Hongyang Lin
IMUSIC: IMU-based Facial Expression Capture
Feb 03, 2024



Abstract:For facial motion capture and analysis, the dominated solutions are generally based on visual cues, which cannot protect privacy and are vulnerable to occlusions. Inertial measurement units (IMUs) serve as potential rescues yet are mainly adopted for full-body motion capture. In this paper, we propose IMUSIC to fill the gap, a novel path for facial expression capture using purely IMU signals, significantly distant from previous visual solutions.The key design in our IMUSIC is a trilogy. We first design micro-IMUs to suit facial capture, companion with an anatomy-driven IMU placement scheme. Then, we contribute a novel IMU-ARKit dataset, which provides rich paired IMU/visual signals for diverse facial expressions and performances. Such unique multi-modality brings huge potential for future directions like IMU-based facial behavior analysis. Moreover, utilizing IMU-ARKit, we introduce a strong baseline approach to accurately predict facial blendshape parameters from purely IMU signals. Specifically, we tailor a Transformer diffusion model with a two-stage training strategy for this novel tracking task. The IMUSIC framework empowers us to perform accurate facial capture in scenarios where visual methods falter and simultaneously safeguard user privacy. We conduct extensive experiments about both the IMU configuration and technical components to validate the effectiveness of our IMUSIC approach. Notably, IMUSIC enables various potential and novel applications, i.e., privacy-protecting facial capture, hybrid capture against occlusions, or detecting minute facial movements that are often invisible through visual cues. We will release our dataset and implementations to enrich more possibilities of facial capture and analysis in our community.
Video-driven Neural Physically-based Facial Asset for Production
Feb 18, 2022
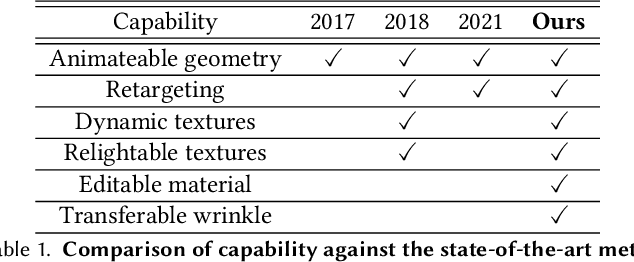
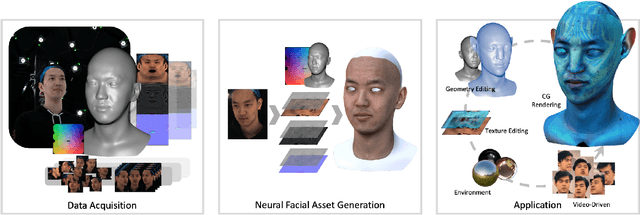
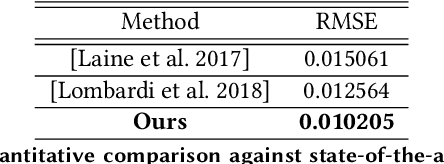
Abstract:Production-level workflows for producing convincing 3D dynamic human faces have long relied on a disarray of labor-intensive tools for geometry and texture generation, motion capture and rigging, and expression synthesis. Recent neural approaches automate individual components but the corresponding latent representations cannot provide artists explicit controls as in conventional tools. In this paper, we present a new learning-based, video-driven approach for generating dynamic facial geometries with high-quality physically-based assets. Two key components are well-structured latent spaces due to dense temporal samplings from videos and explicit facial expression controls to regulate the latent spaces. For data collection, we construct a hybrid multiview-photometric capture stage, coupling with an ultra-fast video camera to obtain raw 3D facial assets. We then model the facial expression, geometry and physically-based textures using separate VAEs with a global MLP-based expression mapping across the latent spaces, to preserve characteristics across respective attributes while maintaining explicit controls over geometry and texture. We also introduce to model the delta information as wrinkle maps for physically-base textures, achieving high-quality rendering of dynamic textures. We demonstrate our approach in high-fidelity performer-specific facial capture and cross-identity facial motion retargeting. In addition, our neural asset along with fast adaptation schemes can also be deployed to handle in-the-wild videos. Besides, we motivate the utility of our explicit facial disentangle strategy by providing promising physically-based editing results like geometry and material editing or winkle transfer with high realism. Comprehensive experiments show that our technique provides higher accuracy and visual fidelity than previous video-driven facial reconstruction and animation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge