Huiyu Cai
E3Bind: An End-to-End Equivariant Network for Protein-Ligand Docking
Oct 12, 2022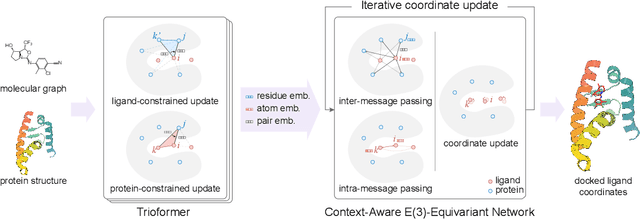
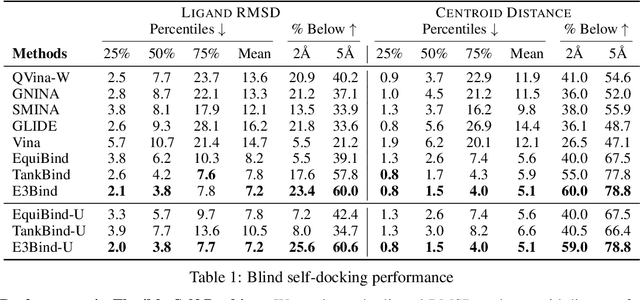
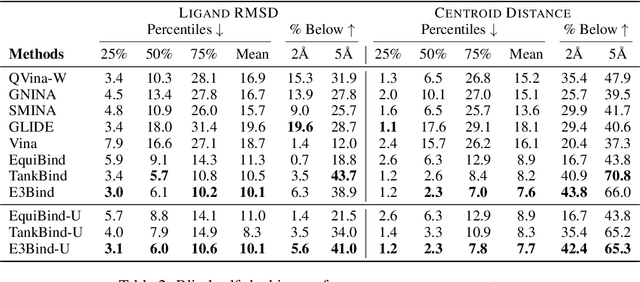
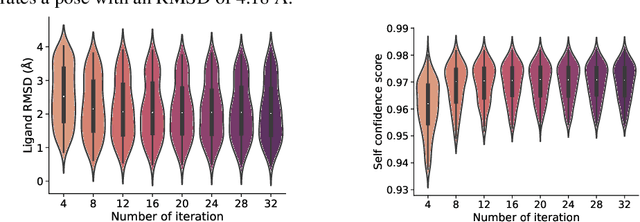
Abstract:In silico prediction of the ligand binding pose to a given protein target is a crucial but challenging task in drug discovery. This work focuses on blind flexible selfdocking, where we aim to predict the positions, orientations and conformations of docked molecules. Traditional physics-based methods usually suffer from inaccurate scoring functions and high inference cost. Recently, data-driven methods based on deep learning techniques are attracting growing interest thanks to their efficiency during inference and promising performance. These methods usually either adopt a two-stage approach by first predicting the distances between proteins and ligands and then generating the final coordinates based on the predicted distances, or directly predicting the global roto-translation of ligands. In this paper, we take a different route. Inspired by the resounding success of AlphaFold2 for protein structure prediction, we propose E3Bind, an end-to-end equivariant network that iteratively updates the ligand pose. E3Bind models the protein-ligand interaction through careful consideration of the geometric constraints in docking and the local context of the binding site. Experiments on standard benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our end-to-end trainable model compared to traditional and recently-proposed deep learning methods.
Neural Structured Prediction for Inductive Node Classification
Apr 15, 2022



Abstract:This paper studies node classification in the inductive setting, i.e., aiming to learn a model on labeled training graphs and generalize it to infer node labels on unlabeled test graphs. This problem has been extensively studied with graph neural networks (GNNs) by learning effective node representations, as well as traditional structured prediction methods for modeling the structured output of node labels, e.g., conditional random fields (CRFs). In this paper, we present a new approach called the Structured Proxy Network (SPN), which combines the advantages of both worlds. SPN defines flexible potential functions of CRFs with GNNs. However, learning such a model is nontrivial as it involves optimizing a maximin game with high-cost inference. Inspired by the underlying connection between joint and marginal distributions defined by Markov networks, we propose to solve an approximate version of the optimization problem as a proxy, which yields a near-optimal solution, making learning more efficient. Extensive experiments on two settings show that our approach outperforms many competitive baselines.
Structured Multi-task Learning for Molecular Property Prediction
Feb 22, 2022



Abstract:Multi-task learning for molecular property prediction is becoming increasingly important in drug discovery. However, in contrast to other domains, the performance of multi-task learning in drug discovery is still not satisfying as the number of labeled data for each task is too limited, which calls for additional data to complement the data scarcity. In this paper, we study multi-task learning for molecular property prediction in a novel setting, where a relation graph between tasks is available. We first construct a dataset including around 400 tasks as well as a task relation graph. Then to better utilize such relation graph, we propose a method called SGNN-EBM to systematically investigate the structured task modeling from two perspectives. (1) In the \emph{latent} space, we model the task representations by applying a state graph neural network (SGNN) on the relation graph. (2) In the \emph{output} space, we employ structured prediction with the energy-based model (EBM), which can be efficiently trained through noise-contrastive estimation (NCE) approach. Empirical results justify the effectiveness of SGNN-EBM. Code is available on https://github.com/chao1224/SGNN-EBM.
TorchDrug: A Powerful and Flexible Machine Learning Platform for Drug Discovery
Feb 16, 2022

Abstract:Machine learning has huge potential to revolutionize the field of drug discovery and is attracting increasing attention in recent years. However, lacking domain knowledge (e.g., which tasks to work on), standard benchmarks and data preprocessing pipelines are the main obstacles for machine learning researchers to work in this domain. To facilitate the progress of machine learning for drug discovery, we develop TorchDrug, a powerful and flexible machine learning platform for drug discovery built on top of PyTorch. TorchDrug benchmarks a variety of important tasks in drug discovery, including molecular property prediction, pretrained molecular representations, de novo molecular design and optimization, retrosynthsis prediction, and biomedical knowledge graph reasoning. State-of-the-art techniques based on geometric deep learning (or graph machine learning), deep generative models, reinforcement learning and knowledge graph reasoning are implemented for these tasks. TorchDrug features a hierarchical interface that facilitates customization from both novices and experts in this domain. Tutorials, benchmark results and documentation are available at https://torchdrug.ai. Code is released under Apache License 2.0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge