Hsien-Te Kao
SOTOPIA-S4: a user-friendly system for flexible, customizable, and large-scale social simulation
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Social simulation through large language model (LLM) agents is a promising approach to explore and validate hypotheses related to social science questions and LLM agents behavior. We present SOTOPIA-S4, a fast, flexible, and scalable social simulation system that addresses the technical barriers of current frameworks while enabling practitioners to generate multi-turn and multi-party LLM-based interactions with customizable evaluation metrics for hypothesis testing. SOTOPIA-S4 comes as a pip package that contains a simulation engine, an API server with flexible RESTful APIs for simulation management, and a web interface that enables both technical and non-technical users to design, run, and analyze simulations without programming. We demonstrate the usefulness of SOTOPIA-S4 with two use cases involving dyadic hiring negotiation and multi-party planning scenarios.
Exploratory Models of Human-AI Teams: Leveraging Human Digital Twins to Investigate Trust Development
Nov 01, 2024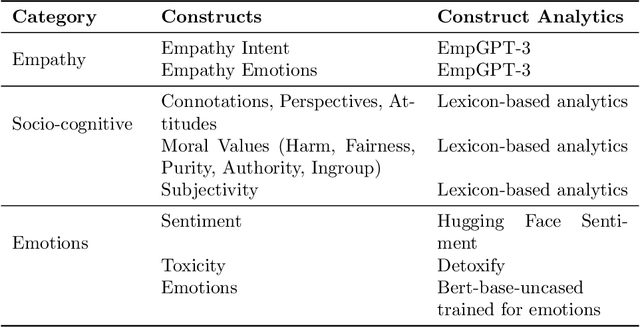
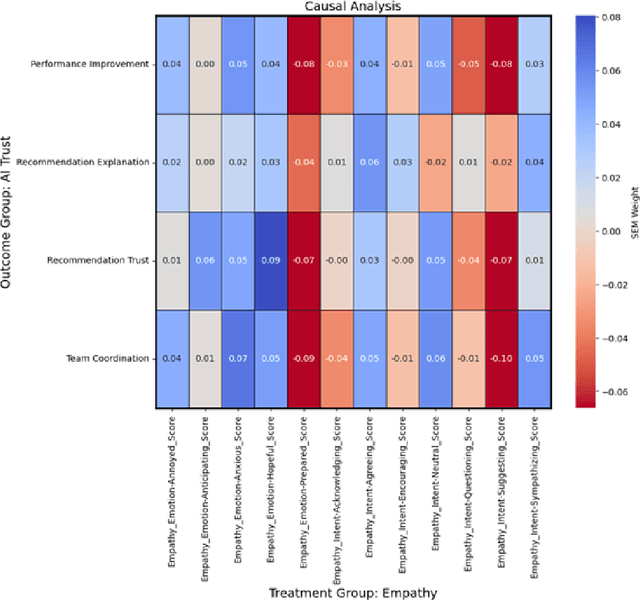
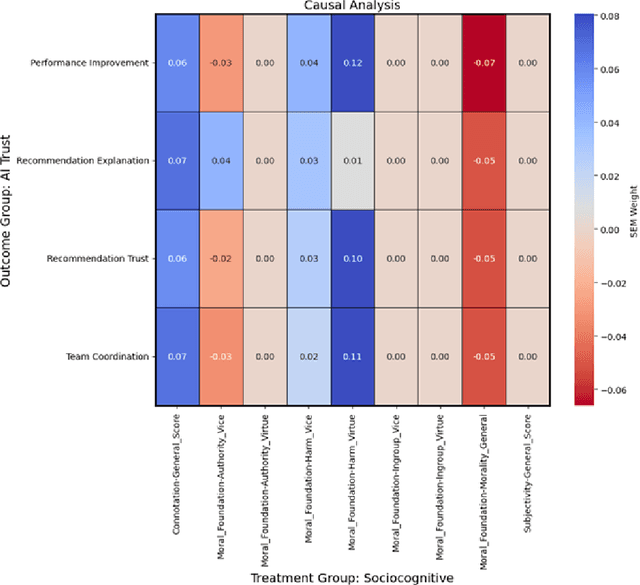
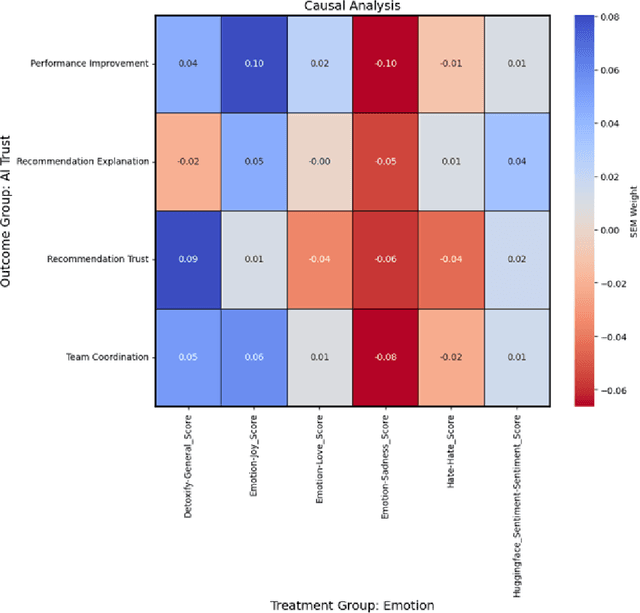
Abstract:As human-agent teaming (HAT) research continues to grow, computational methods for modeling HAT behaviors and measuring HAT effectiveness also continue to develop. One rising method involves the use of human digital twins (HDT) to approximate human behaviors and socio-emotional-cognitive reactions to AI-driven agent team members. In this paper, we address three research questions relating to the use of digital twins for modeling trust in HATs. First, to address the question of how we can appropriately model and operationalize HAT trust through HDT HAT experiments, we conducted causal analytics of team communication data to understand the impact of empathy, socio-cognitive, and emotional constructs on trust formation. Additionally, we reflect on the current state of the HAT trust science to discuss characteristics of HAT trust that must be replicable by a HDT such as individual differences in trust tendencies, emergent trust patterns, and appropriate measurement of these characteristics over time. Second, to address the question of how valid measures of HDT trust are for approximating human trust in HATs, we discuss the properties of HDT trust: self-report measures, interaction-based measures, and compliance type behavioral measures. Additionally, we share results of preliminary simulations comparing different LLM models for generating HDT communications and analyze their ability to replicate human-like trust dynamics. Third, to address how HAT experimental manipulations will extend to human digital twin studies, we share experimental design focusing on propensity to trust for HDTs vs. transparency and competency-based trust for AI agents.
Towards Safer Online Spaces: Simulating and Assessing Intervention Strategies for Eating Disorder Discussions
Sep 06, 2024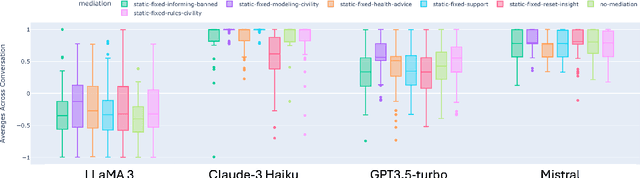
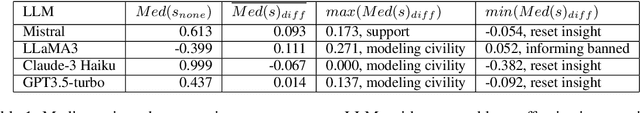
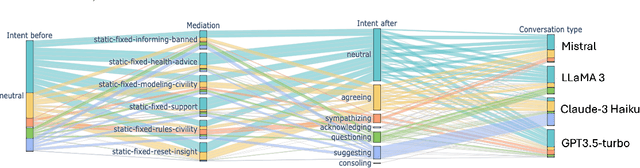
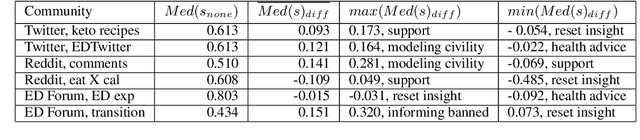
Abstract:Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that affect millions of people around the world. Effective interventions on social media platforms are crucial, yet testing strategies in situ can be risky. We present a novel LLM-driven experimental testbed for simulating and assessing intervention strategies in ED-related discussions. Our framework generates synthetic conversations across multiple platforms, models, and ED-related topics, allowing for controlled experimentation with diverse intervention approaches. We analyze the impact of various intervention strategies on conversation dynamics across four dimensions: intervention type, generative model, social media platform, and ED-related community/topic. We employ cognitive domain analysis metrics, including sentiment, emotions, etc., to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. Our findings reveal that civility-focused interventions consistently improve positive sentiment and emotional tone across all dimensions, while insight-resetting approaches tend to increase negative emotions. We also uncover significant biases in LLM-generated conversations, with cognitive metrics varying notably between models (Claude-3 Haiku $>$ Mistral $>$ GPT-3.5-turbo $>$ LLaMA3) and even between versions of the same model. These variations highlight the importance of model selection in simulating realistic discussions related to ED. Our work provides valuable information on the complex dynamics of ED-related discussions and the effectiveness of various intervention strategies.
Discovering Hidden Structure in High Dimensional Human Behavioral Data via Tensor Factorization
May 21, 2019
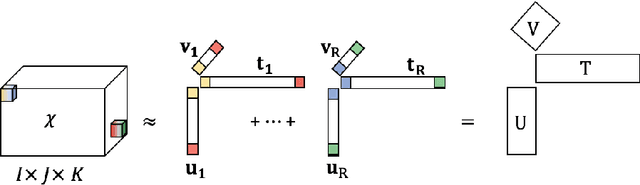
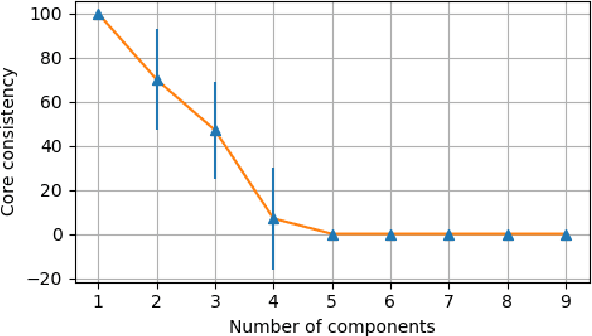
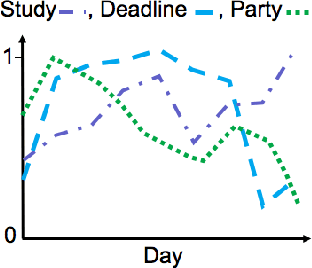
Abstract:In recent years, the rapid growth in technology has increased the opportunity for longitudinal human behavioral studies. Rich multimodal data, from wearables like Fitbit, online social networks, mobile phones etc. can be collected in natural environments. Uncovering the underlying low-dimensional structure of noisy multi-way data in an unsupervised setting is a challenging problem. Tensor factorization has been successful in extracting the interconnected low-dimensional descriptions of multi-way data. In this paper, we apply non-negative tensor factorization on a real-word wearable sensor data, StudentLife, to find latent temporal factors and group of similar individuals. Meta data is available for the semester schedule, as well as the individuals' performance and personality. We demonstrate that non-negative tensor factorization can successfully discover clusters of individuals who exhibit higher academic performance, as well as those who frequently engage in leisure activities. The recovered latent temporal patterns associated with these groups are validated against ground truth data to demonstrate the accuracy of our framework.
* 2018 WSDM Heteronam Workshop
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge