Ishmam Zabir
Phi-4-Mini Technical Report: Compact yet Powerful Multimodal Language Models via Mixture-of-LoRAs
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Phi-4-Mini and Phi-4-Multimodal, compact yet highly capable language and multimodal models. Phi-4-Mini is a 3.8-billion-parameter language model trained on high-quality web and synthetic data, significantly outperforming recent open-source models of similar size and matching the performance of models twice its size on math and coding tasks requiring complex reasoning. This achievement is driven by a carefully curated synthetic data recipe emphasizing high-quality math and coding datasets. Compared to its predecessor, Phi-3.5-Mini, Phi-4-Mini features an expanded vocabulary size of 200K tokens to better support multilingual applications, as well as group query attention for more efficient long-sequence generation. Phi-4-Multimodal is a multimodal model that integrates text, vision, and speech/audio input modalities into a single model. Its novel modality extension approach leverages LoRA adapters and modality-specific routers to allow multiple inference modes combining various modalities without interference. For example, it now ranks first in the OpenASR leaderboard to date, although the LoRA component of the speech/audio modality has just 460 million parameters. Phi-4-Multimodal supports scenarios involving (vision + language), (vision + speech), and (speech/audio) inputs, outperforming larger vision-language and speech-language models on a wide range of tasks. Additionally, we experiment to further train Phi-4-Mini to enhance its reasoning capabilities. Despite its compact 3.8-billion-parameter size, this experimental version achieves reasoning performance on par with or surpassing significantly larger models, including DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B.
POROver: Improving Safety and Reducing Overrefusal in Large Language Models with Overgeneration and Preference Optimization
Oct 16, 2024
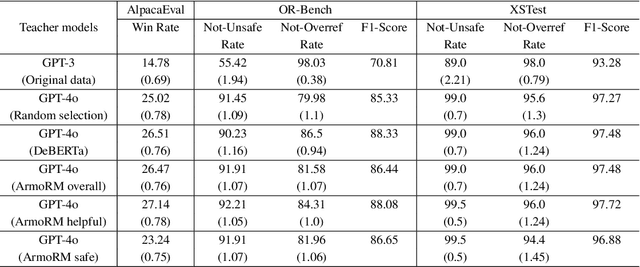
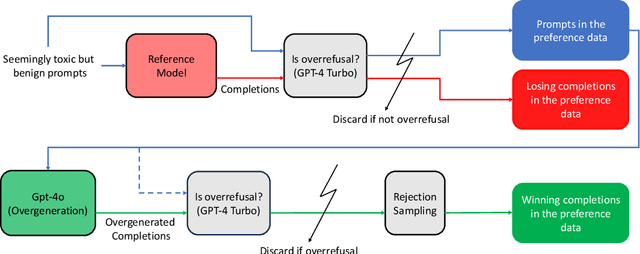

Abstract:Balancing safety and usefulness in large language models has become a critical challenge in recent years. Models often exhibit unsafe behavior or adopt an overly cautious approach, leading to frequent overrefusal of benign prompts, which reduces their usefulness. Addressing these issues requires methods that maintain safety while avoiding overrefusal. In this work, we examine how the overgeneration of training data using advanced teacher models (e.g., GPT-4o), including responses to both general-purpose and toxic prompts, influences the safety and overrefusal balance of instruction-following language models. Additionally, we present POROver, a strategy to use preference optimization methods in order to reduce overrefusal, via employing a superior teacher model's completions. Our results show that overgenerating completions for general-purpose prompts significantly improves the balance between safety and usefulness. Specifically, the F1 score calculated between safety and usefulness increases from 70.8% to 88.3%. Moreover, overgeneration for toxic prompts substantially reduces overrefusal, decreasing it from 94.4% to 45.2%. Furthermore, preference optimization algorithms, when applied with carefully curated preference data, can effectively reduce a model's overrefusal from 45.2% to 15.0% while maintaining comparable safety levels. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/batuhankmkaraman/POROver.
Balancing Interpretability and Predictive Accuracy for Unsupervised Tensor Mining
Sep 04, 2017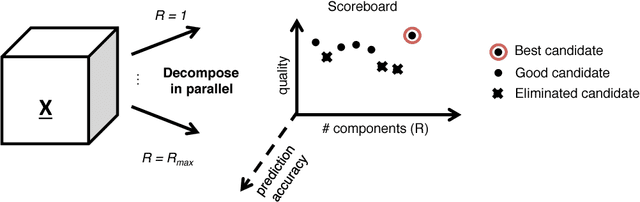
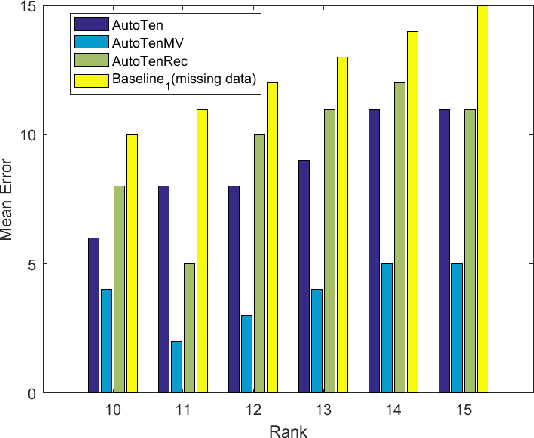
Abstract:The PARAFAC tensor decomposition has enjoyed an increasing success in exploratory multi-aspect data mining scenarios. A major challenge remains the estimation of the number of latent factors (i.e., the rank) of the decomposition, which yields high-quality, interpretable results. Previously, we have proposed an automated tensor mining method which leverages a well-known quality heuristic from the field of Chemometrics, the Core Consistency Diagnostic (CORCONDIA), in order to automatically determine the rank for the PARAFAC decomposition. In this work we set out to explore the trade-off between 1) the interpretability/quality of the results (as expressed by CORCONDIA), and 2) the predictive accuracy of the results, in order to further improve the rank estimation quality. Our preliminary results indicate that striking a good balance in that trade-off benefits rank estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge