Ieva Daukantas
Safe and Reliable Training of Learning-Based Aerospace Controllers
Jul 09, 2024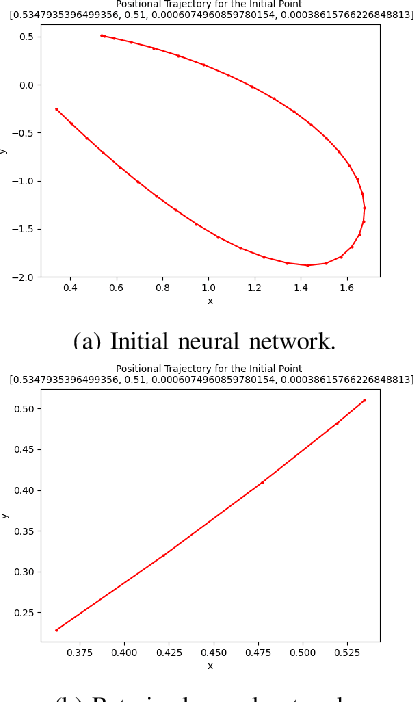


Abstract:In recent years, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approaches have generated highly successful controllers for a myriad of complex domains. However, the opaque nature of these models limits their applicability in aerospace systems and safety-critical domains, in which a single mistake can have dire consequences. In this paper, we present novel advancements in both the training and verification of DRL controllers, which can help ensure their safe behavior. We showcase a design-for-verification approach utilizing k-induction and demonstrate its use in verifying liveness properties. In addition, we also give a brief overview of neural Lyapunov Barrier certificates and summarize their capabilities on a case study. Finally, we describe several other novel reachability-based approaches which, despite failing to provide guarantees of interest, could be effective for verification of other DRL systems, and could be of further interest to the community.
Formally Verifying Deep Reinforcement Learning Controllers with Lyapunov Barrier Certificates
May 22, 2024
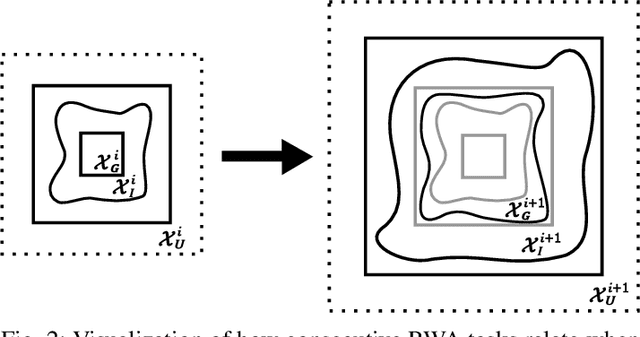
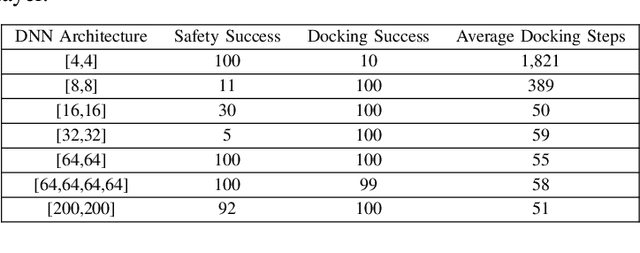
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is a powerful machine learning paradigm for generating agents that control autonomous systems. However, the "black box" nature of DRL agents limits their deployment in real-world safety-critical applications. A promising approach for providing strong guarantees on an agent's behavior is to use Neural Lyapunov Barrier (NLB) certificates, which are learned functions over the system whose properties indirectly imply that an agent behaves as desired. However, NLB-based certificates are typically difficult to learn and even more difficult to verify, especially for complex systems. In this work, we present a novel method for training and verifying NLB-based certificates for discrete-time systems. Specifically, we introduce a technique for certificate composition, which simplifies the verification of highly-complex systems by strategically designing a sequence of certificates. When jointly verified with neural network verification engines, these certificates provide a formal guarantee that a DRL agent both achieves its goals and avoids unsafe behavior. Furthermore, we introduce a technique for certificate filtering, which significantly simplifies the process of producing formally verified certificates. We demonstrate the merits of our approach with a case study on providing safety and liveness guarantees for a DRL-controlled spacecraft.
Towards Efficient Verification of Quantized Neural Networks
Dec 27, 2023



Abstract:Quantization replaces floating point arithmetic with integer arithmetic in deep neural network models, providing more efficient on-device inference with less power and memory. In this work, we propose a framework for formally verifying properties of quantized neural networks. Our baseline technique is based on integer linear programming which guarantees both soundness and completeness. We then show how efficiency can be improved by utilizing gradient-based heuristic search methods and also bound-propagation techniques. We evaluate our approach on perception networks quantized with PyTorch. Our results show that we can verify quantized networks with better scalability and efficiency than the previous state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge