Jón Atli Benediktsson
Evolving Restricted Boltzmann Machine-Kohonen Network for Online Clustering
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:A novel online clustering algorithm is presented where an Evolving Restricted Boltzmann Machine (ERBM) is embedded with a Kohonen Network called ERBM-KNet. The proposed ERBM-KNet efficiently handles streaming data in a single-pass mode using the ERBM, employing a bias-variance strategy for neuron growing and pruning, as well as online clustering based on a cluster update strategy for cluster prediction and cluster center update using KNet. Initially, ERBM evolves its architecture while processing unlabeled image data, effectively disentangling the data distribution in the latent space. Subsequently, the KNet utilizes the feature extracted from ERBM to predict the number of clusters and updates the cluster centers. By overcoming the common challenges associated with clustering algorithms, such as prior initialization of the number of clusters and subpar clustering accuracy, the proposed ERBM-KNet offers significant improvements. Extensive experimental evaluations on four benchmarks and one industry dataset demonstrate the superiority of ERBM-KNet compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
DRBM-ClustNet: A Deep Restricted Boltzmann-Kohonen Architecture for Data Clustering
May 13, 2022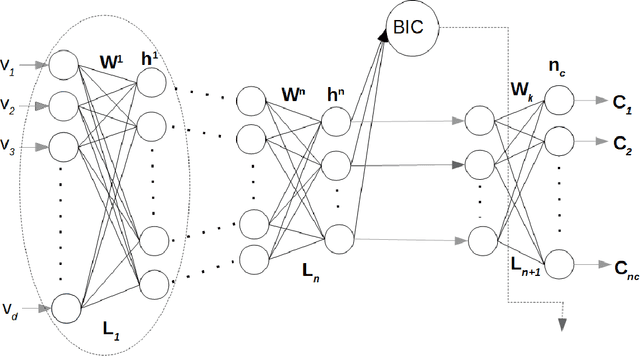
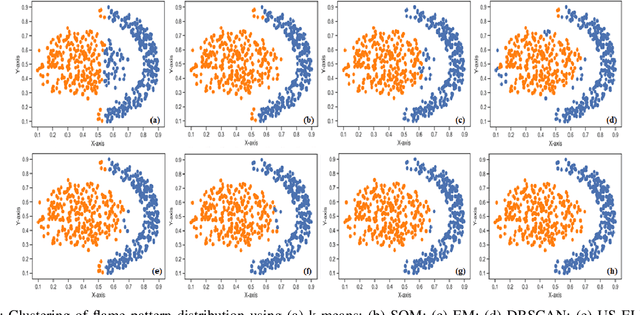
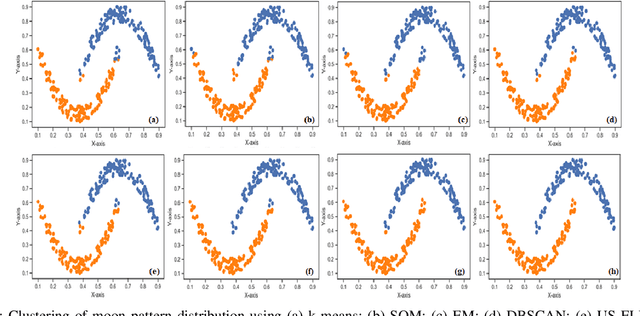
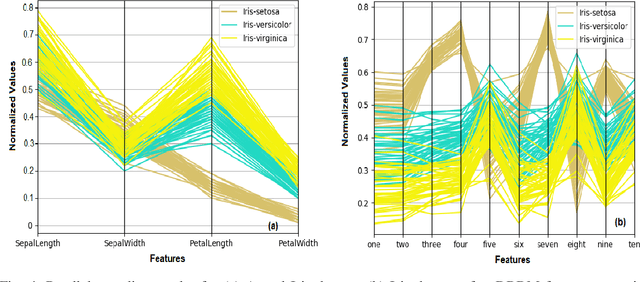
Abstract:A Bayesian Deep Restricted Boltzmann-Kohonen architecture for data clustering termed as DRBM-ClustNet is proposed. This core-clustering engine consists of a Deep Restricted Boltzmann Machine (DRBM) for processing unlabeled data by creating new features that are uncorrelated and have large variance with each other. Next, the number of clusters are predicted using the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), followed by a Kohonen Network-based clustering layer. The processing of unlabeled data is done in three stages for efficient clustering of the non-linearly separable datasets. In the first stage, DRBM performs non-linear feature extraction by capturing the highly complex data representation by projecting the feature vectors of $d$ dimensions into $n$ dimensions. Most clustering algorithms require the number of clusters to be decided a priori, hence here to automate the number of clusters in the second stage we use BIC. In the third stage, the number of clusters derived from BIC forms the input for the Kohonen network, which performs clustering of the feature-extracted data obtained from the DRBM. This method overcomes the general disadvantages of clustering algorithms like the prior specification of the number of clusters, convergence to local optima and poor clustering accuracy on non-linear datasets. In this research we use two synthetic datasets, fifteen benchmark datasets from the UCI Machine Learning repository, and four image datasets to analyze the DRBM-ClustNet. The proposed framework is evaluated based on clustering accuracy and ranked against other state-of-the-art clustering methods. The obtained results demonstrate that the DRBM-ClustNet outperforms state-of-the-art clustering algorithms.
Asymmetric Hash Code Learning for Remote Sensing Image Retrieval
Jan 15, 2022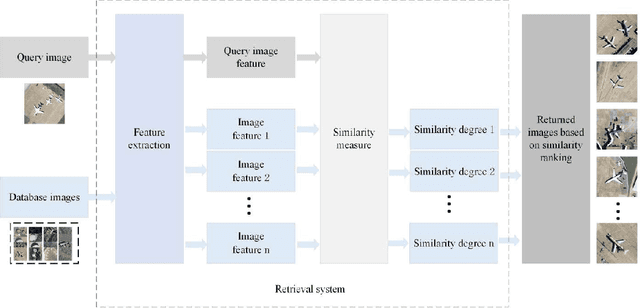
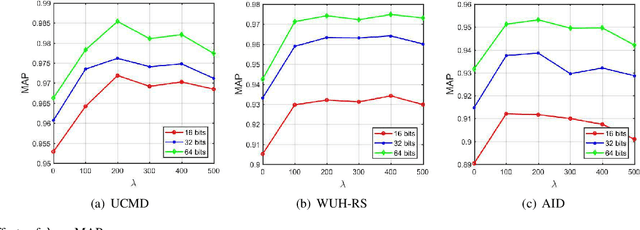
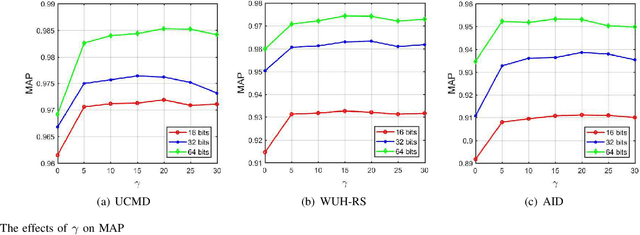
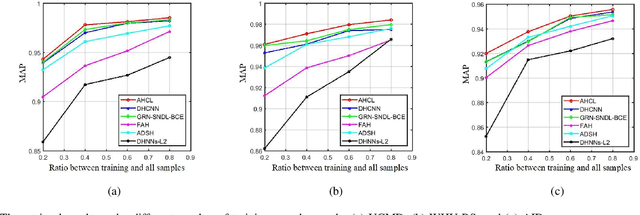
Abstract:Remote sensing image retrieval (RSIR), aiming at searching for a set of similar items to a given query image, is a very important task in remote sensing applications. Deep hashing learning as the current mainstream method has achieved satisfactory retrieval performance. On one hand, various deep neural networks are used to extract semantic features of remote sensing images. On the other hand, the hashing techniques are subsequently adopted to map the high-dimensional deep features to the low-dimensional binary codes. This kind of methods attempts to learn one hash function for both the query and database samples in a symmetric way. However, with the number of database samples increasing, it is typically time-consuming to generate the hash codes of large-scale database images. In this paper, we propose a novel deep hashing method, named asymmetric hash code learning (AHCL), for RSIR. The proposed AHCL generates the hash codes of query and database images in an asymmetric way. In more detail, the hash codes of query images are obtained by binarizing the output of the network, while the hash codes of database images are directly learned by solving the designed objective function. In addition, we combine the semantic information of each image and the similarity information of pairs of images as supervised information to train a deep hashing network, which improves the representation ability of deep features and hash codes. The experimental results on three public datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms symmetric methods in terms of retrieval accuracy and efficiency. The source code is available at https://github.com/weiweisong415/Demo AHCL for TGRS2022.
Deep Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification: An Overview
Oct 26, 2019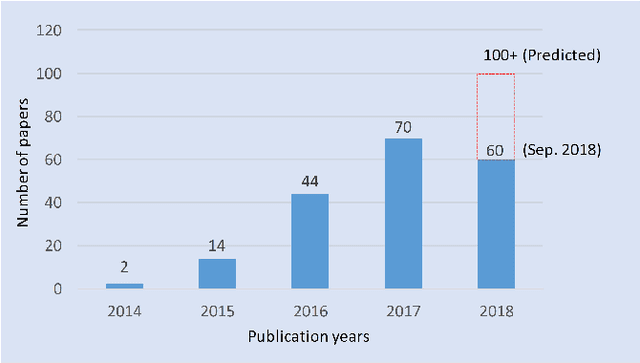
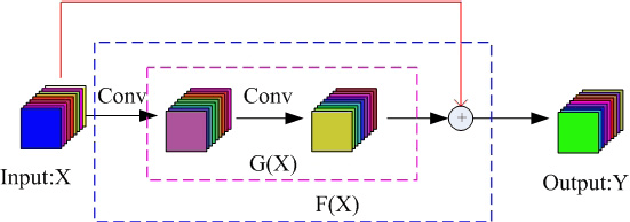
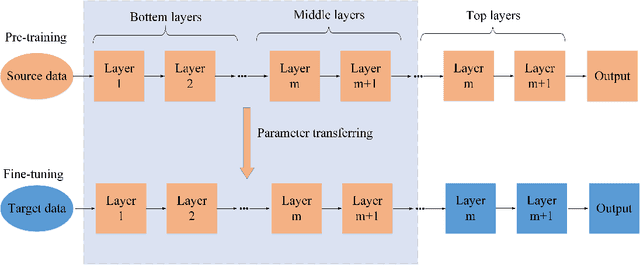
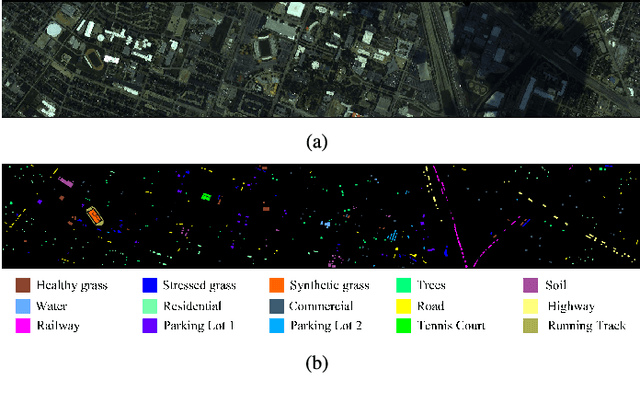
Abstract:Hyperspectral image (HSI) classification has become a hot topic in the field of remote sensing. In general, the complex characteristics of hyperspectral data make the accurate classification of such data challenging for traditional machine learning methods. In addition, hyperspectral imaging often deals with an inherently nonlinear relation between the captured spectral information and the corresponding materials. In recent years, deep learning has been recognized as a powerful feature-extraction tool to effectively address nonlinear problems and widely used in a number of image processing tasks. Motivated by those successful applications, deep learning has also been introduced to classify HSIs and demonstrated good performance. This survey paper presents a systematic review of deep learning-based HSI classification literatures and compares several strategies for this topic. Specifically, we first summarize the main challenges of HSI classification which cannot be effectively overcome by traditional machine learning methods, and also introduce the advantages of deep learning to handle these problems. Then, we build a framework which divides the corresponding works into spectral-feature networks, spatial-feature networks, and spectral-spatial-feature networks to systematically review the recent achievements in deep learning-based HSI classification. In addition, considering the fact that available training samples in the remote sensing field are usually very limited and training deep networks require a large number of samples, we include some strategies to improve classification performance, which can provide some guidelines for future studies on this topic. Finally, several representative deep learning-based classification methods are conducted on real HSIs in our experiments.
Advances in Hyperspectral Image Classification: Earth monitoring with statistical learning methods
Oct 18, 2013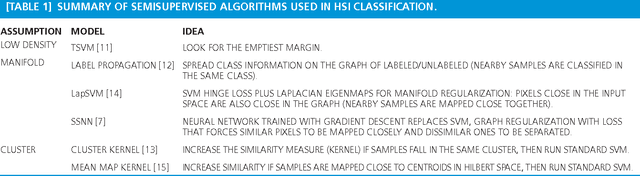
Abstract:Hyperspectral images show similar statistical properties to natural grayscale or color photographic images. However, the classification of hyperspectral images is more challenging because of the very high dimensionality of the pixels and the small number of labeled examples typically available for learning. These peculiarities lead to particular signal processing problems, mainly characterized by indetermination and complex manifolds. The framework of statistical learning has gained popularity in the last decade. New methods have been presented to account for the spatial homogeneity of images, to include user's interaction via active learning, to take advantage of the manifold structure with semisupervised learning, to extract and encode invariances, or to adapt classifiers and image representations to unseen yet similar scenes. This tutuorial reviews the main advances for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification through illustrative examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge