Huadeng Wang
Gland segmentation via dual encoders and boundary-enhanced attention
Jan 29, 2024



Abstract:Accurate and automated gland segmentation on pathological images can assist pathologists in diagnosing the malignancy of colorectal adenocarcinoma. However, due to various gland shapes, severe deformation of malignant glands, and overlapping adhesions between glands. Gland segmentation has always been very challenging. To address these problems, we propose a DEA model. This model consists of two branches: the backbone encoding and decoding network and the local semantic extraction network. The backbone encoding and decoding network extracts advanced Semantic features, uses the proposed feature decoder to restore feature space information, and then enhances the boundary features of the gland through boundary enhancement attention. The local semantic extraction network uses the pre-trained DeepLabv3+ as a Local semantic-guided encoder to realize the extraction of edge features. Experimental results on two public datasets, GlaS and CRAG, confirm that the performance of our method is better than other gland segmentation methods.
Rethinking Mitosis Detection: Towards Diverse Data and Feature Representation
Jul 12, 2023Abstract:Mitosis detection is one of the fundamental tasks in computational pathology, which is extremely challenging due to the heterogeneity of mitotic cell. Most of the current studies solve the heterogeneity in the technical aspect by increasing the model complexity. However, lacking consideration of the biological knowledge and the complex model design may lead to the overfitting problem while limited the generalizability of the detection model. In this paper, we systematically study the morphological appearances in different mitotic phases as well as the ambiguous non-mitotic cells and identify that balancing the data and feature diversity can achieve better generalizability. Based on this observation, we propose a novel generalizable framework (MitDet) for mitosis detection. The data diversity is considered by the proposed diversity-guided sample balancing (DGSB). And the feature diversity is preserved by inter- and intra- class feature diversity-preserved module (InCDP). Stain enhancement (SE) module is introduced to enhance the domain-relevant diversity of both data and features simultaneously. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that our proposed model outperforms all the SOTA approaches in several popular mitosis detection datasets in both internal and external test sets using minimal annotation efforts with point annotations only. Comprehensive ablation studies have also proven the effectiveness of the rethinking of data and feature diversity balancing. By analyzing the results quantitatively and qualitatively, we believe that our proposed model not only achieves SOTA performance but also might inspire the future studies in new perspectives. Source code is at https://github.com/Onehour0108/MitDet.
A novel dataset and a two-stage mitosis nuclei detection method based on hybrid anchor branch
Jan 18, 2023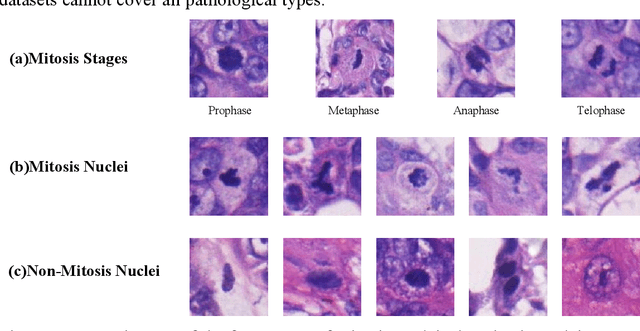

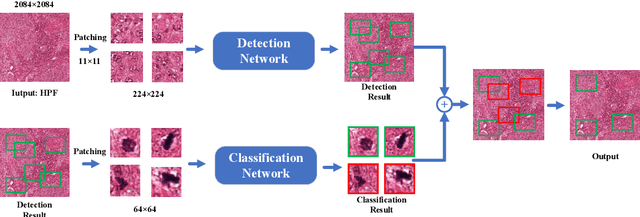
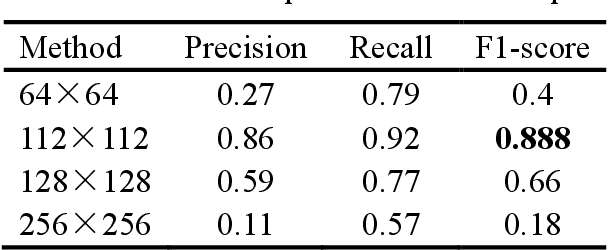
Abstract:Mitosis detection is one of the challenging problems in computational pathology, and mitotic count is an important index of cancer grading for pathologists. However, current counts of mitotic nuclei rely on pathologists looking microscopically at the number of mitotic nuclei in hot spots, which is subjective and time-consuming. In this paper, we propose a two-stage cascaded network, named FoCasNet, for mitosis detection. In the first stage, a detection network named M_det is proposed to detect as many mitoses as possible. In the second stage, a classification network M_class is proposed to refine the results of the first stage. In addition, the attention mechanism, normalization method, and hybrid anchor branch classification subnet are introduced to improve the overall detection performance. Our method achieves the current highest F1-score of 0.888 on the public dataset ICPR 2012. We also evaluated our method on the GZMH dataset released by our research team for the first time and reached the highest F1-score of 0.563, which is also better than multiple classic detection networks widely used at present. It confirmed the effectiveness and generalization of our method. The code will be available at: https://github.com/antifen/mitosis-nuclei-detection.
A Novel Dataset and a Deep Learning Method for Mitosis Nuclei Segmentation and Classification
Dec 27, 2022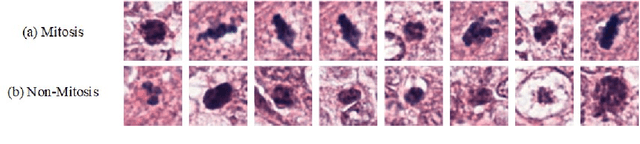
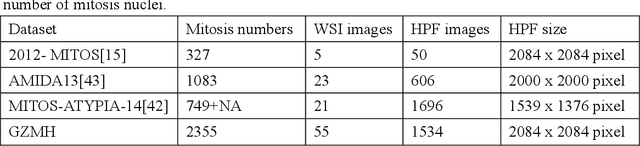
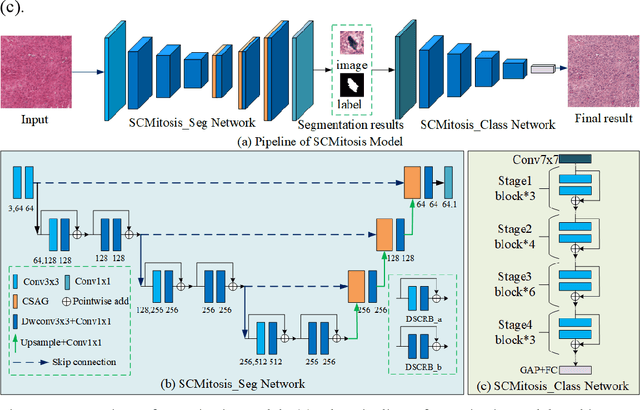
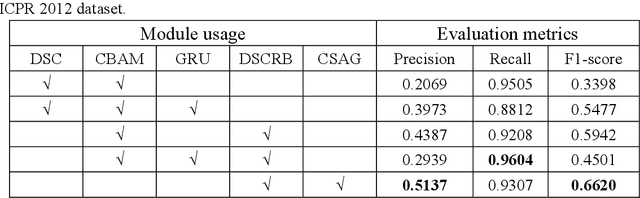
Abstract:Mitosis nuclei count is one of the important indicators for the pathological diagnosis of breast cancer. The manual annotation needs experienced pathologists, which is very time-consuming and inefficient. With the development of deep learning methods, some models with good performance have emerged, but the generalization ability should be further strengthened. In this paper, we propose a two-stage mitosis segmentation and classification method, named SCMitosis. Firstly, the segmentation performance with a high recall rate is achieved by the proposed depthwise separable convolution residual block and channel-spatial attention gate. Then, a classification network is cascaded to further improve the detection performance of mitosis nuclei. The proposed model is verified on the ICPR 2012 dataset, and the highest F-score value of 0.8687 is obtained compared with the current state-of-the-art algorithms. In addition, the model also achieves good performance on GZMH dataset, which is prepared by our group and will be firstly released with the publication of this paper. The code will be available at: https://github.com/antifen/mitosis-nuclei-segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge