Hongbo Bo
Failing on Bias Mitigation: Investigating Why Predictive Models Struggle with Government Data
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:The potential for bias and unfairness in AI-supporting government services raises ethical and legal concerns. Using crime rate prediction with the Bristol City Council data as a case study, we examine how these issues persist. Rather than auditing real-world deployed systems, our goal is to understand why widely adopted bias mitigation techniques often fail when applied to government data. Our findings reveal that bias mitigation approaches applied to government data are not always effective -- not because of flaws in model architecture or metric selection, but due to the inherent properties of the data itself. Through comparing a set of comprehensive models and fairness methods, our experiments consistently show that the mitigation efforts cannot overcome the embedded unfairness in the data -- further reinforcing that the origin of bias lies in the structure and history of government datasets. We then explore the reasons for the mitigation failures in predictive models on government data and highlight the potential sources of unfairness posed by data distribution shifts, the accumulation of historical bias, and delays in data release. We also discover the limitations of the blind spots in fairness analysis and bias mitigation methods when only targeting a single sensitive feature through a set of intersectional fairness experiments. Although this study is limited to one city, the findings are highly suggestive, which can contribute to an early warning that biases in government data may persist even with standard mitigation methods.
Mitigating Degree Bias Adaptively with Hard-to-Learn Nodes in Graph Contrastive Learning
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) often suffer from degree bias in node classification tasks, where prediction performance varies across nodes with different degrees. Several approaches, which adopt Graph Contrastive Learning (GCL), have been proposed to mitigate this bias. However, the limited number of positive pairs and the equal weighting of all positives and negatives in GCL still lead to low-degree nodes acquiring insufficient and noisy information. This paper proposes the Hardness Adaptive Reweighted (HAR) contrastive loss to mitigate degree bias. It adds more positive pairs by leveraging node labels and adaptively weights positive and negative pairs based on their learning hardness. In addition, we develop an experimental framework named SHARP to extend HAR to a broader range of scenarios. Both our theoretical analysis and experiments validate the effectiveness of SHARP. The experimental results across four datasets show that SHARP achieves better performance against baselines at both global and degree levels.
DGDNN: Decoupled Graph Diffusion Neural Network for Stock Movement Prediction
Jan 03, 2024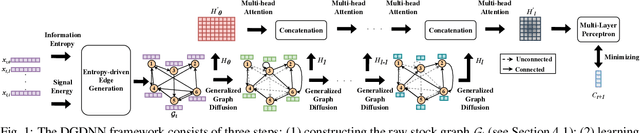



Abstract:Forecasting future stock trends remains challenging for academia and industry due to stochastic inter-stock dynamics and hierarchical intra-stock dynamics influencing stock prices. In recent years, graph neural networks have achieved remarkable performance in this problem by formulating multiple stocks as graph-structured data. However, most of these approaches rely on artificially defined factors to construct static stock graphs, which fail to capture the intrinsic interdependencies between stocks that rapidly evolve. In addition, these methods often ignore the hierarchical features of the stocks and lose distinctive information within. In this work, we propose a novel graph learning approach implemented without expert knowledge to address these issues. First, our approach automatically constructs dynamic stock graphs by entropy-driven edge generation from a signal processing perspective. Then, we further learn task-optimal dependencies between stocks via a generalized graph diffusion process on constructed stock graphs. Last, a decoupled representation learning scheme is adopted to capture distinctive hierarchical intra-stock features. Experimental results demonstrate substantial improvements over state-of-the-art baselines on real-world datasets. Moreover, the ablation study and sensitivity study further illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in modeling the time-evolving inter-stock and intra-stock dynamics.
High-Fidelity Face Swapping with Style Blending
Dec 17, 2023Abstract:Face swapping has gained significant traction, driven by the plethora of human face synthesis facilitated by deep learning methods. However, previous face swapping methods that used generative adversarial networks (GANs) as backbones have faced challenges such as inconsistency in blending, distortions, artifacts, and issues with training stability. To address these limitations, we propose an innovative end-to-end framework for high-fidelity face swapping. First, we introduce a StyleGAN-based facial attributes encoder that extracts essential features from faces and inverts them into a latent style code, encapsulating indispensable facial attributes for successful face swapping. Second, we introduce an attention-based style blending module to effectively transfer Face IDs from source to target. To ensure accurate and quality transferring, a series of constraint measures including contrastive face ID learning, facial landmark alignment, and dual swap consistency is implemented. Finally, the blended style code is translated back to the image space via the style decoder, which is of high training stability and generative capability. Extensive experiments on the CelebA-HQ dataset highlight the superior visual quality of generated images from our face-swapping methodology when compared to other state-of-the-art methods, and the effectiveness of each proposed module. Source code and weights will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge