Hengyan Liu
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on High Dynamic Range Imaging: Methods and Results
May 25, 2022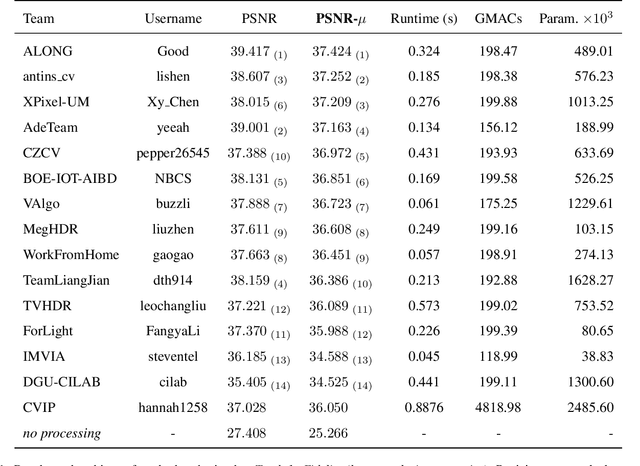
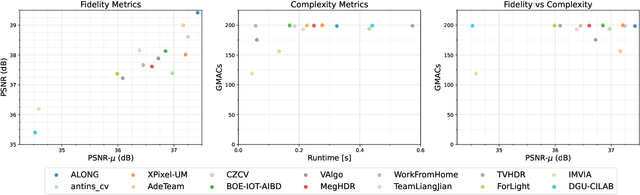
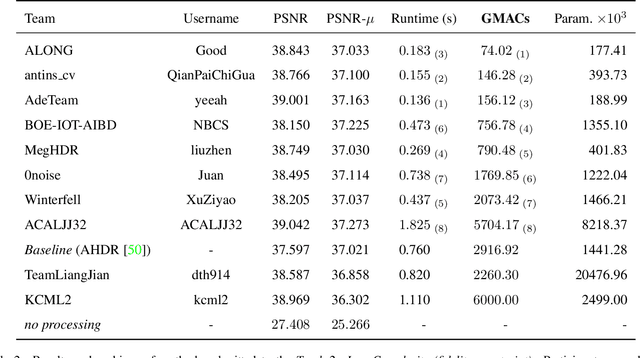
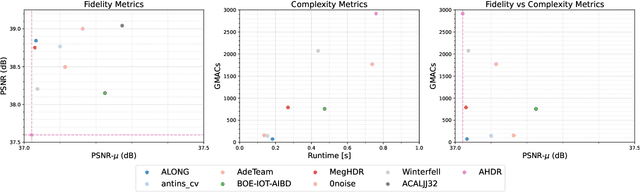
Abstract:This paper reviews the challenge on constrained high dynamic range (HDR) imaging that was part of the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement (NTIRE) workshop, held in conjunction with CVPR 2022. This manuscript focuses on the competition set-up, datasets, the proposed methods and their results. The challenge aims at estimating an HDR image from multiple respective low dynamic range (LDR) observations, which might suffer from under- or over-exposed regions and different sources of noise. The challenge is composed of two tracks with an emphasis on fidelity and complexity constraints: In Track 1, participants are asked to optimize objective fidelity scores while imposing a low-complexity constraint (i.e. solutions can not exceed a given number of operations). In Track 2, participants are asked to minimize the complexity of their solutions while imposing a constraint on fidelity scores (i.e. solutions are required to obtain a higher fidelity score than the prescribed baseline). Both tracks use the same data and metrics: Fidelity is measured by means of PSNR with respect to a ground-truth HDR image (computed both directly and with a canonical tonemapping operation), while complexity metrics include the number of Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) operations and runtime (in seconds).
* CVPR Workshops 2022. 15 pages, 21 figures, 2 tables
Diversity-based Trajectory and Goal Selection with Hindsight Experience Replay
Aug 17, 2021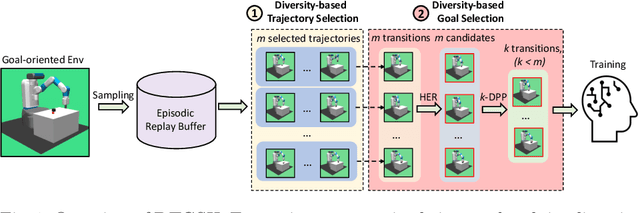
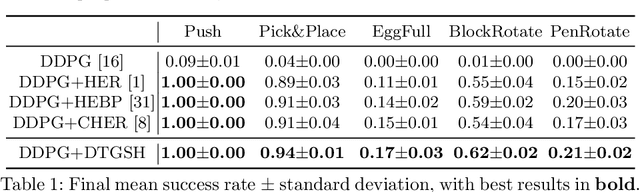
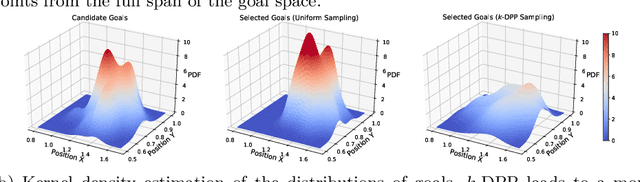

Abstract:Hindsight experience replay (HER) is a goal relabelling technique typically used with off-policy deep reinforcement learning algorithms to solve goal-oriented tasks; it is well suited to robotic manipulation tasks that deliver only sparse rewards. In HER, both trajectories and transitions are sampled uniformly for training. However, not all of the agent's experiences contribute equally to training, and so naive uniform sampling may lead to inefficient learning. In this paper, we propose diversity-based trajectory and goal selection with HER (DTGSH). Firstly, trajectories are sampled according to the diversity of the goal states as modelled by determinantal point processes (DPPs). Secondly, transitions with diverse goal states are selected from the trajectories by using k-DPPs. We evaluate DTGSH on five challenging robotic manipulation tasks in simulated robot environments, where we show that our method can learn more quickly and reach higher performance than other state-of-the-art approaches on all tasks.
Episodic Self-Imitation Learning with Hindsight
Nov 26, 2020



Abstract:Episodic self-imitation learning, a novel self-imitation algorithm with a trajectory selection module and an adaptive loss function, is proposed to speed up reinforcement learning. Compared to the original self-imitation learning algorithm, which samples good state-action pairs from the experience replay buffer, our agent leverages entire episodes with hindsight to aid self-imitation learning. A selection module is introduced to filter uninformative samples from each episode of the update. The proposed method overcomes the limitations of the standard self-imitation learning algorithm, a transitions-based method which performs poorly in handling continuous control environments with sparse rewards. From the experiments, episodic self-imitation learning is shown to perform better than baseline on-policy algorithms, achieving comparable performance to state-of-the-art off-policy algorithms in several simulated robot control tasks. The trajectory selection module is shown to prevent the agent learning undesirable hindsight experiences. With the capability of solving sparse reward problems in continuous control settings, episodic self-imitation learning has the potential to be applied to real-world problems that have continuous action spaces, such as robot guidance and manipulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge