Eunjung Lee
Enhancing Contrastive Learning with Efficient Combinatorial Positive Pairing
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:In the past few years, contrastive learning has played a central role for the success of visual unsupervised representation learning. Around the same time, high-performance non-contrastive learning methods have been developed as well. While most of the works utilize only two views, we carefully review the existing multi-view methods and propose a general multi-view strategy that can improve learning speed and performance of any contrastive or non-contrastive method. We first analyze CMC's full-graph paradigm and empirically show that the learning speed of $K$-views can be increased by $_{K}\mathrm{C}_{2}$ times for small learning rate and early training. Then, we upgrade CMC's full-graph by mixing views created by a crop-only augmentation, adopting small-size views as in SwAV multi-crop, and modifying the negative sampling. The resulting multi-view strategy is called ECPP (Efficient Combinatorial Positive Pairing). We investigate the effectiveness of ECPP by applying it to SimCLR and assessing the linear evaluation performance for CIFAR-10 and ImageNet-100. For each benchmark, we achieve a state-of-the-art performance. In case of ImageNet-100, ECPP boosted SimCLR outperforms supervised learning.
AID-Purifier: A Light Auxiliary Network for Boosting Adversarial Defense
Jul 14, 2021



Abstract:We propose an AID-purifier that can boost the robustness of adversarially-trained networks by purifying their inputs. AID-purifier is an auxiliary network that works as an add-on to an already trained main classifier. To keep it computationally light, it is trained as a discriminator with a binary cross-entropy loss. To obtain additionally useful information from the adversarial examples, the architecture design is closely related to information maximization principles where two layers of the main classification network are piped to the auxiliary network. To assist the iterative optimization procedure of purification, the auxiliary network is trained with AVmixup. AID-purifier can be used together with other purifiers such as PixelDefend for an extra enhancement. The overall results indicate that the best performing adversarially-trained networks can be enhanced by the best performing purification networks, where AID-purifier is a competitive candidate that is light and robust.
DEEP-BO for Hyperparameter Optimization of Deep Networks
May 23, 2019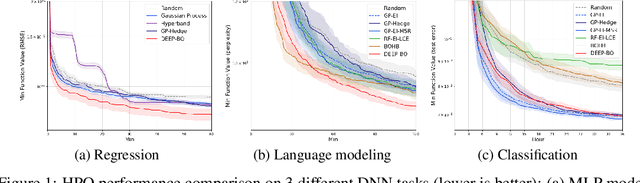
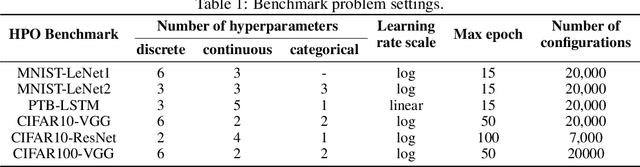
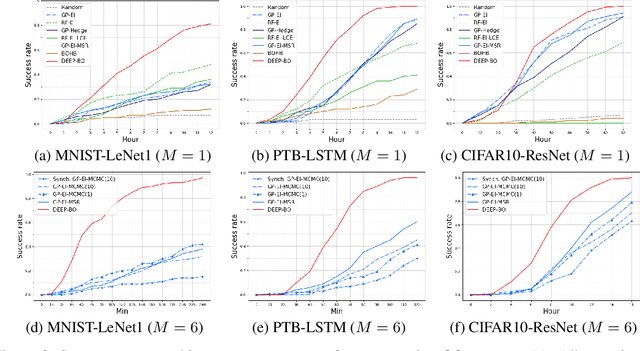
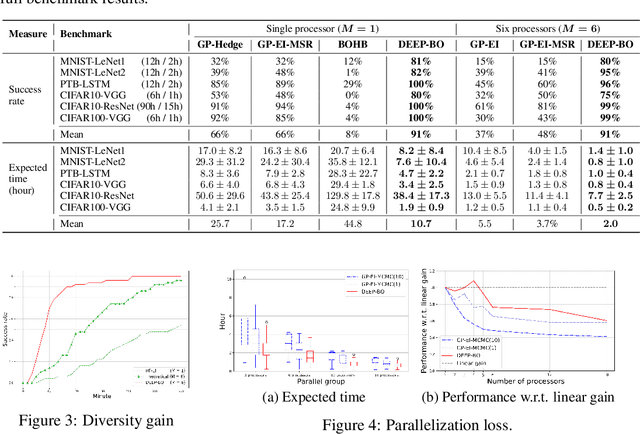
Abstract:The performance of deep neural networks (DNN) is very sensitive to the particular choice of hyper-parameters. To make it worse, the shape of the learning curve can be significantly affected when a technique like batchnorm is used. As a result, hyperparameter optimization of deep networks can be much more challenging than traditional machine learning models. In this work, we start from well known Bayesian Optimization solutions and provide enhancement strategies specifically designed for hyperparameter optimization of deep networks. The resulting algorithm is named as DEEP-BO (Diversified, Early-termination-Enabled, and Parallel Bayesian Optimization). When evaluated over six DNN benchmarks, DEEP-BO easily outperforms or shows comparable performance with some of the well-known solutions including GP-Hedge, Hyperband, BOHB, Median Stopping Rule, and Learning Curve Extrapolation. The code used is made publicly available at https://github.com/snu-adsl/DEEP-BO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge