Jaeill Kim
Unveiling Key Aspects of Fine-Tuning in Sentence Embeddings: A Representation Rank Analysis
May 18, 2024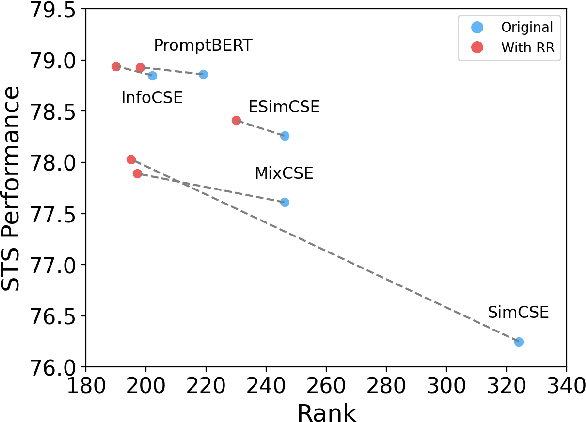
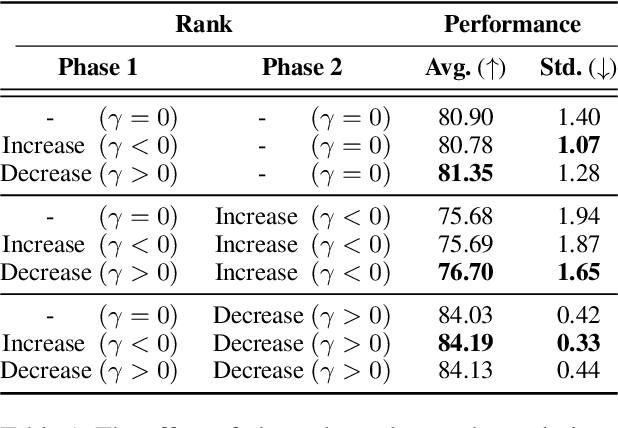
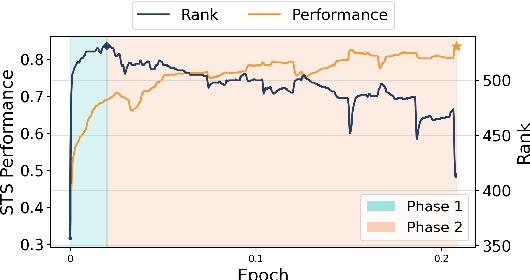

Abstract:The latest advancements in unsupervised learning of sentence embeddings predominantly involve employing contrastive learning-based (CL-based) fine-tuning over pre-trained language models. In this study, we analyze the latest sentence embedding methods by adopting representation rank as the primary tool of analysis. We first define Phase 1 and Phase 2 of fine-tuning based on when representation rank peaks. Utilizing these phases, we conduct a thorough analysis and obtain essential findings across key aspects, including alignment and uniformity, linguistic abilities, and correlation between performance and rank. For instance, we find that the dynamics of the key aspects can undergo significant changes as fine-tuning transitions from Phase 1 to Phase 2. Based on these findings, we experiment with a rank reduction (RR) strategy that facilitates rapid and stable fine-tuning of the latest CL-based methods. Through empirical investigations, we showcase the efficacy of RR in enhancing the performance and stability of five state-of-the-art sentence embedding methods.
Improving Forward Compatibility in Class Incremental Learning by Increasing Representation Rank and Feature Richness
Mar 22, 2024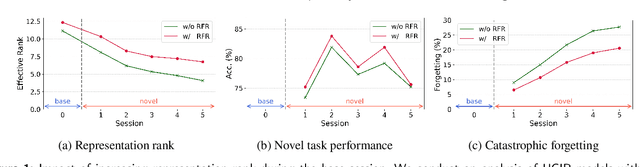
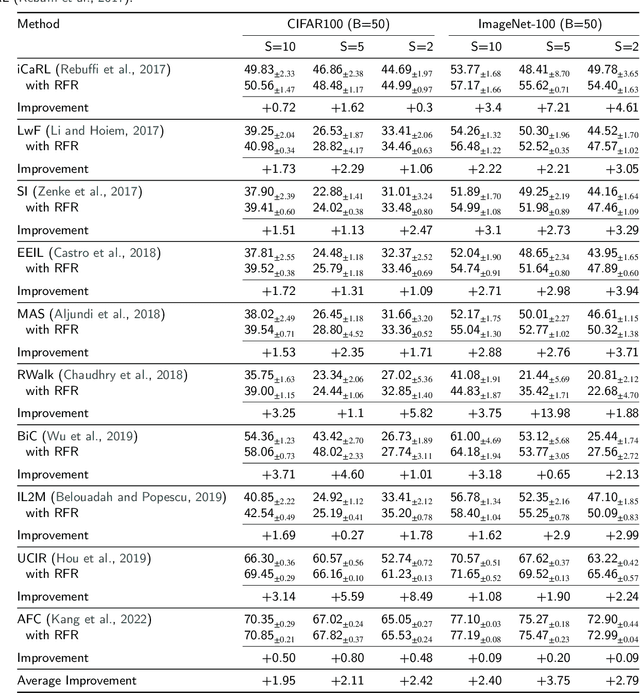
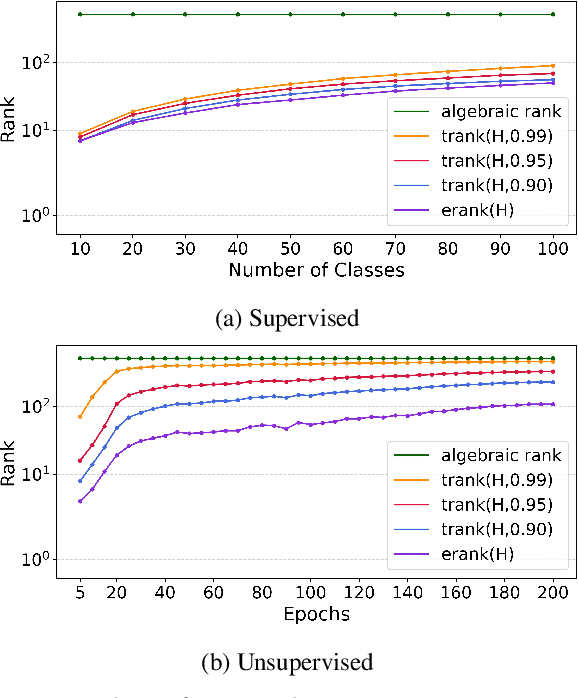
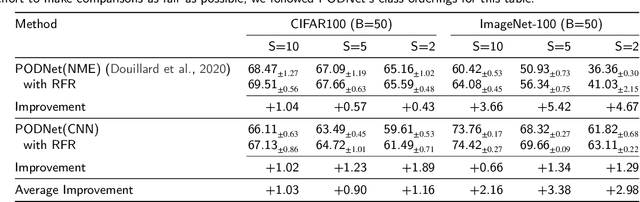
Abstract:Class Incremental Learning (CIL) constitutes a pivotal subfield within continual learning, aimed at enabling models to progressively learn new classification tasks while retaining knowledge obtained from prior tasks. Although previous studies have predominantly focused on backward compatible approaches to mitigate catastrophic forgetting, recent investigations have introduced forward compatible methods to enhance performance on novel tasks and complement existing backward compatible methods. In this study, we introduce an effective-Rank based Feature Richness enhancement (RFR) method, designed for improving forward compatibility. Specifically, this method increases the effective rank of representations during the base session, thereby facilitating the incorporation of more informative features pertinent to unseen novel tasks. Consequently, RFR achieves dual objectives in backward and forward compatibility: minimizing feature extractor modifications and enhancing novel task performance, respectively. To validate the efficacy of our approach, we establish a theoretical connection between effective rank and the Shannon entropy of representations. Subsequently, we conduct comprehensive experiments by integrating RFR into eleven well-known CIL methods. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing novel-task performance while mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Furthermore, our method notably improves the average incremental accuracy across all eleven cases examined.
Enhancing Contrastive Learning with Efficient Combinatorial Positive Pairing
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:In the past few years, contrastive learning has played a central role for the success of visual unsupervised representation learning. Around the same time, high-performance non-contrastive learning methods have been developed as well. While most of the works utilize only two views, we carefully review the existing multi-view methods and propose a general multi-view strategy that can improve learning speed and performance of any contrastive or non-contrastive method. We first analyze CMC's full-graph paradigm and empirically show that the learning speed of $K$-views can be increased by $_{K}\mathrm{C}_{2}$ times for small learning rate and early training. Then, we upgrade CMC's full-graph by mixing views created by a crop-only augmentation, adopting small-size views as in SwAV multi-crop, and modifying the negative sampling. The resulting multi-view strategy is called ECPP (Efficient Combinatorial Positive Pairing). We investigate the effectiveness of ECPP by applying it to SimCLR and assessing the linear evaluation performance for CIFAR-10 and ImageNet-100. For each benchmark, we achieve a state-of-the-art performance. In case of ImageNet-100, ECPP boosted SimCLR outperforms supervised learning.
Towards a Rigorous Analysis of Mutual Information in Contrastive Learning
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:Contrastive learning has emerged as a cornerstone in recent achievements of unsupervised representation learning. Its primary paradigm involves an instance discrimination task with a mutual information loss. The loss is known as InfoNCE and it has yielded vital insights into contrastive learning through the lens of mutual information analysis. However, the estimation of mutual information can prove challenging, creating a gap between the elegance of its mathematical foundation and the complexity of its estimation. As a result, drawing rigorous insights or conclusions from mutual information analysis becomes intricate. In this study, we introduce three novel methods and a few related theorems, aimed at enhancing the rigor of mutual information analysis. Despite their simplicity, these methods can carry substantial utility. Leveraging these approaches, we reassess three instances of contrastive learning analysis, illustrating their capacity to facilitate deeper comprehension or to rectify pre-existing misconceptions. Specifically, we investigate small batch size, mutual information as a measure, and the InfoMin principle.
VNE: An Effective Method for Improving Deep Representation by Manipulating Eigenvalue Distribution
Apr 04, 2023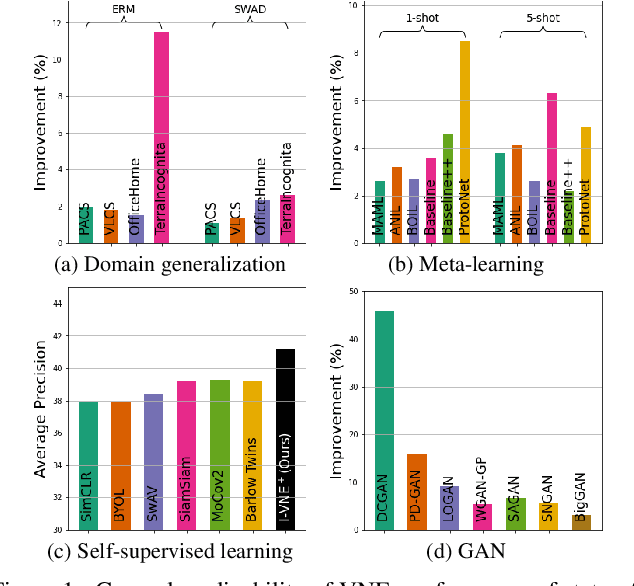
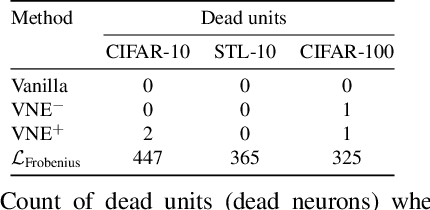
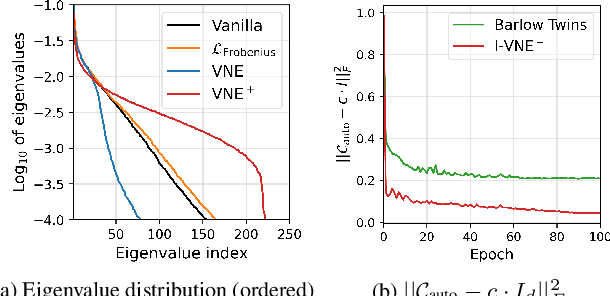
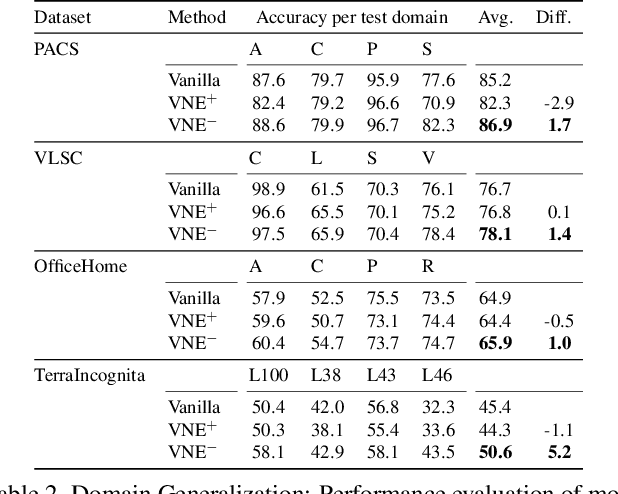
Abstract:Since the introduction of deep learning, a wide scope of representation properties, such as decorrelation, whitening, disentanglement, rank, isotropy, and mutual information, have been studied to improve the quality of representation. However, manipulating such properties can be challenging in terms of implementational effectiveness and general applicability. To address these limitations, we propose to regularize von Neumann entropy~(VNE) of representation. First, we demonstrate that the mathematical formulation of VNE is superior in effectively manipulating the eigenvalues of the representation autocorrelation matrix. Then, we demonstrate that it is widely applicable in improving state-of-the-art algorithms or popular benchmark algorithms by investigating domain-generalization, meta-learning, self-supervised learning, and generative models. In addition, we formally establish theoretical connections with rank, disentanglement, and isotropy of representation. Finally, we provide discussions on the dimension control of VNE and the relationship with Shannon entropy. Code is available at: https://github.com/jaeill/CVPR23-VNE.
DR.CPO: Diversified and Realistic 3D Augmentation via Iterative Construction, Random Placement, and HPR Occlusion
Mar 20, 2023



Abstract:In autonomous driving, data augmentation is commonly used for improving 3D object detection. The most basic methods include insertion of copied objects and rotation and scaling of the entire training frame. Numerous variants have been developed as well. The existing methods, however, are considerably limited when compared to the variety of the real world possibilities. In this work, we develop a diversified and realistic augmentation method that can flexibly construct a whole-body object, freely locate and rotate the object, and apply self-occlusion and external-occlusion accordingly. To improve the diversity of the whole-body object construction, we develop an iterative method that stochastically combines multiple objects observed from the real world into a single object. Unlike the existing augmentation methods, the constructed objects can be randomly located and rotated in the training frame because proper occlusions can be reflected to the whole-body objects in the final step. Finally, proper self-occlusion at each local object level and external-occlusion at the global frame level are applied using the Hidden Point Removal (HPR) algorithm that is computationally efficient. HPR is also used for adaptively controlling the point density of each object according to the object's distance from the LiDAR. Experiment results show that the proposed DR.CPO algorithm is data-efficient and model-agnostic without incurring any computational overhead. Also, DR.CPO can improve mAP performance by 2.08% when compared to the best 3D detection result known for KITTI dataset. The code is available at https://github.com/SNU-DRL/DRCPO.git
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge