Jungmin Ko
Cross-Attention Head Position Patterns Can Align with Human Visual Concepts in Text-to-Image Generative Models
Dec 03, 2024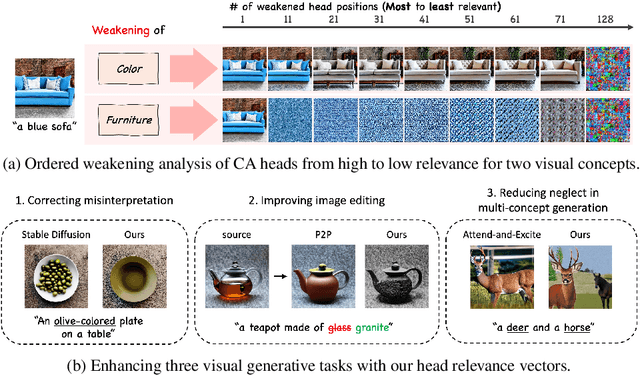
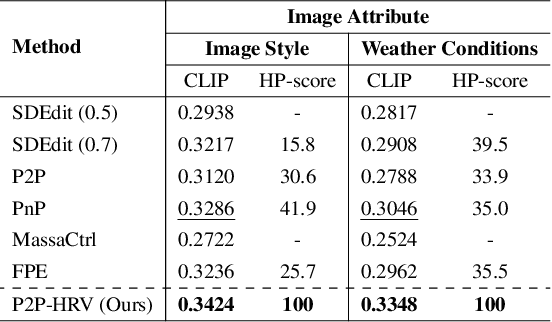
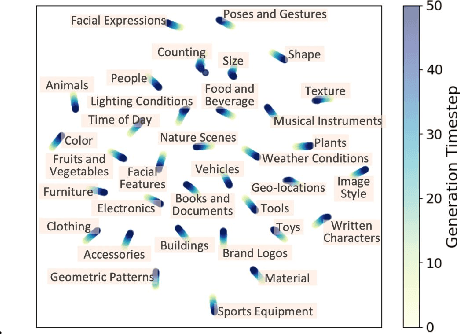

Abstract:Recent text-to-image diffusion models leverage cross-attention layers, which have been effectively utilized to enhance a range of visual generative tasks. However, our understanding of cross-attention layers remains somewhat limited. In this study, we present a method for constructing Head Relevance Vectors (HRVs) that align with useful visual concepts. An HRV for a given visual concept is a vector with a length equal to the total number of cross-attention heads, where each element represents the importance of the corresponding head for the given visual concept. We develop and employ an ordered weakening analysis to demonstrate the effectiveness of HRVs as interpretable features. To demonstrate the utility of HRVs, we propose concept strengthening and concept adjusting methods and apply them to enhance three visual generative tasks. We show that misinterpretations of polysemous words in image generation can be corrected in most cases, five challenging attributes in image editing can be successfully modified, and catastrophic neglect in multi-concept generation can be mitigated. Overall, our work provides an advancement in understanding cross-attention layers and introduces new approaches for fine-controlling these layers at the head level.
Unveiling Key Aspects of Fine-Tuning in Sentence Embeddings: A Representation Rank Analysis
May 18, 2024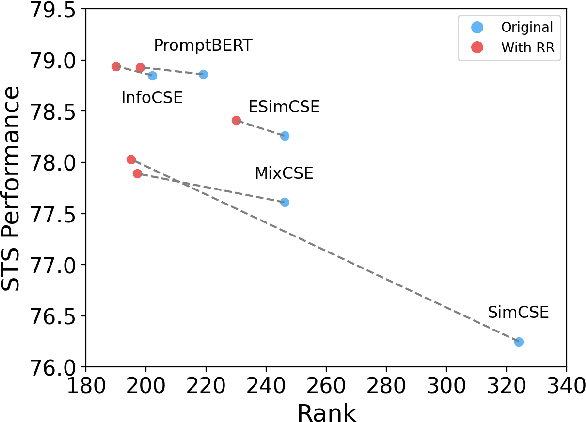
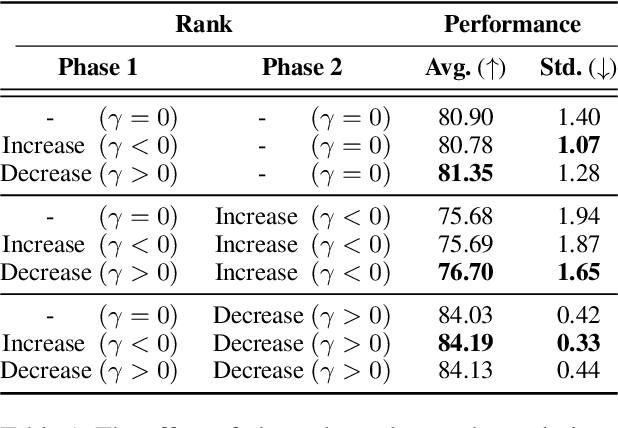
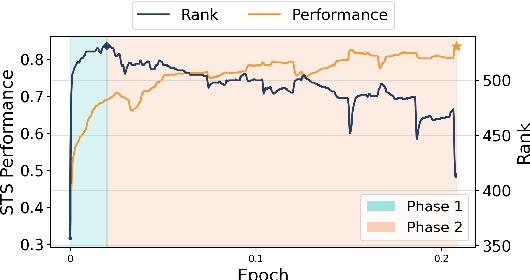

Abstract:The latest advancements in unsupervised learning of sentence embeddings predominantly involve employing contrastive learning-based (CL-based) fine-tuning over pre-trained language models. In this study, we analyze the latest sentence embedding methods by adopting representation rank as the primary tool of analysis. We first define Phase 1 and Phase 2 of fine-tuning based on when representation rank peaks. Utilizing these phases, we conduct a thorough analysis and obtain essential findings across key aspects, including alignment and uniformity, linguistic abilities, and correlation between performance and rank. For instance, we find that the dynamics of the key aspects can undergo significant changes as fine-tuning transitions from Phase 1 to Phase 2. Based on these findings, we experiment with a rank reduction (RR) strategy that facilitates rapid and stable fine-tuning of the latest CL-based methods. Through empirical investigations, we showcase the efficacy of RR in enhancing the performance and stability of five state-of-the-art sentence embedding methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge