The fine-tuned BERT model obtained an F1 score of 0.8605 and removed 43.86% of the relations, improving the precision of the relations by 26.4% compared to pre-filtering. SuppKG consists of 2,928 DS-specific nodes. Manual review of findings identified 44 (88%) proposed DS-Gene-Drug and 32 (64%) proposed DS-Gene1-Function-Gene2-Drug pathways to be mechanistically plausible. DISCUSSION: The additional relations extracted using SemRepDS generated SuppKG that was used to find plausible DSI not found in the current literature. By the nature of the SuppKG, these interactions are unlikely to have been found using SemRep without the expanded DS terminology. CONCLUSION: We successfully extend SemRep to include DS information and produce SuppKG which can be used to find potential DS-Drug interactions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge