Hojun Chung
Adversarial Environment Design via Regret-Guided Diffusion Models
Oct 25, 2024


Abstract:Training agents that are robust to environmental changes remains a significant challenge in deep reinforcement learning (RL). Unsupervised environment design (UED) has recently emerged to address this issue by generating a set of training environments tailored to the agent's capabilities. While prior works demonstrate that UED has the potential to learn a robust policy, their performance is constrained by the capabilities of the environment generation. To this end, we propose a novel UED algorithm, adversarial environment design via regret-guided diffusion models (ADD). The proposed method guides the diffusion-based environment generator with the regret of the agent to produce environments that the agent finds challenging but conducive to further improvement. By exploiting the representation power of diffusion models, ADD can directly generate adversarial environments while maintaining the diversity of training environments, enabling the agent to effectively learn a robust policy. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method successfully generates an instructive curriculum of environments, outperforming UED baselines in zero-shot generalization across novel, out-of-distribution environments. Project page: https://github.com/rllab-snu.github.io/projects/ADD
Spectral-Risk Safe Reinforcement Learning with Convergence Guarantees
May 29, 2024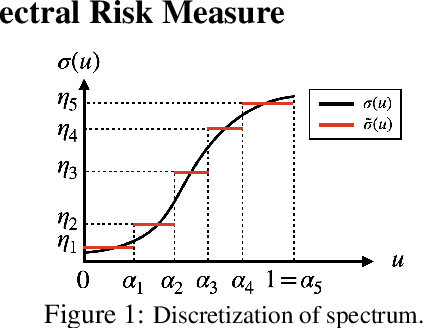
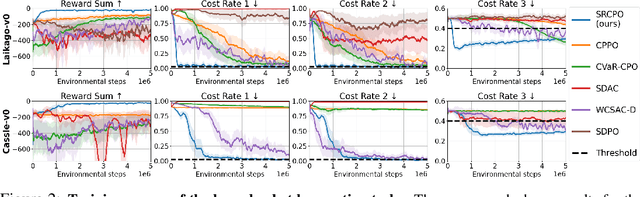
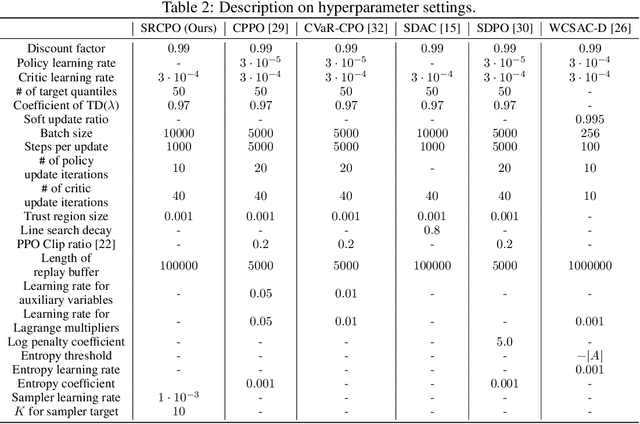
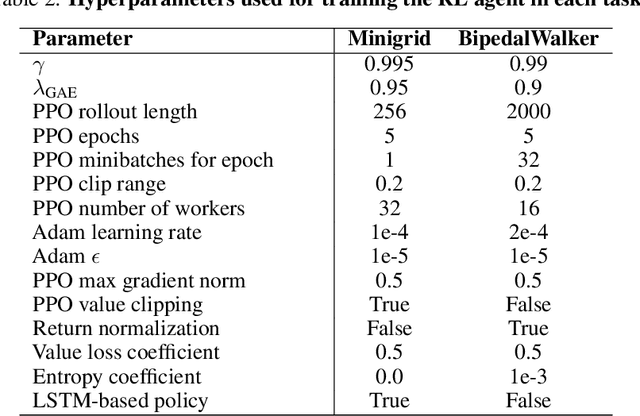
Abstract:The field of risk-constrained reinforcement learning (RCRL) has been developed to effectively reduce the likelihood of worst-case scenarios by explicitly handling risk-measure-based constraints. However, the nonlinearity of risk measures makes it challenging to achieve convergence and optimality. To overcome the difficulties posed by the nonlinearity, we propose a spectral risk measure-constrained RL algorithm, spectral-risk-constrained policy optimization (SRCPO), a bilevel optimization approach that utilizes the duality of spectral risk measures. In the bilevel optimization structure, the outer problem involves optimizing dual variables derived from the risk measures, while the inner problem involves finding an optimal policy given these dual variables. The proposed method, to the best of our knowledge, is the first to guarantee convergence to an optimum in the tabular setting. Furthermore, the proposed method has been evaluated on continuous control tasks and showed the best performance among other RCRL algorithms satisfying the constraints.
Towards Defensive Autonomous Driving: Collecting and Probing Driving Demonstrations of Mixed Qualities
Sep 18, 2021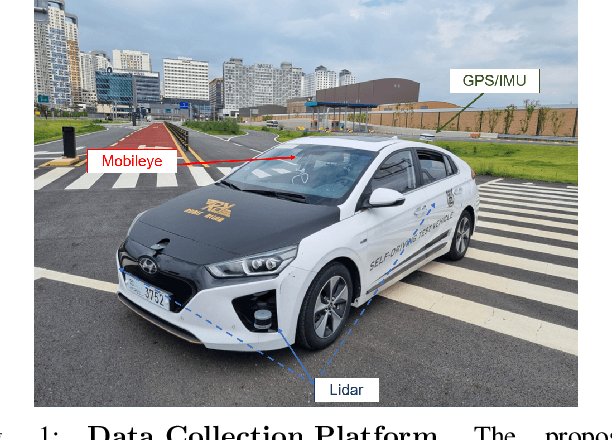
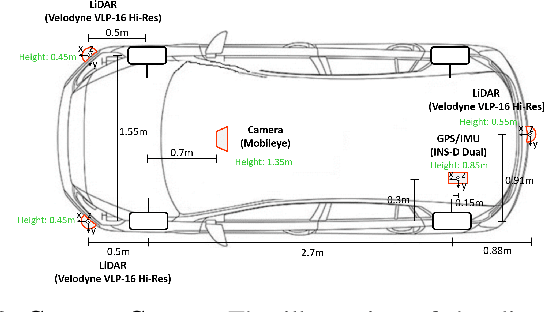

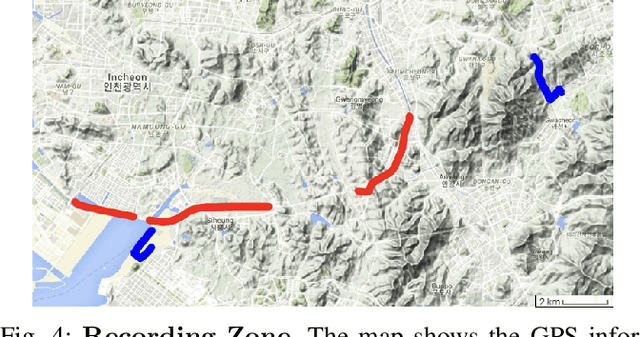
Abstract:Designing or learning an autonomous driving policy is undoubtedly a challenging task as the policy has to maintain its safety in all corner cases. In order to secure safety in autonomous driving, the ability to detect hazardous situations, which can be seen as an out-of-distribution (OOD) detection problem, becomes crucial. However, most conventional datasets only provide expert driving demonstrations, although some non-expert or uncommon driving behavior data are needed to implement a safety guaranteed autonomous driving platform. To this end, we present a novel dataset called the R3 Driving Dataset, composed of driving data with different qualities. The dataset categorizes abnormal driving behaviors into eight categories and 369 different detailed situations. The situations include dangerous lane changes and near-collision situations. To further enlighten how these abnormal driving behaviors can be detected, we utilize different uncertainty estimation and anomaly detection methods to the proposed dataset. From the results of the proposed experiment, it can be inferred that by using both uncertainty estimation and anomaly detection, most of the abnormal cases in the proposed dataset can be discriminated. The dataset of this paper can be downloaded from https://rllab-snu.github.io/projects/R3-Driving-Dataset/doc.html.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge